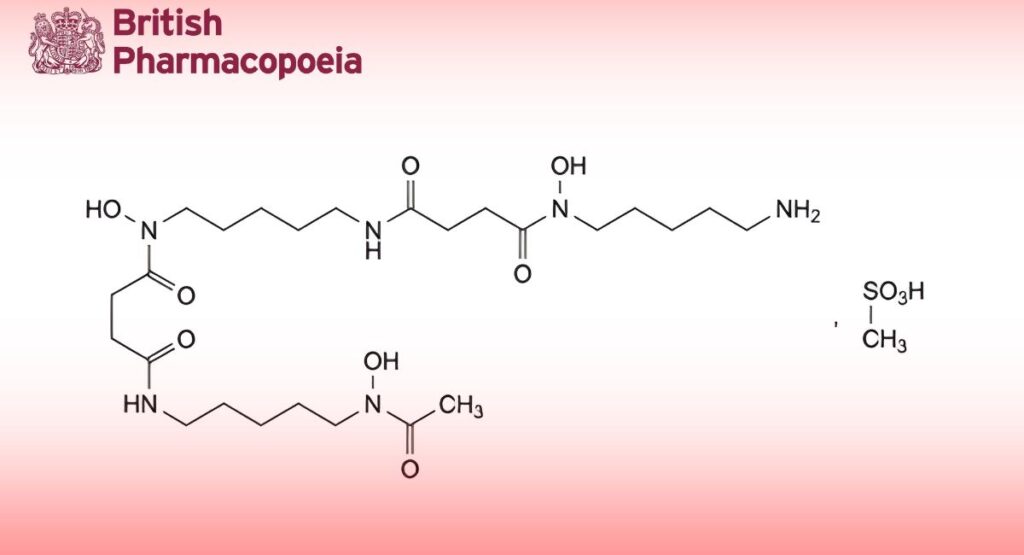
(Deferoxamine Mesilate, Ph. Eur. monograph 0896)
C26H52N6O11S 657 38-14-7
Action and use
Chelating agent (iron).
Preparation
Desferrioxamine Injection
DEFINITION
N -[5-(4-[(5-Aminopentyl)(hydroxy)amino]-4-oxobutanamido)pentyl]-N -hydroxy-N -[5-(N-
hydroxyacetamido)pentyl]butanediamide methanesulfonate.
Content
98.0 per cent to 102.0 per cent (anhydrous substance).
PRODUCTION
It is considered that alkyl methanesulfonate esters are genotoxic and are potential impurities in deferoxamine mesilate.
The manufacturing process should be developed taking into consideration the principles of quality risk management, together with considerations of the quality of starting materials, process capability and validation. The general methods 2.5.37. Methyl, ethyl and isopropyl methanesulfonate in methanesulfonic acid, 2.5.38. Methyl, ethyl and isopropyl methanesulfonate in active substances and 2.5.39. Methanesulfonyl chloride in methanesulfonic acid are available to assist manufacturers.
CHARACTERS
Appearance
White or almost white powder.
Solubility
Freely soluble in water, slightly soluble in methanol, very slightly soluble in ethanol (96 per cent).
IDENTIFICATION
A. Infrared absorption spectrophotometry (2.2.24).
Comparison: deferoxamine mesilate CRS.
B. Dissolve 0.1 g in 5 mL of dilute hydrochloric acid R. Add 1 mL of barium chloride solution R2. The solution is clear. In a porcelain crucible, mix 0.1 g with 1 g of anhydrous sodium carbonate R, heat and ignite over a naked flame. Allow to cool.
Dissolve the residue in 10 mL of water R, heating if necessary, and filter. The filtrate gives reaction (a) of sulfates (2.3.1).
TESTS
Solution S
Dissolve 2.5 g in carbon dioxide-free water R prepared from distilled water R and dilute to 25 mL with the same solvent.
Appearance of solution
Solution S is clear (2.2.1) and not more intensely coloured than reference solution Y5 (2.2.2, Method II).
pH (2.2.3)
4.0 to 6.0.
Dilute 1 mL of freshly prepared solution S to 10 mL with carbon dioxide-free water R prepared from distilled water R.
Related substances
Liquid chromatography (2.2.29). Prepare the solutions immediately before use and protect from light.
A. Deferoxamine mesilate produced by fermentation.
Solvent mixture: acetonitrile R, water R (6:94 V/V).
Test solution: Dissolve 25 mg of the substance to be examined in 10 mL of the solvent mixture and dilute to 25.0 mL with the solvent mixture.
Reference solution (a): Dilute 1.0 mL of the test solution to 100.0 mL with the solvent mixture.
Reference solution (b): Dissolve 5 mg of deferoxamine for system suitability CRS (containing impurity A) in mobile phase A and dilute to 5 mL with the solvent mixture.
Column:
— size: l = 0.075 m, Ø = 4.6 mm;
— stationary phase: octadecylsilyl silica gel for chromatography R (3.5 μm);
— temperature: 32 °C.
