(Ph. Eur. monograph 0551)
C34H41N5O8S 680 6190-39-2
Action and use
Vasodilator.
DEFINITION
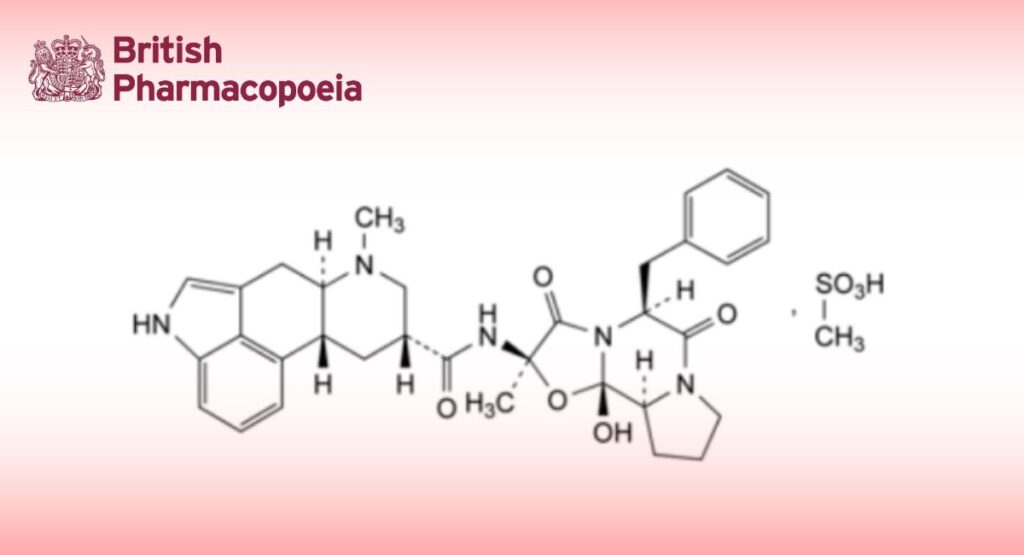
(6aR,9R,10aR)-N-[(2R,5S,10aS,10bS)-5-Benzyl-10b-hydroxy-2-methyl-3,6-dioxooctahydro-8H-oxazolo[3,2-a]pyrrolo[2,1-c]pyrazin-2-yl]-7-methyl-4,6,6a,7,8,9,10,10a-octahydroindolo[4,3-fg]quinoline-9-carboxamide methanesulfonate.
Content
98.0 per cent to 101.0 per cent (dried substance).
PRODUCTION
It is considered that alkyl methanesulfonate esters are genotoxic and are potential impurities in dihydroergotamine mesilate. The manufacturing process should be developed taking into consideration the principles of quality risk management, together with considerations of the quality of starting materials, process capability and validation. The general methods 2.5.37. Methyl, ethyl and isopropyl methanesulfonate in methanesulfonic acid, 2.5.38. Methyl, ethyl and isopropyl methanesulfonate in active substances and 2.5.39. Methanesulfonyl chloride in methanesulfonic acid are available to assist manufacturers.
CHARACTERS
Appearance
White or almost white, crystalline powder or colourless crystals.
Solubility
Slightly soluble in water, sparingly soluble in methanol, slightly soluble in ethanol (96 per cent).
IDENTIFICATION
First identification: B, C.
Second identification: A, C, D.
A. Ultraviolet and visible absorption spectrophotometry (2.2.25).
Test solution: Dissolve 5.0 mg in methanol R and dilute to 100.0 mL with the same solvent.
Spectral range: 250-350 nm.
Absorption maxima: 281 nm and 291 nm.
Shoulder: 275 nm.
Absorbance: Negligible above 320 nm.
Specific absorbance at the absorption maximum at 281 nm 95 to 105 (dried substance).
B. Infrared absorption spectrophotometry (2.2.24).
Comparison: dihydroergotamine mesilate CRS.
C. Thin-layer chromatography (2.2.27). Prepare the reference solution and the test solution immediately before use.
Solvent mixture methanol R, methylene chloride R (10:90 V/V).
Test solution: Dissolve 5 mg of the substance to be examined in the solvent mixture and dilute to 2.5 mL with the solvent mixture.
