(Ph. Eur. monograph 3095)
C35H45N7O8S 724 872728-81-9
DEFINITION
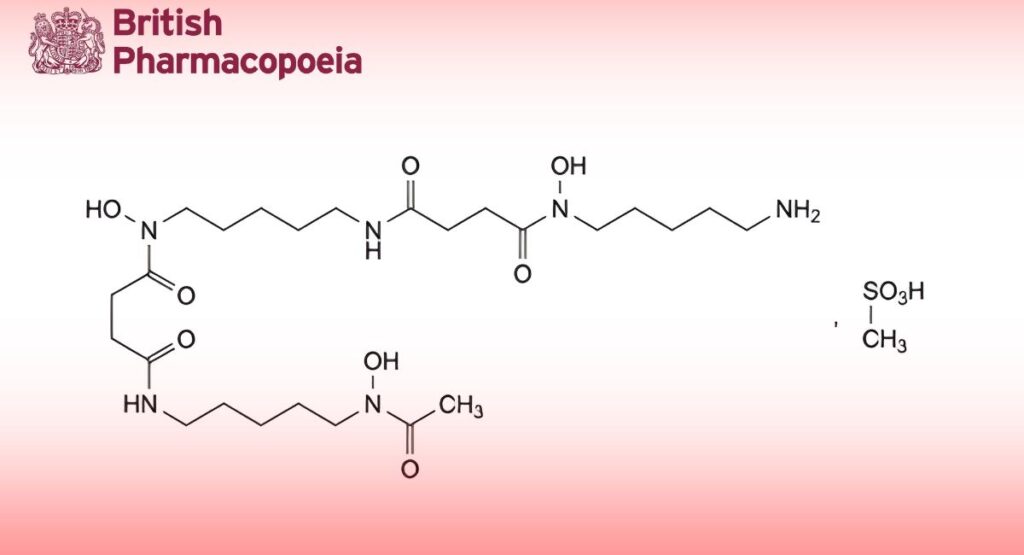
Ethyl 3-[2-[[4-[N′-[(hexyloxy)carbonyl]carbamimidoyl]anilino]methyl]-1-methyl-N-(pyridin-2-yl)-1H-benzimidazole-5- carboxamido]propanoate methanesulfonate.
Content
98.0 per cent to 102.0 per cent of C35H45N7O8S (anhydrous substance).
PRODUCTION
It is considered that alkyl methanesulfonate esters are genotoxic and are potential impurities in dabigatran etexilate mesilate. The manufacturing process should be developed taking into consideration the principles of quality risk management, together with considerations of the quality of starting materials, process capability and validation. The general methods 2.5.37. Methyl, ethyl and isopropyl methanesulfonate in methanesulfonic acid and 2.5.39. Methanesulfonyl chloride in methanesulfonic acid are available to assist manufacturers.
CHARACTERS
Appearance
White to yellowish-white or yellow, crystalline powder.
Solubility
Very slightly soluble or practically insoluble in water, soluble or sparingly soluble in anhydrous ethanol, practically insoluble in heptane.
It shows polymorphism (5.9).
IDENTIFICATION
Infrared absorption spectrophotometry (2.2.24).
Comparison: dabigatran etexilate mesilate CRS.
If the spectra obtained in the solid state show differences, dissolve the substance to be examined and the reference substance separately in anhydrous ethanol R, evaporate to dryness and record new spectra using the residues.
TESTS
Related substances
Liquid chromatography (2.2.29).
Buffer solution: A 2.0 g/L solution of potassium dihydrogen phosphate R adjusted to pH 6.0 with a 40 g/L solution of sodium hydroxide R.
Test solution: Dissolve 40.0 mg of the substance to be examined in 2 mL of anhydrous ethanol R and dilute to 10.0 mL with acetonitrile R.
Reference solution (a): Disperse 5 mg of dabigatran etexilate impurity A CRS, 5 mg of dabigatran etexilate
impurity B CRS and 5 mg of dabigatran etexilate impurity C CRS in 2 mL of anhydrous ethanol R, add 100 μL of a 103 g/L solution of hydrochloric acid R and dilute to 10.0 mL with acetonitrile R.
