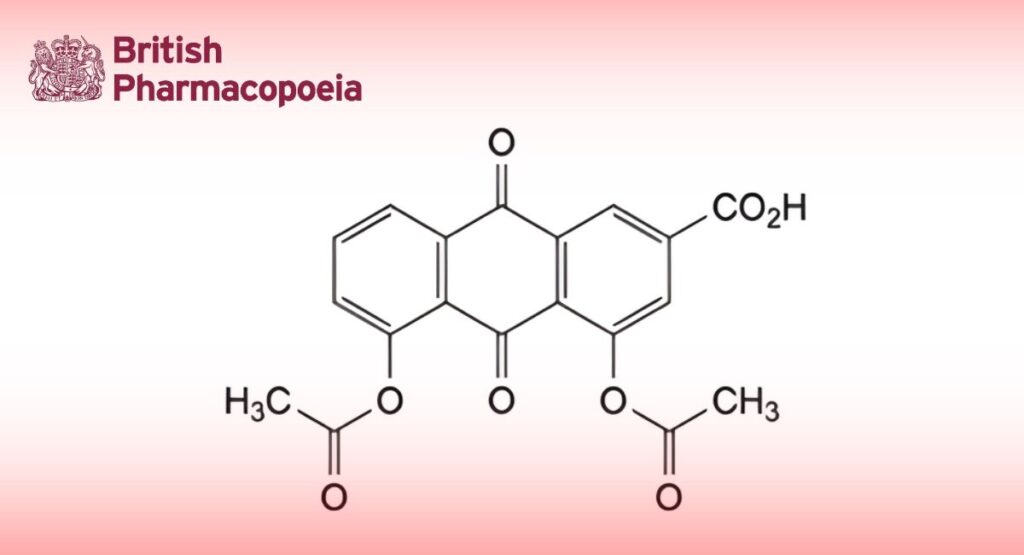
(Ph. Eur. monograph 2409)
C19H12O8 368.3 13739-02-1
Action and use
Anti-inflammatory used in the treatment of arthritis and osteoarthritis.
DEFINITION
4,5-Bis(acetyloxy)-9,10-dioxo-9,10-dihydroanthracene-2-carboxylic acid.
Content
98.0 per cent to 102.0 per cent (dried substance).
CHARACTERS
Appearance
Yellow, crystalline powder.
Solubility
Practically insoluble in water, soluble in dimethylacetamide, slightly soluble in tetrahydrofuran, practically insoluble in anhydrous ethanol.
IDENTIFICATION
Infrared absorption spectrophotometry (2.2.24).
Comparison: diacerein CRS.
TESTS
Impurities B and H
Liquid chromatography (2.2.29). Carry out the test protected from light.
Solution A: Dissolve 10 g of sodium hydroxide R in 500 mL of water R.
Solution B: Dissolve 14.7 g of sodium chloride R and 18.8 g of glycine R in 500 mL of water R.
Solution C: Mix 25.3 volumes of solution A and 74.6 volumes of solution B. If necessary, adjust to pH 9.5 using dilute sodium hydroxide solution R or dilute sulfuric acid R.
Solution D: Dilute 5 mL of dilute sulfuric acid R to 500 mL with water R.
Test solution: Dissolve 0.100 g of the substance to be examined in 30 mL of solution A and mix for 10 min. Add 70 mL of solution B and adjust to pH 9.5 with dilute sodium hydroxide solution R or dilute sulfuric acid R, if necessary. Extract with 3 quantities, each of 25 mL, of methylene chloride R. Combine the methylene chloride extracts and wash with 2 quantities, each of 8 mL, of solution C and then once with 10 mL of solution D. Evaporate the organic layer to dryness at 33 °C, completing the drying procedure using compressed air. Dissolve the residue in 2.0 mL of the mobile phase.