Reference solution: Dissolve 5 mg of dihydroergotamine mesilate CRS in the solvent mixture and dilute to 2.5 mL with the solvent mixture.
Plate: TLC silica gel G plate R.
Mobile phase: concentrated ammonia R, methanol R, ethyl acetate R, methylene chloride R (1:6:50:50 V/V/V/V).
Application: 5 μL.
Development: Protected from light, over a path of 15 cm; dry in a current of cold air for not longer than 1 min and repeat the development protected from light over a path of 15 cm using a freshly prepared amount of the mobile phase.
Drying: In a current of cold air.
Detection: Spray abundantly with dimethylaminobenzaldehyde solution R7 and dry in a current of hot air for about 2 min.
Results: The principal spot in the chromatogram obtained with the test solution is similar in position, colour and size to the principal spot in the chromatogram obtained with the reference solution.
D. To 0.1 g of the substance to be examined, add 5 mL of dilute hydrochloric acid R and shake for about 5 min. Filter, then add 1 mL of barium chloride solution R1. The filtrate remains clear. Mix 0.1 g of the substance to be examined with 0.4 g of powdered sodium hydroxide R, heat to fusion and continue to heat for 1 min. Cool, add 5 mL of water R, boil and filter. Acidify the filtrate with hydrochloric acid R1 and filter again. The filtrate gives reaction (a) of sulfates (2.3.1).
TESTS
Appearance of solution
The solution is clear (2.2.1) and not more intensely coloured than reference solution Y7 or BY7 (2.2.2, Method II).
Dissolve 0.10 g in a mixture of 0.1 mL of a 70 g/L solution of methanesulfonic acid R and 50 mL of water R.
pH (2.2.3)
4.4 to 5.4.
Dissolve 0.10 g in carbon dioxide-free water R and dilute to 100 mL with the same solvent.
Specific optical rotation (2.2.7)
-47 to -42 (dried substance).
Dissolve 0.250 g in anhydrous pyridine R and dilute to 25.0 mL with the same solvent.
Related substances
Liquid chromatography (2.2.29). Carry out the test protected from light.
Solvent mixture: acetonitrile R, water R (50:50 V/V).
Test solution: Dissolve 70 mg of the substance to be examined in the solvent mixture and dilute to 100.0 mL with the solvent mixture.
Reference solution (a): Dilute 1.0 mL of the test solution to 10.0 mL with the solvent mixture. Dilute 1.0 mL of this solution to 100.0 mL with the solvent mixture.
Reference solution (b): Dissolve 7 mg of the substance to be examined and 6.8 mg of ergotamine tartrate CRS (impurity A) (equivalent to 7 mg of ergotamine mesilate) in the solvent mixture and dilute to 100 mL with the solvent mixture. Dilute 5 mL of this solution to 10 mL with the solvent mixture.
Reference solution (c): Dissolve 5 mg of dihydroergotamine for peak identification CRS (containing impurities A, B, C, D and E) in the solvent mixture, add 100 μL of dilute sulfuric acid R and dilute to 5 mL with the solvent mixture.
Column:
— size: l = 0.15 m, Ø = 4.6 mm;
— stationary phase: spherical base-deactivated end-capped octadecylsilyl silica gel for chromatography R (3 μm);
— temperature: 25 °C.
Mobile phase:
— mobile phase A: 3 g/L solution of sodium heptanesulfonate monohydrate R adjusted to pH 2.0 with phosphoric acid R;
— mobile phase B: mobile phase A, acetonitrile for chromatography R (20:80 V/V);
| Time
(min) |
Mobile phase A
(per cent V/V) |
Mobile phase B
(per cent V/V) |
| 0 – 15 | 58 → 40 | 42 → 60 |
Flow rate: 1.5 mL/min.
Detection: Spectrophotometer at 220 nm.
Injection: 5 μL.
Identification of impurities: Use the chromatogram supplied with dihydroergotamine for peak identification CRS and the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (c) to identify the peaks due to impurities A, B, C, D and E.
Relative retention: With reference to dihydroergotamine (retention time = about 6.5 min): impurity D = about 0.7; impurity C = about 0.86; impurity A = about 0.95; impurity B = about 1.2; impurity E = about 1.4.
System suitability: Reference solution (b):
— resolution: minimum 1.5 between the peaks due to impurity A and dihydroergotamine.