Reference solution (b): Dissolve 40 mg of the substance to be examined in 2 mL of anhydrous ethanol R, add 400 μL of reference solution (a) and dilute to 10 mL with acetonitrile R.
Reference solution (c): Dilute 1.0 mL of the test solution to 100.0 mL with a mixture of 20 volumes of anhydrous ethanol R and 80 volumes of acetonitrile R. Dilute 1.0 mL of this solution to 10.0 mL with acetonitrile R.
Column:
— size: l = 0.05 m, Ø = 4.6 mm;
— stationary phase: end-capped octadecylsilyl silica gel for chromatography R (1.8 μm).
Mobile phase:
— mobile phase A: methanol R1, buffer solution (10:90 V/V);
— mobile phase B: buffer solution, methanol R1 (10:90 V/V);
| Time (min) |
Mobile phase A (per cent V/V) |
Mobile phase B (per cent V/V) |
| 0 – 2 | 87.5 | 12.5 |
| 2 – 5 | 87.5 → 47.5 | 12.5 → 52.5 |
| 5 – 22 | 47.5 → 6.3 | 52.5 → 93.7 |
Flow rate: 1.2 mL/min.
Detection: Spectrophotometer at 224 nm.
Temperature: 35 °C.
Injection: 1 μL of the test solution and reference solutions (b) and (c).
Identification of impurities: Use the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b) to identify the peaks due to impurities A, B and C.
Relative retention: With reference to dabigatran etexilate (retention time = about 14 min): impurity B = about 0.4; impurity A = about 0.9; impurity C = about 0.96.
System suitability: Reference solution (b):
— resolution: minimum 2.5 between the peaks due to impurity C and dabigatran etexilate.
Calculation of percentage contents:
— for each impurity, use the concentration of the substance to be examined in reference solution (c).
Limits:
— impurity A: maximum 0.60 per cent;
— impurity B: maximum 0.20 per cent;
— unspecified impurities: for each impurity, maximum 0.10 per cent;
— total: maximum 1.0 per cent;
— reporting threshold: 0.05 per cent.
Impurity D
Gas chromatography (2.2.28) coupled with mass spectrometry (2.2.43). Prepare the test solution immediately before use.
Internal standard solution: A solution of hexane R containing 0.1 μg/mL of butyl methanesulfonate R (BMS).
Test solution: Weigh 200.0 mg of the substance to be examined, add 1.0 mL of the internal standard solution, shake and sonicate for 10 min twice. Centrifuge at 2500 g at 5 °C for 10 min. Inject the supernatant.
Reference solution (a): Dissolve 20.0 mg of hexyl methanesulfonate R (HMS, dabigatran etexilate impurity D) in the internal standard solution and dilute to 100.0 mL with the same solution. Dilute 1.0 mL of this solution to 100.0 mL with the internal standard solution.
Reference solution (b): Dilute 4.0 mL of reference solution (a) to 10.0 mL with the internal standard solution (equivalent to 4 ppm of HMS).
Reference solution (c): Dilute 3.0 mL of reference solution (a) to 10.0 mL with the internal standard solution (equivalent to 3 ppm of HMS).
Reference solution (d): Dilute 2.0 mL of reference solution (a) to 10.0 mL with the internal standard solution (equivalent to 2 ppm of HMS).
Reference solution (e): Dilute 1.5 mL of reference solution (a) to 10.0 mL with the internal standard solution (equivalent to 1.5 ppm of HMS).
Reference solution (f): Dilute 1.0 mL of reference solution (a) to 10.0 mL with the internal standard solution (equivalent to 1 ppm of HMS).
Reference solution (g): Dilute 2.5 mL of reference solution (d) to 10.0 mL with the internal standard solution (equivalent to 0.5 ppm of HMS).
