(Ph. Eur. monograph 0801)
Action and use
Excipient.
DEFINITION
Mixture of cetostearyl alcohol and sodium cetostearyl sulfate. A suitable buffer may be added.
Content
— cetostearyl alcohol: minimum 80.0 per cent (anhydrous substance);
— sodium cetostearyl sulfate: minimum 7.0 per cent (anhydrous substance).
CHARACTERS
Appearance
White or pale yellow, waxy mass, plates, flakes or granules.
Solubility
Soluble in hot water giving an opalescent solution, practically insoluble in cold water, slightly soluble in ethanol (96 per cent).
IDENTIFICATION
First identification: B, C, D.
Second identification: A, C, D.
A. Thin-layer chromatography (2.2.27).
Test solution (a): Dissolve 0.1 g of the substance to be examined in 10 mL of trimethylpentane R, heating on a water-bath.
Shake with 2 mL of ethanol (70 per cent V/V) R and allow to separate. Use the lower layer as test solution (b). Dilute 1 mL of the upper layer to 8 mL with trimethylpentane R.
Test solution (b): Use the lower layer obtained in the preparation of test solution (a).
Reference solution (a): Dissolve 24 mg of cetyl alcohol CRS and 16 mg of stearyl alcohol CRS in 10 mL of trimethylpentane R.
Reference solution (b): Dissolve 20 mg of sodium cetostearyl sulfate R in 10 mL of ethanol (70 per cent V/V) R, heating on a water-bath.
Plate: TLC octadecylsilyl silica gel F254 plate R.
Mobile phase: water R, acetone R, methanol R (20:40:40 V/V/V).
Application: 10 μL.
Development: Over 2/3 of the plate.
Drying: In air.
Detection: Spray with a 50 g/L solution of phosphomolybdic acid R in ethanol (96 per cent) R; heat at 120 °C until spots appear (about 5 min).
Results:
— the 2 principal spots in the chromatogram obtained with test solution (a) are similar in position and colour to the principal spots in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a);
— 2 of the spots in the chromatogram obtained with test solution (b) are similar in position and colour to the principal spots in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b).
B. Examine the chromatograms obtained in the assay of cetostearyl alcohol.
Results: The 2 principal peaks in the chromatogram obtained with the test solution are similar in retention time to the 2 principal peaks in the chromatograms obtained with reference solutions (a) and (b).
C. It gives a yellow colour to a non-luminous flame.
D. To 0.3 g add 20 mL of anhydrous ethanol R and heat to boiling on a water-bath with shaking. Filter the mixture immediately, evaporate to dryness and take up the residue in 7 mL of water R. To 1 mL of the solution add 0.1 mL of a 1 g/L solution of methylene blue R, 2 mL of dilute sulfuric acid R and 2 mL of methylene chloride R and shake. A blue
colour develops in the lower layer.
TESTS
Acid value (2.5.1)
Maximum 2.0.
Iodine value (2.5.4, Method A)
Maximum 3.0.
Dissolve 2.00 g in 25 mL of methylene chloride R.
Saponification value (2.5.6)
Maximum 2.0.
Water (2.5.12)
Maximum 3.0 per cent, determined on 2.50 g.
ASSAY
Cetostearyl alcohol
Gas chromatography (2.2.28).
Internal standard solution Dissolve 0.200 g of 1-nonadecanol CRS in anhydrous ethanol R and dilute to 100.0 mL with the same solvent.
Test solution: Dissolve 0.200 g of the substance to be examined in 25.0 mL of the internal standard solution. Add 25 mL of water R and shake with 4 quantities, each of 25 mL, of pentane R, adding sodium chloride R, if necessary, to facilitate the separation of the layers. Combine the upper layers, wash with 2 quantities, each of 30 mL, of water R, dry over anhydrous sodium sulfate R and filter.
Reference solution (a): Dissolve 0.100 g of cetyl alcohol CRS in 25.0 mL of the internal standard solution. Add 25 mL of water R and shake with 4 quantities, each of 25 mL, of pentane R, adding sodium chloride R, if necessary, to facilitate the separation of the layers. Combine the upper layers, wash with 2 quantities, each of 30 mL, of water R, dry over anhydrous sodium sulfate R and filter.
Reference solution (b): Dissolve 0.100 g of stearyl alcohol CRS in 25.0 mL of the internal standard solution. Add 25 mL of water R and shake with 4 quantities, each of 25 mL, of pentane R, adding sodium chloride R, if necessary, to facilitate the separation of the layers. Combine the upper layers, wash with 2 quantities, each of 30 mL, of water R, dry over anhydrous sodium sulfate R and filter.
Column:
— material: fused silica;
— size: l = 25 m, Ø = 0.25 mm;
— stationary phase: methylpolysiloxane R (film thickness 0.25 μm).
Carrier gas helium for chromatography R.
Flow rate 1 mL/min.
Split ratio 1:100.
Temperature:
| Time
(min) |
Temperature
(°C) |
|
| Column | 0 – 20 | 150 → 250 |
| Injection port | 250 | |
| Detector | 250 |
Detection: Flame ionisation.
Injection: 1 μL.
Elution order: Cetyl alcohol, stearyl alcohol, 1-nonadecanol.
Calculate the percentage content of cetyl alcohol in the substance to be examined using the following expression and taking into account the assigned content of cetyl alcohol CRS:
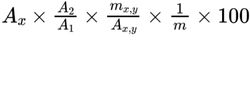
Ax = area of the peak due to cetyl alcohol in the chromatogram obtained with the test solution;
Ax,y = area of the peak due to cetyl alcohol CRS in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a);
A1 = area of the peak due to the internal standard in the chromatogram obtained with the test solution;
A2 = area of the peak due to the internal standard in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a);
m = mass of the substance to be examined in the test solution, in milligrams;
mx,y = mass of cetyl alcohol CRS in reference solution (a), in milligrams.
Calculate the percentage content of stearyl alcohol in the substance to be examined using the following expression and taking into account the assigned content of stearyl alcohol CRS:
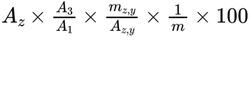
Az = area of the peak due to stearyl alcohol in the chromatogram obtained with the test solution;
Az,y = area of the peak due to stearyl alcohol CRS in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b);
A1 = area of the peak due to the internal standard in the chromatogram obtained with the test solution;
A3 = area of the peak due to the internal standard in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b);
m = mass of the substance to be examined in the test solution, in milligrams;
mz,y = mass of stearyl alcohol CRS in reference solution (b), in milligrams.
The percentage content of cetostearyl alcohol corresponds to the sum of the percentage contents of cetyl alcohol and stearyl alcohol.
Sodium cetostearyl sulfate
Disperse 0.300 g in 25 mL of methylene chloride R. Add 50 mL of water R and 10 mL of dimidium bromide-sulfan blue mixed solution R. Titrate with 0.004 M benzethonium chloride, using sonication, heating, and allowing the layers to separate before each addition, until the colour of the lower layer changes from pink to grey.
1 mL of 0.004 M benzethonium chloride is equivalent to 1.434 mg of sodium cetostearyl sulfate.
LABELLING
The label states, where applicable, the name and concentration of any added buffer.






