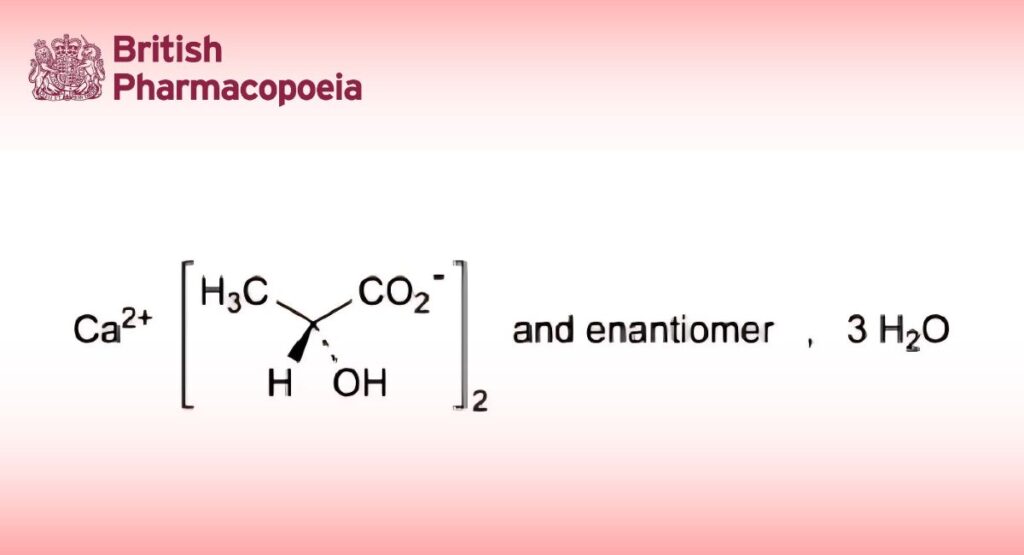
(Ph. Eur. monograph 0469)
C6H10CaO6, 3H2O 272.3Action and use
Used in treatment of calcium deficiency.
Preparation
Calcium Lactate Tablets
DEFINITION
Calcium bis[(2Ξ)-2-hydroxypropanoate] or mixture of calcium (2R)-, (2S)- and (2RS)-2-hydroxypropanoates trihydrates.
Content
98.0 per cent to 102.0 per cent (dried substance).
CHARACTERS
Appearance
White or almost white, crystalline or granular powder.
Solubility
Soluble in water, freely soluble in boiling water, very slightly soluble in ethanol (96 per cent).
IDENTIFICATION
A. Loss on drying (see Tests).
B. It gives the reaction of lactates (2.3.1).
C. It gives reaction (b) of calcium (2.3.1).
TESTS
Solution S
Dissolve 6.2 g (equivalent to 5.0 g of the dried substance) with heating in carbon dioxide-free water R prepared from distilled water R, allow to cool and dilute to 100 mL with the same solvent.
Appearance of solution
Solution S is not more opalescent than reference suspension II (2.2.1) and not more intensely coloured than reference solution BY6 (2.2.2, Method II).
Acidity or alkalinity
To 10 mL of solution S add 0.1 mL of phenolphthalein solution R and 0.5 mL of 0.01 M hydrochloric acid. The solution is colourless. Not more than 2.0 mL of 0.01 M sodium hydroxide is required to change the colour of the indicator to pink.
Chlorides (2.4.4)
Maximum 200 ppm.
Dilute 5 mL of solution S to 15 mL with water R.
Sulfates (2.4.13)
Maximum 400 ppm.
Dilute 7.5 mL of solution S to 15 mL with distilled water R.
Iron (2.4.9)
Maximum 50 ppm.
Dilute 4 mL of solution S to 10 mL with water R.
Magnesium and alkali salts
Maximum 1 per cent.
To 20 mL of solution S add 20 mL of water R, 2 g of ammonium chloride R and 2 mL of dilute ammonia R1. Heat to boiling and rapidly add 40 mL of hot ammonium oxalate solution R. Allow to stand for 4 h, dilute to 100.0 mL with water R and filter. To 50.0 mL of the filtrate add 0.5 mL of sulfuric acid R. Evaporate to dryness and ignite the residue to constant mass
at 600 ± 50 °C. The residue weighs a maximum of 5 mg.
Loss on drying (2.2.32)
15.0 per cent to 20.0 per cent, determined on 0.500 g by drying in an oven at 125 °C.
ASSAY
Dissolve a quantity equivalent to 0.200 g of the dried substance in water R and dilute to 300 mL with the same solvent.
Carry out the complexometric titration of calcium (2.5.11).
1 mL of 0.1 M sodium edetate is equivalent to 21.82 mg of C6H10CaO6