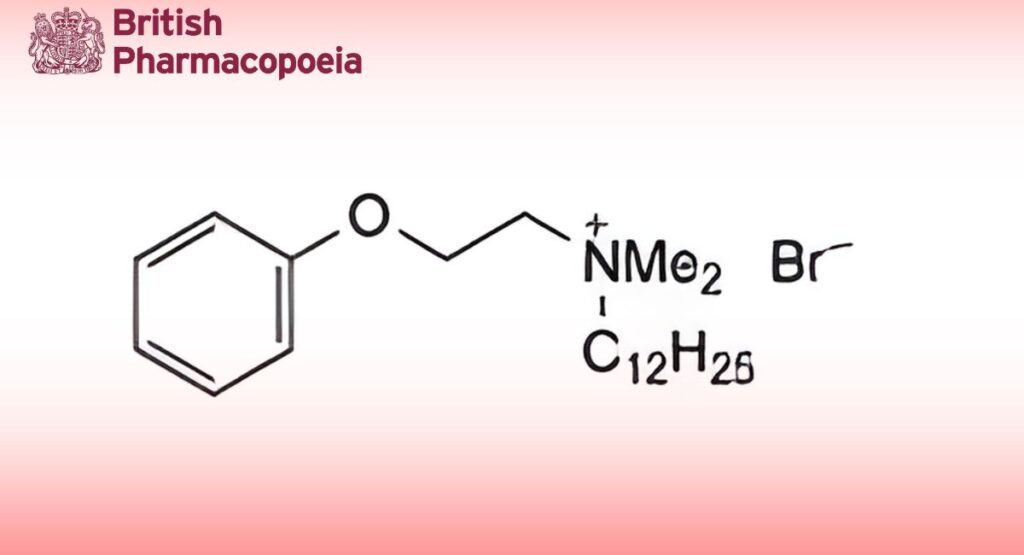
C22H40BrNO 414.5 538-71-6
Action and use
Antiseptic.
DEFINITION
Domiphen Bromide consists chiefly of dodecyldimethyl-2-phenoxyethylammonium bromide. It contains not less than 97.0%
and not more than 100.5% of C22H40BrNO, calculated with reference to the dried substance.
CHARACTERISTICS
Colourless or faintly yellow, crystalline flakes.
Freely soluble in water and in ethanol (96%); soluble in acetone.
IDENTIFICATION
A. The infrared absorption spectrum, Appendix II A, is concordant with the reference spectrum of domiphen bromide (RS 383).
B. Dissolve 10 mg in 10 mL of water and add 0.1 mL of a 0.5% w/v solution of eosin and 100 mL of water. An intense pink colour is produced.
C. Yields the reactions characteristic of bromides, Appendix VI.
TESTS
Acidity or alkalinity
Add 0.5 mL of bromothymol blue solution R3 to each of 10 mL of phosphate buffer pH 6.4 (solution A) and 10 mL of phosphate buffer pH 7.6 (solution B). Dissolve 0.10 g in 10 mL of carbon dioxide-free water and add 0.5 mL of bromothymol blue solution R3. The resulting solution is not more yellow than solution A and not more blue than solution B.
Clarity and colour of solution
Dissolve 1.0 g in 10 mL of carbon dioxide-free water. The solution is not more opalescent than reference suspension II, Appendix IV A, and not more intensely coloured than reference solution Y7, Appendix IV B, Method I.
Non-quaternary amines
Carry out the Assay described below using a further 25 mL of the original solution and 10 mL of 0.1M hydrochloric acid in place of the 0.1M sodium hydroxide. The difference between the volume of 0.05M potassium iodate VS required in this titration and that required in the Assay is not more than 0.5 mL for each g of substance taken.
Loss on drying
When dried to constant weight at 70° at a pressure not exceeding 0.7 kPa, loses not more than 1.0% of its weight. Use 1 g.
Sulfated ash
Not more than 0.1%, Appendix IX A.
ASSAY
Dissolve 2 g in sufficient water to produce 100 mL. Transfer 25 mL to a separating funnel and add 25 mL of chloroform, 10 mL of 0.1M sodium hydroxide and 10 mL of a freshly prepared 5% w/v solution of potassium iodide. Shake well, allow to separate and discard the chloroform layer. Wash the aqueous layer with three 10-mL quantities of chloroform and discard the chloroform solutions. Add 40 mL of hydrochloric acid, allow to cool and titrate with 0.05M potassium iodate VS until the deep brown colour is discharged. Add 2 mL of chloroform and continue the titration, shaking vigorously, until the
chloroform layer no longer changes colour. Carry out a blank titration on a mixture of 10 mL of the freshly prepared potassium iodide solution, 20 mL of water and 40 mL of hydrochloric acid. The difference between the titrations represents the amount of potassium iodate required. Each mL of 0.05M potassium iodate VS is equivalent to 41.45 mg of C22H40BrNO.