(Ph. Eur. monograph 1413)
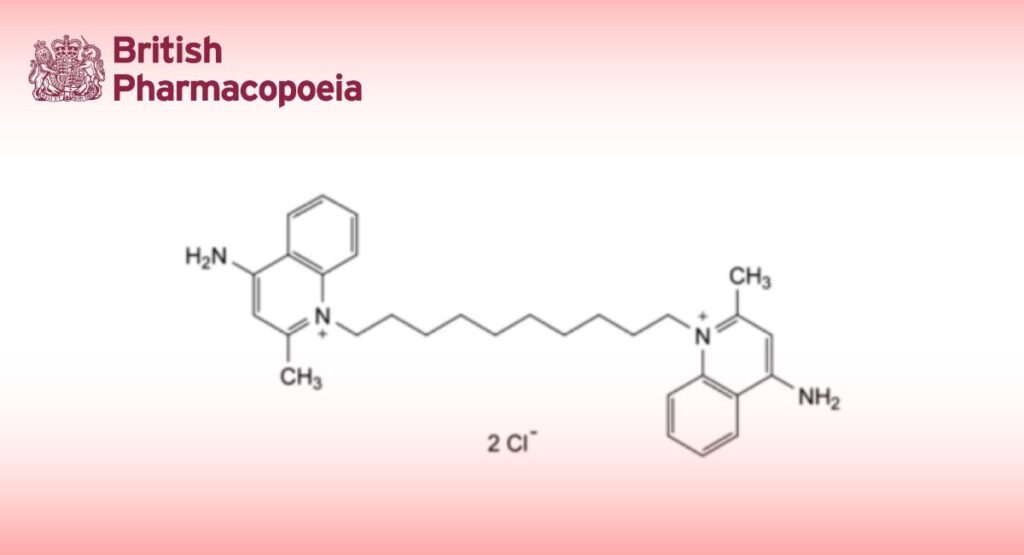
C30H40Cl2N4 527.6 522-51-0
Action and use
Antiseptic.
DEFINITION
1,1′-(Decane-1,10-diyl)bis(4-amino-2-methylquinolin-1-ium) dichloride.
Content
98.0 per cent to 102.0 per cent (anhydrous substance).
It contains a variable quantity of water.
CHARACTERS
Appearance
White or yellowish-white powder, hygroscopic.
Solubility
Slightly to very slightly soluble in water and slightly soluble in ethanol (96 per cent).
IDENTIFICATION
Dequalinium Chloride
First identification: B, E.
Second identification: A, C, D, E.
A. Ultraviolet and visible absorption spectrophotometry (2.2.25).
Test solution: Dissolve about 10 mg in water R and dilute to 100 mL with the same solvent. Dilute 10 mL of the solution to 100 mL with water R.
Spectral range: 230-350 nm.
Absorption maxima: At 240 nm and 326 nm.
Shoulder: At 336 nm.
Absorbance ratios:
— A240/A326 = 1.56 to 1.80;
— A326/A336 = 1.12 to 1.30.
B. Infrared absorption spectrophotometry (2.2.24).
Spectral range 600-2000 cm .
Comparison: dequalinium chloride for ID CRS.
C. To 5 mL of solution S (see Tests) add 5 mL of potassium ferricyanide solution R. A yellow precipitate is formed.
D. To 10 mL of solution S add 1 mL of dilute nitric acid R. A white precipitate is formed. Filter and reserve the filtrate for identification test E.
E. To 10 mL of solution S (see Tests) add 1 mL of dilute nitric acid R and filter off the precipitate. The filtrate gives reaction (a) of chlorides (2.3.1).
TESTS
Solution S
Dissolve 0.2 g in 90 mL of carbon dioxide-free water R, heating if necessary, and dilute to 100 mL with the same solvent.
Appearance of solution
Solution S is clear (2.2.1) and colourless (2.2.2, Method II).
Acidity or alkalinity
To 5 mL of solution S add 0.1 mL of bromothymol blue solution R1. Not more than 0.2 mL of 0.01 M hydrochloric acid or 0.01 M sodium hydroxide is required to change the colour of the indicator.
Related substances
Liquid chromatography (2.2.29).