Limits:
— correction factors: for the calculation of content, multiply the peak areas of the following impurities by the corresponding correction factor: impurity A = 1.3; impurity C = 1.3;
— impurities B, E: for each impurity, not more than 5 times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a) (0.5 per cent);
— impurity C: not more than 3 times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a) (0.3 per cent);
— impurities A, D: for each impurity, not more than 1.5 times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a) (0.15 per cent);
— unspecified impurities: for each impurity, not more than the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a) (0.10 per cent);
— total: not more than 10 times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a) (1.0 per cent);
— disregard limit: 0.5 times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a) (0.05 per cent).
Loss on drying (2.2.32)
Maximum 4.0 per cent, determined on 0.500 g by drying at 105 °C in vacuo for 5 h.
ASSAY
Dissolve 0.500 g in a mixture of 10 mL of anhydrous acetic acid R and 70 mL of acetic anhydride R. Titrate with 0.1 M perchloric acid, determining the end-point potentiometrically (2.2.20).
1 mL of 0.1 M perchloric acid is equivalent to 68.00 mg of C34H41N5O8S.
STORAGE
Protected from light.
IMPURITIES
Specified impurities A, B, C, D, E.
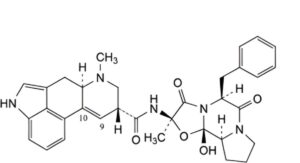
A. (6aR,9R)-N-[(2R,5S,10aS,10bS)-5-benzyl-10b-hydroxy-2-methyl-3,6-dioxooctahydro-8H-oxazolo[3,2-a]pyrrolo[2,1-c]pyrazin-2-yl]-7-methyl-4,6,6a,7,8,9-hexahydroindolo[4,3-fg]quinoline-9-carboxamide (ergotamine),
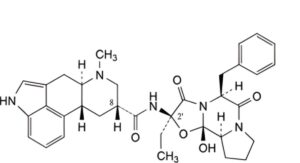
B. (6aR,9R,10aR)-N-[(2R,5S,10aS,10bS)-5-benzyl-2-ethyl-10b-hydroxy-3,6-dioxooctahydro-8H-oxazolo[3,2-a]pyrrolo[2,1-c]pyrazin-2-yl]-7-methyl-4,6,6a,7,8,9,10,10a-octahydroindolo[4,3-fg]quinoline-9-carboxamide (9,10-dihydroergostine),
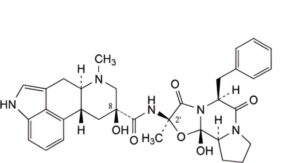
C. (6aR,9S,10aR)-N-[(2R,5S,10aS,10bS)-5-benzyl-10b-hydroxy-2-methyl-3,6-dioxooctahydro-8H-oxazolo[3,2-a]pyrrolo[2,1-c]pyrazin-2-yl]-9-hydroxy-7-methyl-4,6,6a,7,8,9,10,10aoctahydroindolo[4,3-fg]quinoline-9-carboxamide (8-hydroxy-9,10-dihydroergotamine),
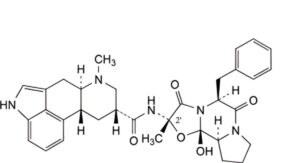
D. (6aR,9R,10aR)-N-[(2S,5S,10aS,10bS)-5-benzyl-10b-hydroxy-2-methyl-3,6-dioxooctahydro-8H-oxazolo[3,2-a]pyrrolo[2,1-c]pyrazin-2-yl]-7-methyl-4,6,6a,7,8,9,10,10aoctahydroindolo[4,3-fg]quinoline-9-carboxamide (2′-epi-9,10-dihydroergotamine),
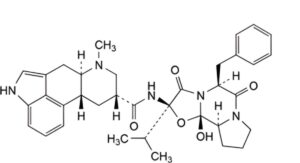
E. (6aR,9R,10aR)-N-[(2R,5S,10aS,10bS)-5-benzyl-10b-hydroxy-2-(1-methylethyl)-3,6-dioxo-octahydro-8H-oxazolo[3,2-a]pyrrolo[2,1-c]pyrazin-2-yl]-7-methyl-4,6,6a,7,8,9,10,10a-octahydroindolo[4,3-fg]quinoline-9-carboxamide (dihydroergocristine).