Column:
— material: fused silica;
— size: l = 30 m, Ø = 0.25 mm;
— stationary phase: macrogol 20 000 R (film thickness 0.50 μm).
Carrier gas: helium for chromatography R.
Flow rate: 1.5 mL/min.
Split ratio: 1:2.
Temperature:
| Time (min) |
Temperature (°C) |
||
| Column | 0 – 2 | 80 | |
| 2 – 14 | 80 → 200 | ||
| 14 – 30 | 200 | ||
| Injection port | – | 220 | |
| Detector | transfer line | – | 280 |
| ion source | – | 230 | |
| quadrupole | – | 150 |
Detection: Mass spectrometer as described below; adjust the detector settings so as to comply with the system suitability criteria:
— quadrupole mass spectrometer equipped with an electron impact ionisation mode (70 eV);
— mass spectrometer parameters for the fragmentometric mode (single-ion monitoring (SIM)) set as follows:
| Substance | m/z |
| Butyl methanesulfonate (BMS) | 56, 79 or 109 |
| Hexyl methanesulfonate (impurity D) | 56, 97 and 109 |
Injection: 2 μL.
Relative retention: With reference to the internal standard (BMS) (retention time = about 12.8 min): impurity D (HMS) = about 1.2.
System suitability: Reference solution (g):
— sensitivity: minimum 10 for the signal-to-noise ratio for the peak due to impurity D.
Quantification: Establish a 6-point calibration curve with the concentration of impurity D in reference solutions (b) to (g) as the abscissa and the mean ratio of the peak area of impurity D to the peak area of the internal standard in the corresponding chromatograms as the ordinate.
Limits:
— impurity D: maximum 1.9 ppm;
— reporting threshold: 0.5 ppm (reference solution (g)).
Water (2.5.12)
Maximum 0.8 per cent, determined on 2.00 g.
Sulfated ash (2.4.14)
Maximum 0.1 per cent determined on 2.0 g.
ASSAY
Liquid chromatography (2.2.29).
Test solution: Dissolve 30.0 mg of the substance to be examined in 5 mL of anhydrous ethanol R and dilute to 100.0 mL with acetonitrile R.
Reference solution (a): Dissolve 30.0 mg of dabigatran etexilate mesilate CRS in 5 mL of anhydrous ethanol R and dilute to 100.0 mL with acetonitrile R.
Reference solution (b): Disperse 3 mg of dabigatran etexilate impurity A CRS in 2.5 mL of anhydrous ethanol R, add 100 μL of a 103 g/L solution of hydrochloric acid R and dilute to 50 mL with reference solution (a).
Column:
— size: l = 0.1 m, Ø = 4.6 mm;
— stationary phase: end-capped monolithic octadecylsilyl silica gel for chromatography R (2.0 μm);
— temperature: 35 °C.
Mobile phase: methanol R1, acetonitrile for chromatography R, a 2 g/L solution of potassium dihydrogen phosphate R previously adjusted to pH 6.0 with a 40 g/L solution of sodium hydroxide R (20:35:45 V/V/V).
Flow rate: 4.0 mL/min.
Detection: Spectrophotometer at 224 nm.
Injection volume: 5 μL.
Run time: 2.5 times the retention time of dabigatran etexilate.
Relative retention: With reference to dabigatran etexilate (retention time = about 1.6 min): impurity A = about 0.8.
System suitability: Reference solution (b):
— resolution: minimum 1.5 between the peaks due to impurity A and dabigatran etexilate.
Calculate the percentage content of C35H45N7O8S taking into account the assigned content of dabigatran etexilate mesilate CRS.
IMPURITIES
Specified impurities A, B, D.
Other detectable impurities (the following substances would, if present at a sufficient level, be detected by one or other of the tests in the monograph. They are limited by the general acceptance criterion for other/unspecified impurities and/or by the general monograph Substances for pharmaceutical use (2034). It is therefore not necessary to identify these impurities for demonstration of compliance. See also 5.10. Control of impurities in substances for pharmaceutical use) C, E, F, G.