Mobile phase:
— mobile phase A: 1.32 g/L solution of ammonium phosphate R adjusted to pH 3.0 with phosphoric acid R;
— mobile phase B: mixture of equal volumes of acetonitrile for chromatography R and mobile phase A;
| Time (min) |
Mobile phase A (per cent V/V) |
Mobile phase B (per cent V/V) |
| 0 – 4 | 88 | 12 |
| 4 – 20 | 88 → 80 | 12 → 20 |
| 20 – 35 | 80 → 57.5 | 20 → 42.5 |
Flow rate: 1.5 mL/min.
Detection: Spectrophotometer at 220 nm.
Injection: 20 μL.
Identification of impurities: Use the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b) to identify the peak due to impurity A.
Relative retention: With reference to deferoxamine (retention time = about 18 min): impurity A = about 0.9.
System suitability Reference solution (b):
— resolution: minimum 2.0 between the peaks due to impurity A and deferoxamine.
Calculation of percentage contents:
— for each impurity, use the concentration of deferoxamine mesilate in reference solution (a).
Limits:
— impurity A: maximum 2.0 per cent;
— any other impurity: for each impurity, maximum 0.8 per cent;
— total: maximum 5.0 per cent;
— reporting threshold: 0.05 per cent.
The thresholds indicated under Related substances (Table 2034.-1) in the general monograph Substances for pharmaceutical use (2034) do not apply.
B. Deferoxamine mesilate produced by a synthetic process.
Solvent mixture: Mobile phase B, mobile phase A (20:80 V/V).
Test solution: Dissolve 0.125 g of the substance to be examined in the solvent mixture and dilute to 10.0 mL with the solvent mixture.
Reference solution (a): Dilute 1.0 mL of the test solution to 100.0 mL with the solvent mixture. Dilute 1.0 mL of this solution to 10.0 mL with the solvent mixture.
Reference solution (b): Dissolve 12.5 mg of deferoxamine for peak identification CRS (containing impurities F, G, H, I and J) in the solvent mixture and dilute to 1 mL with the solvent mixture.
Column:
— size: l = 0.15 m, Ø = 4.6 mm;
— stationary phase: end-capped octadecylsilyl silica gel for chromatography R (5 μm);
— temperature: 25 °C.
Mobile phase:
— mobile phase A: dissolve 0.605 g of sodium edetate R in 900 mL of water for chromatography R, add 1.0 mL of phosphoric acid R and adjust to pH 6.0 with concentrated ammonia R; dilute to 1000 mL with water for chromatography R;
— mobile phase B: dissolve 0.780 g of sodium edetate R in 750 mL of water for chromatography R and add 1.0 mL of phosphoric acid R; add 250 mL of acetonitrile for chromatography R, mix thoroughly and adjust the apparent pH to 6.0 with concentrated ammonia R;
| Time (min) |
Mobile phase A (per cent V/V) |
Mobile phase B (per cent V/V) |
| 0 | 80 | 20 |
| 0 – 21.6 | 80 → 20 | 20 → 80 |
| 21.6 – 31.6 | 20 | 80 |
Flow rate: 1.5 mL/min.
Detection: Spectrophotometer at 220 nm.
Injection: 20 μL.
Identification of impurities: Use the chromatogram supplied with deferoxamine for peak identification CRS and the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b) to identify the peaks due to impurities F, G, H, I and J.
Relative retention: With reference to deferoxamine (retention time = about 12.9 min): impurity I = about 0.5;
impurity F = about 0.96; impurity G = about 0.98; impurity H = about 1.2; impurities J and K = about 1.37.
System suitability: Reference solution (b):
— peak-to-valley ratio: minimum 3.0, where Hp = height above the baseline of the peak due to impurity G and Hv = height above the baseline of the lowest point of the curve separating this peak from the peak due to deferoxamine.
Calculation of percentage contents:
— correction factor: multiply the peak area of impurity I by 1.4;
— for each impurity, use the concentration of deferoxamine mesilate in reference solution (a).
Limits:
— impurities F, H: for each impurity, maximum 0.5 per cent;
— impurities G, I: for each impurity, maximum 0.3 per cent;
— sum of impurities J and K: maximum 0.5 per cent;
— unspecified impurities: for each impurity, maximum 0.20 per cent;
— total: maximum 2.0 per cent;
— reporting threshold: 0.03 per cent.
The thresholds indicated under Related substances (Table 2034.-1) in the general monograph Substances for pharmaceutical use (2034) do not apply.
Chlorides (2.4.4)
Maximum 330 ppm.
Dilute 2 mL of solution S to 20 mL with water R.
Sulfates (2.4.13)
Maximum 400 ppm.
Dilute 5 mL of solution S to 20 mL with distilled water R.
Water (2.5.12)
Maximum 2.0 per cent, determined on 1.000 g.
Sulfated ash (2.4.14)
Maximum 0.1 per cent, determined on 1.0 g.