Reference solution (a): Dissolve 7.5 mg of diacerein impurity B CRS in tetrahydrofuran R and dilute to 25.0 mL with the same solvent. Sonicate for not more than 30 s. Dilute 1.0 mL of the solution to 100.0 mL with solution A. Dilute 5.0 mL of this solution to 50.0 mL with solution A. Mix 5.0 mL of this solution with 25 mL of solution A for 10 min. Add 70 mL of solution B and adjust to pH 9.5 with dilute sodium hydroxide solution R or dilute sulfuric acid R, if necessary. Perform the extraction as described for the test solution.
Care should be taken that the time between dissolution of diacerein impurity B in tetrahydrofuran and extraction does not exceed 30 min.
Reference solution (b): Dilute 1.0 mL of reference solution (a) to 5.0 mL with the mobile phase.
Column:
— size: l = 0.125 m, Ø = 4.6 mm;
— stationary phase: octadecylsilyl silica gel for chromatography R (5 μm);
— temperature: 16 ± 1 °C.
Mobile phase: tetrahydrofuran R, acetonitrile R, 4 g/L solution of citric acid monohydrate R (8:27.5:64.5 V/V/V).
Flow rate: 1.0 mL/min.
Detection: Spectrophotometer at 254 nm.
Injection: 100 μL.
Run time: 2.5 times the retention time of impurity B.
Retention time: Impurity B = about 11 min. During the extraction process, impurity H is hydrolysed into impurity B and both impurities are evaluated together.
System suitability: Reference solution (b):
— signal-to-noise ratio: minimum 10 for the principal peak.
Limit:
— sum of impurities B and H: not more than the area of the peak due to impurity B in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a) (15 ppm).
Related substances
Liquid chromatography (2.2.29). Carry out the test protected from light.
Solvent mixture: Mobile phase A, mobile phase B (50:50 V/V).
Test solution: Dissolve 0.100 g of the substance to be examined in 50 mL of tetrahydrofuran R and dilute to 100.0 mL with the solvent mixture.
Reference solution (a): Dilute 1.0 mL of the test solution to 100.0 mL with tetrahydrofuran R. Dilute 1.0 mL of this solution to 10.0 mL with the solvent mixture.
Reference solution (b): In order to prepare impurities D and E in situ, add 10.0 mL of a 0.4 g/L solution of sodium hydroxide R to 0.100 g of the substance to be examined. Add 40 mL of tetrahydrofuran R and dilute to 100 mL with the solvent mixture.
Reference solution (c): Dissolve the contents of a vial of diacerein impurity mixture CRS (impurities C and F) in a mixture of 0.5 mL of tetrahydrofuran R and 0.5 mL of the solvent mixture.
Column:
— size: l = 0.10 m, Ø = 4.6 mm;
— stationary phase: end-capped polar-embedded octadecylsilyl amorphous organosilica polymer R (5 μm);
— temperature: 30 °C.
Mobile phase:
— mobile phase A: to 353 mL of water for chromatography R add 147 mL of phosphoric acid R and mix; dilute 2 mL of the solution to 1000 mL with water for chromatography R;
— mobile phase B: acetonitrile R;
| Time
(min) |
Mobile phase A
(per cent V/V) |
Mobile phase B
(per cent V/V) |
| 0 – 3 | 80 | 20 |
| 3 – 13 | 80 → 60 | 20 → 40 |
| 13 – 20 | 60 | 40 |
Flow rate: 1.2 mL/min.
Detection: Spectrophotometer at 254 nm.
Injection: 20 μL.
Identification of impurities: Use the chromatogram supplied with diacerein impurity mixture CRS and the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (c) to identify the peaks due to impurities C and F; use the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b) to identify the peaks due to impurities D and E.
Relative retention: With reference to diacerein (retention time = about 13.5 min): impurity D = about 1.1; impurity E = about 1.15; impurity C = about 1.2; impurity F = about 1.3.
System suitability:
— resolution: minimum 1.5 between the peaks due to impurities D and E in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b);
— signal-to-noise ratio: minimum 100 for the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a).
Limits:
— correction factors: multiply the peak area of the impurity by its correction factor: impurity C = 1.4; impurity D = 1.3; impurity E = 1.3; impurity F = 9.5;
— impurities D, E: for each impurity, not more than 5 times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a) (0.5 per cent);
— impurity C: not more than twice the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a) (0.2 per cent);
— impurity F: not more than 1.5 times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a) (0.15 per cent);
— unspecified impurities: for each impurity, not more than the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a) (0.10 per cent);
— total: not more than 20 times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a) (2.0 per cent);
— disregard limit: 0.5 times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a) (0.05 per cent).