Test solution: Dissolve 10.0 mg of the substance to be examined in the mobile phase and dilute to 10.0 mL with the mobile phase.
Reference solution (a): Dissolve 5 mg of dequalinium for system suitability CRS (containing impurities A, B and C) in the mobile phase and dilute to 5 mL with the mobile phase.
Reference solution (b): Dissolve 10.0 mg of dequalinium chloride for ID CRS (with an assigned content) in the mobile phase and dilute to 10.0 mL with the mobile phase. Dilute 1.0 mL of the solution to 50.0 mL with the mobile phase.
Column:
— size: l = 0.25 m, Ø = 4.6 mm;
— stationary phase: end-capped octadecylsilyl silica gel for chromatography R (5 μm).
Mobile phase: Dissolve 2 g of sodium hexanesulfonate R in 300 mL of water for chromatography R; adjust to pH 4.0 with acetic acid R and add 700 mL of methanol R1.
Flow rate: 1.5 mL/min.
Detection: Spectrophotometer at 240 nm.
Injection: 10 μL.
Run time: 5 times the retention time of dequalinium.
Identification of impurities: Use the chromatogram supplied with dequalinium for system suitability CRS and the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a) to identify the peaks due to impurities A, B and C.
Relative retention: With reference to dequalinium (retention time = about 4 min): impurity A = about 0.5; impurity B = about 1.3; impurity C = about 4.
System suitability: Reference solution (a):
— peak-to-valley ratio: minimum 2.0, where Hp = height above the baseline of the peak due to impurity B and Hv = height above the baseline of the lowest point of the curve separating this peak from the peak due to dequalinium.
Calculation of percentage contents:
— correction factors: multiply the peak areas of the following impurities by the corresponding correction factor: impurity A = 0.5; impurity C = 1.5;
— for each impurity, use the concentration of dequalinium chloride in reference solution (b), taking into account the assigned content of dequalinium chloride for ID CRS.
Limits:
— impurity C: maximum 5.0 per cent;
— impurity B: maximum 2.0 per cent;
— impurity A: maximum 0.3 per cent;
— unspecified impurities: for each impurity, maximum 0.10 per cent;
— total: maximum 7.0 per cent;
— reporting threshold: 0.05 per cent.
Readily carbonisable substances
Dissolve 20 mg in 2 mL of sulfuric acid R. After 5 min the solution is not more intensely coloured than reference solution BY4(2.2.2, Method I).
Water (2.5.12)
Maximum 10.0 per cent, determined on 0.08 g. Use as the solvent a mixture of equal volumes of methanol R and formamide R.
Sulfated ash (2.4.14)
Maximum 0.1 per cent, determined on 1.0 g.
ASSAY
In order to avoid overheating in the reaction medium, mix thoroughly throughout and stop the titration immediately after the end-point has been reached.
Dissolve 0.200 g in 5 mL of formic acid R and add 50 mL of acetic anhydride R. Titrate with 0.1 M perchloric acid, determining the end-point potentiometrically (2.2.20).
1 mL of 0.1 M perchloric acid is equivalent to 26.38 mg of C30H40Cl2N4.
STORAGE
In an airtight container.
IMPURITIES
Specified impurities A, B, C.
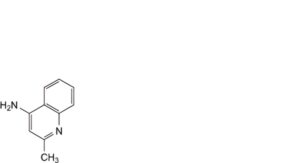
A. 2-methylquinolin-4-amine,
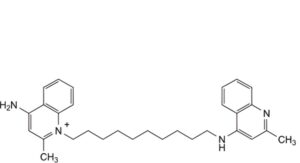
B. 4-amino-2-methyl-1-[10-[(2-methylquinolin-4-yl)amino]decyl]quinolin-1-ium,
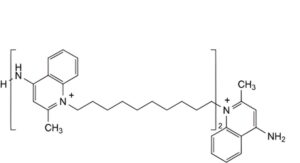
C. 4-amino-1-[10-[[1-[10-(4-amino-2-methylquinolin-1-ium-1-yl)decyl]-2-methylquinolin-1-ium-4-yl]amino]decyl]-2-methylquinolin-1-ium.