Bacterial endotoxins (2.6.14)
Less than 0.025 IU/mg, if intended for use in the manufacture of parenteral preparations without a further appropriate procedure for the removal of bacterial endotoxins. Since deferoxamine mesilate has an inhibitory effect on the bacterial endotoxins test, a suitable procedure is put in place to remove this inhibitory effect. The monocyte-activation test (2.6.30) has been found suitable to overcome this issue.
ASSAY
Dissolve 0.500 g in 50 mL of water R. Add 4 mL of dilute sulfuric acid R1. Titrate with 0.1 M ferric ammonium sulfate. To accelerate the titration, add 4.5 mL quickly, stop for 1.5 min and continue to titrate uniformly at a rate of about 0.2 mL/min.
Determine the end-point potentiometrically (2.2.20) using a platinum indicator electrode and a suitable reference electrode.
1 mL of 0.1 M ferric ammonium sulfate is equivalent to 65.68 mg of C26H52N6O11S.
STORAGE
Protected from light. If the substance is sterile, store in a sterile, airtight, tamper-evident container.
LABELLING
The label states the origin of the substance:
— produced by fermentation;
— produced by a synthetic process.
IMPURITIES
Test A for related substances: A, B, C, J.
Test B for related substances: E, F, G, H, I, J, K.
Specified impurities: A, F, G, H, I, J, K.
Other detectable impurities (the following substances would, if present at a sufficient level, be detected by one or other of the tests in the monograph. They are limited by the general acceptance criterion for other/unspecified impurities. It is therefore not necessary to identify these impurities for demonstration of compliance. See also 5.10. Control of impurities in substances for pharmaceutical use) B, C, E.
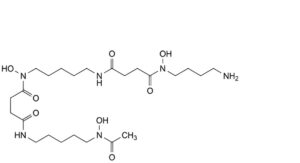
A. N -[5-(4-[(4-aminobutyl)(hydroxy)amino]-4-oxobutanamido)pentyl]-N -hydroxy-N -[5-(N-
hydroxyacetamido)pentyl]butanediamide,
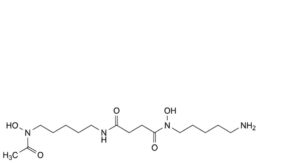
B. N -(5-aminopentyl)-N -hydroxy-N -[5-(N-hydroxyacetamido)pentyl]butanediamide,
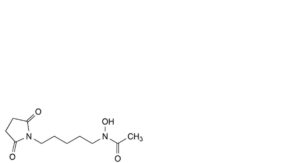
C. N-[5-(2,5-dioxopyrrolidin-1-yl)pentyl]-N-hydroxyacetamide,
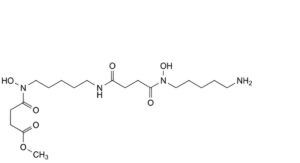
E. methyl 4-[[5-[[4-[(5-aminopentyl)(hydroxy)amino]-4-oxobutanamido]pentyl](hydroxy)amino]-4-oxobutanoate,
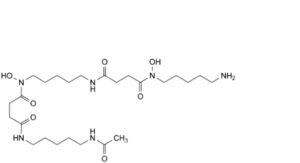
F. N -(5-acetamidopentyl)-N -[5-[4-[(5-aminopentyl)(hydroxyl)amino]-4-oxobutanamido]pentyl]-N -hydroxybutanediamide,
G. unknown structure,
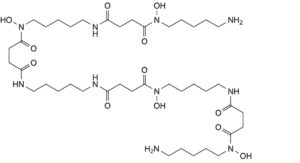
H. N ,N -bis(5-aminopentyl)-N ,N ,11,27-tetrahydroxy-4,12,15,23,26,34-hexaoxo-5,11,16,22,27,33-
hexaazaheptatriacontane-1,37-diamide,
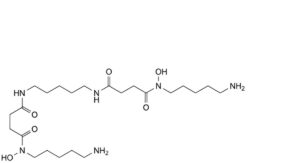
I. N -(5-aminopentyl)-N -[5-(4-[(5-aminopentyl)(hydroxy)amino]-4-oxobutanamido)pentyl]- N -hydroxybutanediamide,
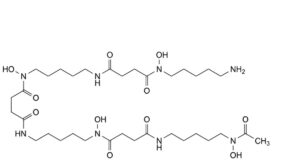
J. N -(5-aminopentyl)-N ,11,22-trihydroxy-N -[5-(N-hydroxyacetamido)pentyl]-4,12,15,23-tetraoxo-5,11,16,22- tetraazahexacosane-1,26-diamide,
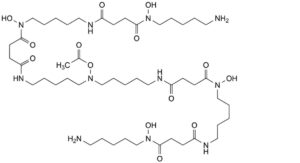
K. 22-(acetyloxy)-N ,N -bis(5-aminopentyl)-N ,N ,11,33-tetrahydroxy-4,12,15,29,32,40-hexaoxo-5,11,16,22,28,33,39- heptaazatritetracontane-1,43-diamide.