Loss on drying (2.2.32)
Maximum 0.5 per cent, determined on 1.000 g by drying in an oven at 105 °C.
Sulfated ash (2.4.14)
Maximum 0.1 per cent, determined on 1.0 g.
ASSAY
Liquid chromatography (2.2.29) as described in the test for related substances with the following modifications.
Test solution: Dissolve 60.0 mg of the substance to be examined in tetrahydrofuran R and dilute to 50.0 mL with the same solvent. Dilute 2.0 mL of the solution to 25.0 mL with the solvent mixture.
Reference solution: Dissolve 60.0 mg of diacerein CRS in tetrahydrofuran R and dilute to 50.0 mL with the same solvent.
Dilute 2.0 mL of the solution to 25.0 mL with the solvent mixture.
Calculate the percentage content of C19H12O8 taking into account the assigned content of diacerein CRS.
STORAGE
In an airtight container, protected from light.
IMPURITIES
Specified impurities B, C, D, E, F, H.
Other detectable impurities (the following substances would, if present at a sufficient level, be detected by one or other of the tests in the monograph. They are limited by the general acceptance criterion for other/unspecified impurities and/or by the general monograph Substances for pharmaceutical use (2034). It is therefore not necessary to identify these impurities for demonstration of compliance. See also 5.10. Control of impurities in substances for pharmaceutical use) G.
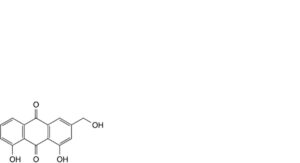
B. 1,8-dihydroxy-3-(hydroxymethyl)anthracene-9,10-dione (aloe-emodin),
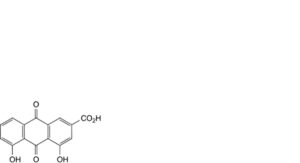
C. 4,5-dihydroxy-9,10-dioxo-9,10-dihydroanthracene-2-carboxylic acid (rhein),
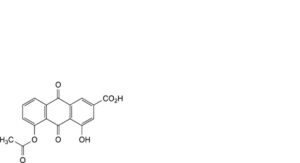
D. 5-(acetyloxy)-4-hydroxy-9,10-dioxo-9,10-dihydroanthracene-2-carboxylic acid (monoacetyl rhein isomer A),
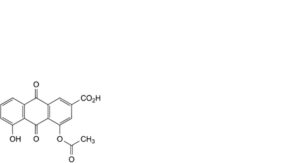
E. 4-(acetyloxy)-5-hydroxy-9,10-dioxo-9,10-dihydroanthracene-2-carboxylic acid (monoacetyl rhein isomer B),
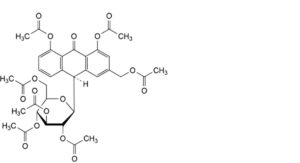
F. (10S)-3-[(acetyloxy)methyl]-10-(2,3,4,6-tetra-O-acetyl-β-D-glucopyranosyl)-9-oxo-9,10-dihydroanthracene-1,8-diyl diacetate (heptaacetyl aloin, heptaacetyl barbaloin),
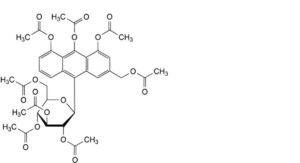
G. 3-[(acetyloxy)methyl]-10-(2,3,4,6-tetra-O-acetyl-β-D-glucopyranosyl)anthracene-1,8,9-triyl triacetate,
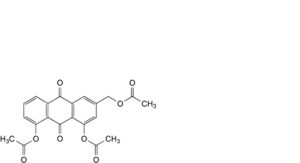
H. 3-[(acetyloxy)methyl]-9,10-dioxo-9,10-dihydroanthracene-1,8-diyl diacetate (triacetyl aloe-emodin).