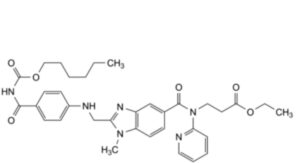
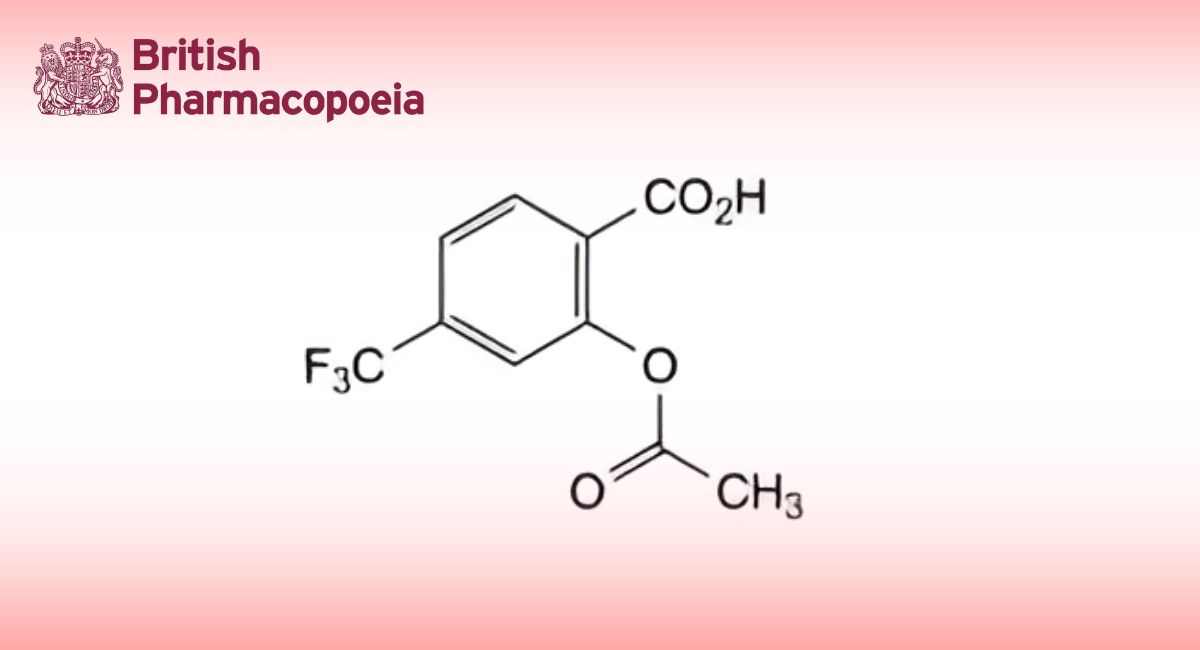
A. ethyl 3-[2-[[4-[[(hexyloxy)carbonyl]carbamoyl]anilino]methyl]-1-methyl-N-(pyridin-2-yl)-1H-benzimidazole-5- carboxamido]propanoate,
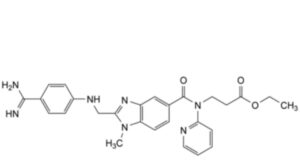
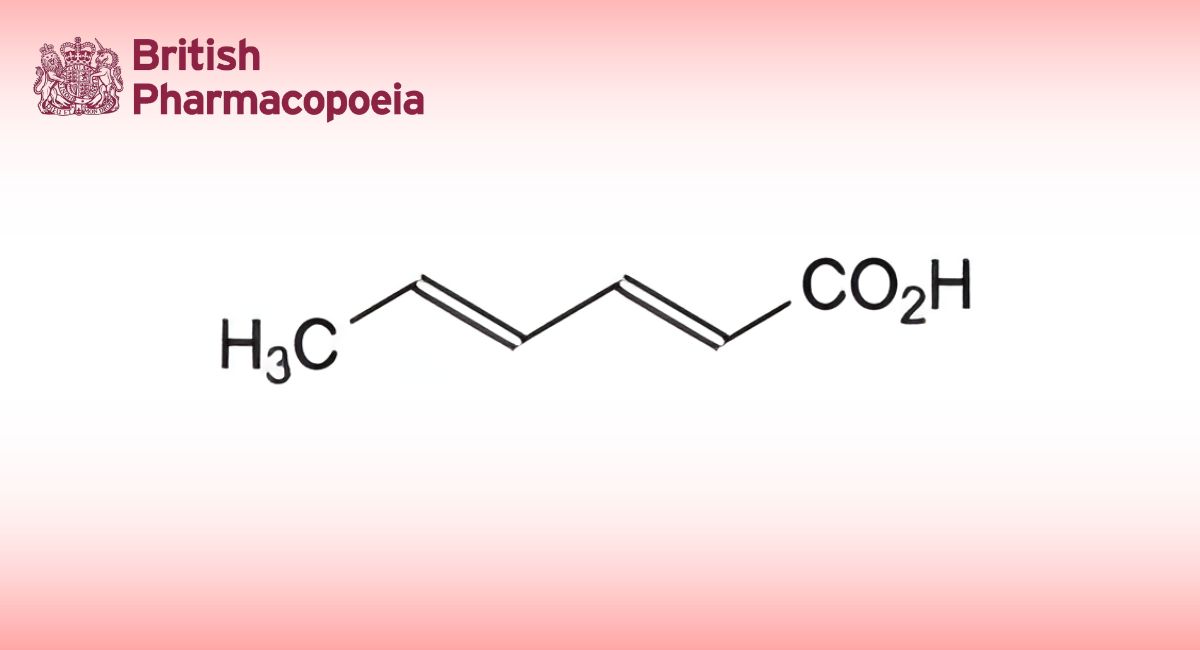
B. ethyl 3-[2-[(4-carbamimidoylanilino)methyl]-1-methyl-N-(pyridin-2-yl)-1H-benzimidazole-5-carboxamido]propanoate,
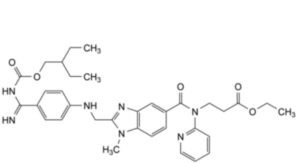
C. ethyl 3-[2-[[4-[N′-[(2-ethylbutoxy)carbonyl]carbamimidoyl]anilino]methyl]-1-methyl-N-(pyridin-2-yl)-1H-benzimidazole-5- carboxamido]propanoate,
