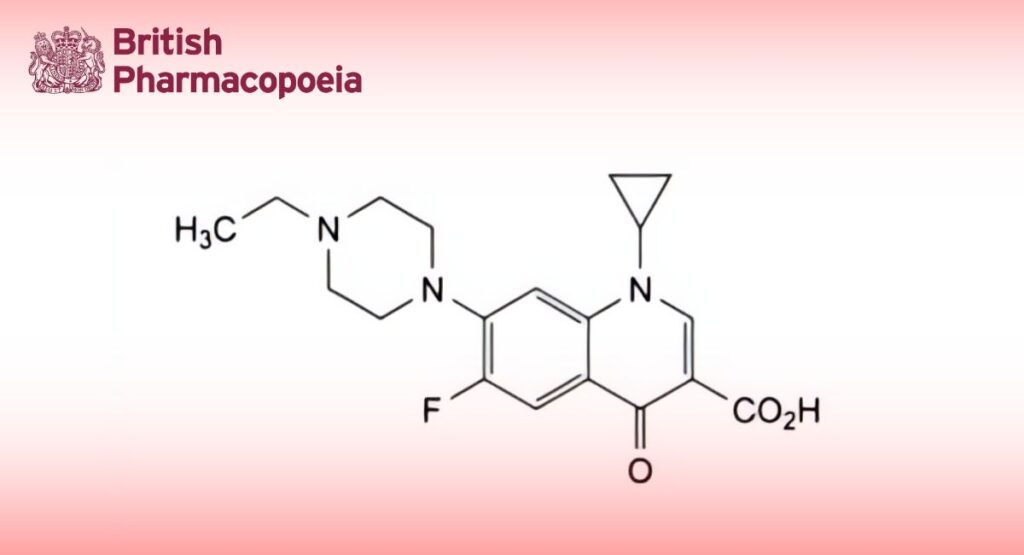
(Enrofloxacin for Veterinary Use, Ph. Eur. monograph 2229)
C19H22FN3O3 359.4 93106-60-6
Action and use
Fluoroquinolone antibacterial (veterinary).
Preparations
Enrofloxacin Concentrate for Oral Solution
Enrofloxacin Injection
Enrofloxacin Oral Solution
Enrofloxacin Oral Suspension
Enrofloxacin Solution for Use in Drinking Water
Enrofloxacin Tablets
DEFINITION
1-Cyclopropyl-7-(4-ethylpiperazin-1-yl)-6-fluoro-4-oxo-1,4-dihydroquinoline-3-carboxylic acid.
Content
98.5 per cent to 101.5 per cent (dried substance).
CHARACTERS
Appearance
Pale yellowish or light yellow, crystalline powder.
Solubility
Practically insoluble in water, freely soluble in methylene chloride, slightly soluble in methanol.
IDENTIFICATION
Infrared absorption spectrophotometry (2.2.24).
Comparison: enrofloxacin CRS.
TESTS
Appearance of solution
The solution is not more opalescent than reference suspension II (2.2.1) and not more intensely coloured than reference solution GY4 (2.2.2, Method II).
To 1.0 g of the substance to be examined add about 0.25 g of potassium hydroxide R and 7 mL of water R. Sonicate to dissolve and dilute to 10.0 mL with water R.
Impurity A
Thin-layer chromatography (2.2.27). Prepare the solutions immediately before use.
Solvent mixture: methanol R, methylene chloride R (50:50 V/V).
Test solution: Dissolve 0.100 g of the substance to be examined in the solvent mixture and dilute to 5.0 mL with the solvent mixture.
Reference solution: Dissolve 5.0 mg of ciprofloxacin impurity A CRS (enrofloxacin impurity A) in the solvent mixture and dilute to 50.0 mL with the solvent mixture. Dilute 4.0 mL of the solution to 10.0 mL with the solvent mixture.
Plate: TLC silica gel F254 plate R (2-10 μm).
Mobile phase: butanol R, water R, anhydrous acetic acid R, ethyl acetate R (15:15:20:50 V/V/V/V).
Application: 10 μL.
Development: Over 3/4 of the plate.
Drying: In air.
Detection: Examine in ultraviolet light at 254 nm.
Results:
— impurity A: any spot due to impurity A is not more intense than the spot in the chromatogram obtained with the reference solution (0.2 per cent).
Related substances
Liquid chromatography (2.2.29).
Test solution: Dissolve 50 mg of the substance to be examined in the mobile phase and dilute to 50.0 mL with the mobile phase.
