(Ph. Eur. monograph 0482)
C47H74O19 943 17598-65-1
Action and use
Na/K-ATPase inhibitor; cardiac glycoside.
DEFINITION
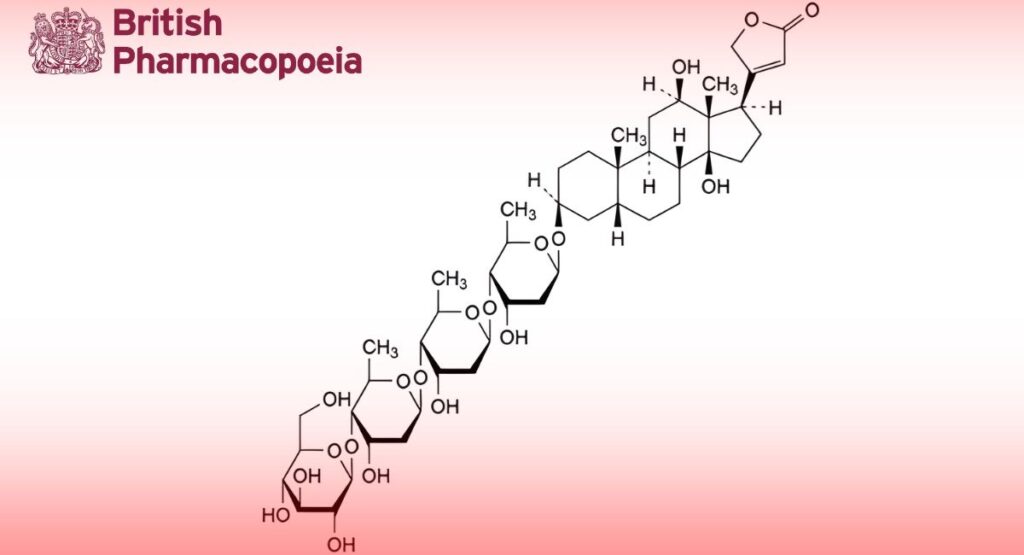
Deslanoside contains not less than 95.0 per cent and not more than the equivalent of 105.0 per cent of 3β-[(O-β-D- glucopyranosyl-(1→4)-O-2,6-dideoxy-β-D-ribo-hexopyranosyl-(1→4)-O-2,6-dideoxy-β-D-ribo-hexopyranosyl-(1→4)-2,6- dideoxy-β-D-ribo-hexopyranosyl)oxy]-12β,14-dihydroxy-5β,14β-card-20(22)-enolide, calculated with reference to the dried substance.
CHARACTERS
A white or almost white, crystalline or finely crystalline powder, hygroscopic, practically insoluble in water, very slightly soluble in ethanol (96 per cent). In an atmosphere of low relative humidity, it loses water.
IDENTIFICATION
First identification: A.
Second identification: B, C, D.
A. Examine by infrared absorption spectrophotometry (2.2.24), comparing with the spectrum obtained with
deslanoside CRS. When comparing the spectra, special attention is given to the absence of a distinct absorption maximum at about 1260 cm and to the intensity of the absorption maximum at about 1740 cm . Examine the substances in discs prepared by dissolving 1 mg of the substance to be examined or 1 mg of the reference substance in 0.3 mL of methanol R and triturating with about 0.4 g of dry, finely powdered potassium bromide R until the mixture is uniform and completely dry.
B. Examine the chromatograms obtained in the test for related substances. The principal zone in the chromatogram obtained with test solution (b) is similar in position, colour and size to the principal zone in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a).
C. Suspend about 0.5 mg in 0.2 mL of alcohol (60 per cent V/V) R. Add 0.1 mL of dinitrobenzoic acid solution R and 0.1 mL of dilute sodium hydroxide solution R. A violet colour develops.
D. Dissolve about 5 mg in 5 mL of glacial acetic acid R and add 0.05 mL of ferric chloride solution R1. Cautiously add 2 mL of sulfuric acid R, avoiding mixing the two liquids. Allow to stand; a brown but not reddish ring develops at the interface and a greenish-yellow, then bluish-green colour diffuses from it to the upper layer.
TESTS
Solution S
Dissolve 0.20 g in a mixture of equal volumes of chloroform R and methanol R and dilute to 10 mL with the same mixture of solvents.
Appearance of solution
Solution S is clear (2.2.1) and colourless (2.2.2, Method II).
Specific optical rotation (2.2.7)
Dissolve 0.200 g in anhydrous pyridine R and dilute to 10.0 mL with the same solvent. The specific optical rotation is + 6.5 to + 8.5, calculated with reference to the dried substance.
Related substances
Examine by thin-layer chromatography (2.2.27), using silica gel G R as the coating substance.
Test solution (a): Use solution S.
Test solution (b): Dilute 1 mL of test solution (a) to 10 mL with a mixture of equal volumes of chloroform R and methanol R.
Reference solution (a): Dissolve 20 mg of deslanoside CRS in a mixture of equal volumes of chloroform R and methanol R and dilute to 10 mL with the same mixture of solvents.
Reference solution (b): Dilute 2.5 mL of reference solution (a) to 10 mL with a mixture of equal volumes of chloroform R and methanol R.
Reference solution (c): Dilute 1 mL of reference solution (a) to 10 mL with a mixture of equal volumes of chloroform R and methanol R.
Apply separately to the plate as 10 mm bands 5 μL of each solution. Develop immediately over a path of 15 cm using a mixture of 3 volumes of water R, 36 volumes of methanol R and 130 volumes of methylene chloride R. Dry the plate in a current of warm air, spray with a mixture of 5 volumes of sulfuric acid R and 95 volumes of alcohol R and heat at 140 °C for 15 min. Examine in daylight. In the chromatogram obtained with test solution (a), any zone, apart from the principal zone, is not more intense than the zone in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b) (2.5 per cent) and at most two such zones are more intense than the zone in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (c) (1.0 per cent).
Loss on drying (2.2.32)
Not more than 5.0 per cent, determined on 0.500 g by drying in vacuo at 105 °C.
Sulfated ash (2.4.14)
Not more than 0.1 per cent, determined on the residue obtained in the test for loss on drying.
ASSAY
Dissolve 50.0 mg in alcohol R and dilute to 50.0 mL with the same solvent. Dilute 5.0 mL of this solution to 100.0 mL with alcohol R. Prepare a reference solution in the same manner, using 50.0 mg of deslanoside CRS (undried). To 5.0 mL of each solution add 3.0 mL of alkaline sodium picrate solution R and allow to stand protected from bright light in a water- bath at 20 ± 1 °C for 40 min. Measure the absorbance (2.2.25) of each solution at the maximum at 484 nm, using as the compensation liquid a mixture of 3.0 mL of alkaline sodium picrate solution R and 5.0 mL of alcohol R prepared at the same time.
Calculate the content of C47H74O19 from the absorbances measured and the concentrations of the solutions.
STORAGE
Store in an airtight, glass container, protected from light, at a temperature below 10 °C.