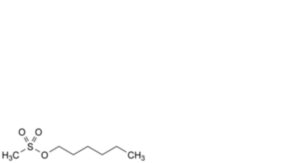
D. hexyl methanesulfonate,
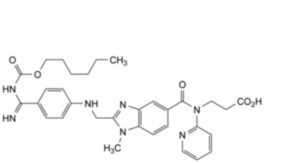
E. 3-[2-[[4-[N′-[(hexyloxy)carbonyl]carbamimidoyl]anilino]methyl]-1-methyl-N-(pyridin-2-yl)-1H-benzimidazole-5- carboxamido]propanoic acid,
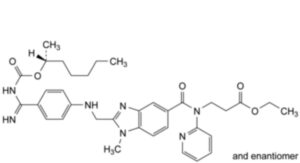
F. ethyl 3-[2-[[4-[N′-[[[(2RS)-heptan-2-yl]oxy]carbonyl]carbamimidoyl]anilino]methyl]-1-methyl-N-(pyridin-2-yl)-1H- benzimidazole-5-carboxamido]propanoate,
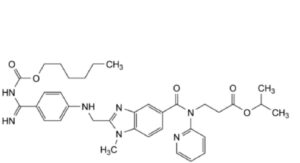
G. propan-2-yl 3-[2-[[4-[N′-[(hexyloxy)carbonyl]carbamimidoyl]anilino]methyl]-1-methyl-N-(pyridin-2-yl)-1H-benzimidazole- 5-carboxamido]propanoate.