Reference solution (a): Dissolve 10 mg of enrofloxacin for system suitability CRS (containing impurities B and C) in the mobile phase and dilute to 10 mL with the mobile phase.
Reference solution (b): Dilute 1.0 mL of the test solution to 50.0 mL with the mobile phase. Dilute 1.0 mL of this solution to 10.0 mL with the mobile phase.
Column:
— size: l = 0.15 m, Ø = 4.6 mm;
— stationary phase: base-deactivated end-capped octadecylsilyl silica gel for chromatography R (5 μm);
— temperature: 40 °C.
Mobile phase: Mix 15 volumes of methanol R and 85 volumes of a 2.9 g/L solution of phosphoric acid R, previously adjusted to pH 2.3 with triethylamine R.
Flow rate: 1.5 mL/min.
Detection: Spectrophotometer at 270 nm.
Injection: 10 μL.
Run time: 3 times the retention time of enrofloxacin.
Identification of impurities: Use the chromatogram supplied with enrofloxacin for system suitability CRS and the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a) to identify the peaks due to impurities B and C.
Relative retention: With reference to enrofloxacin (retention time = about 16 min): impurity C = about 0.6; impurity B = about 0.8.
System suitability: Reference solution (a):
— resolution: minimum 2.0 between the peaks due to impurity B and enrofloxacin.
Limits:
— impurity B: not more than 2.5 times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b) (0.5 per cent);
— impurity C: not more than the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b) (0.2 per cent);
— unspecified impurities: for each impurity, not more than the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b) (0.20 per cent);
— total: not more than 5 times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b) (1.0 per cent);
— disregard limit: 0.5 times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b) (0.1 per cent).
Loss on drying (2.2.32)
Maximum 1.0 per cent, determined on 2.000 g by drying in vacuo at 120 °C for 6 h.
Sulfated ash (2.4.14)
Maximum 0.1 per cent, determined on 1.0 g in a platinum crucible.
ASSAY
Dissolve 0.250 g in 100 mL of anhydrous acetic acid R and titrate with 0.1 M perchloric acid determining the end-point potentiometrically (2.2.20).
1 mL of 0.1 M perchloric acid is equivalent to 35.94 mg of C19H22FN3O3.
STORAGE
Protected from light.
IMPURITIES
Specified impurities A, B, C.
Other detectable impurities (the following substances would, if present at a sufficient level, be detected by one or other of the tests in the monograph. They are limited by the general acceptance criterion for other/unspecified impurities and/or by the general monograph Substances for pharmaceutical use (2034). It is therefore not necessary to identify these impurities for demonstration of compliance. See also 5.10. Control of impurities in substances for pharmaceutical use) E, F, G.
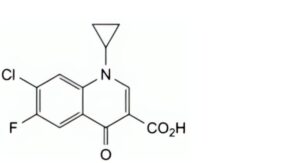
A. 7-chloro-1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-1,4-dihydroquinoline-3-carboxylic acid,
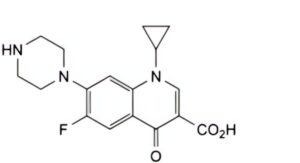
B. ciprofloxacin,
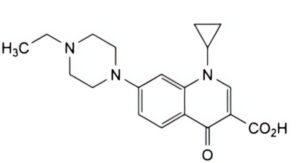
C. 1-cyclopropyl-7-(4-ethylpiperazin-1-yl)-4-oxo-1,4-dihydroquinoline-3-carboxylic acid,
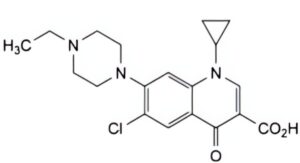
E. 6-chloro-1-cyclopropyl-7-(4-ethylpiperazin-1-yl)-4-oxo-1,4-dihydroquinoline-3-carboxylic acid,
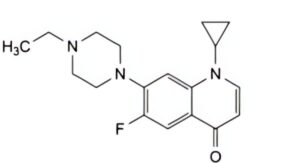
F. 1-cyclopropyl-7-(4-ethylpiperazin-1-yl)-6-fluoroquinolin-4(1H)-one,
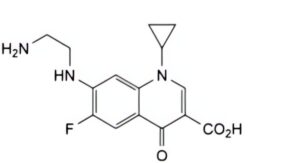
G. 7-[(2-aminoethyl)amino]-1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-1,4-dihydroquinoline-3-carboxylic acid.