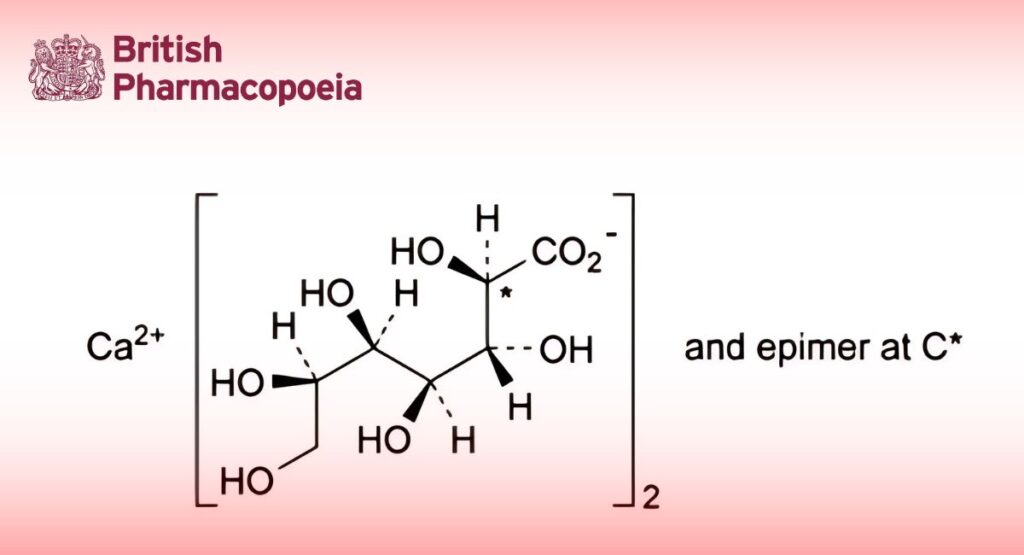
(Ph. Eur. monograph 1399)
C14H26CaO16 490.4
Action and use
Used in treatment of calcium deficiency.
DEFINITION
Mixture in variable proportions, of calcium di(D-glycero-D-gulo-heptonate) and calcium di(D-glycero-D-ido-heptonate).
Content
98.0 per cent to 102.0 per cent of calcium 2,3,4,5,6,7-hexahydroxyheptanoate (dried substance).
CHARACTERS
Appearance
White or very slightly yellow, amorphous powder, hygroscopic.
Solubility
Very soluble in water, practically insoluble in acetone and in ethanol (96 per cent).
IDENTIFICATION
A. Thin-layer chromatography (2.2.27).
Test solution: Dissolve 20 mg of the substance to be examined in 1 mL of water R.
Reference solution (a): Dissolve 20 mg of calcium glucoheptonate CRS in 1 mL of water R.
Reference solution (b): Dissolve 10 mg of calcium gluconate CRS in 0.5 mL of the test solution and dilute to 1 mL with water R.
Plate: cellulose for chromatography R1 as the coating substance.
Mobile phase: formic acid R, water R, acetone R, butanol R (20:20:30:30 V/V/V/V); use a freshly prepared mixture.
Application: 10 μL as bands of 20 mm by 2 mm.
Development: In a tank previously allowed to saturate for 10 min, over a path of 12 cm.
Drying: In air.
Detection: Spray with 0.02 M potassium permanganate.
System suitability: Reference solution (b):
— the chromatogram shows 2 clearly separated spots.
Results: The principal spot in the chromatogram obtained with the test solution is similar in position and size to the principal spot in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a).
B. 0.2 mL of solution S (see Tests) gives reaction (b) of calcium (2.3.1).
TESTS
Solution S
Dissolve 10.0 g in carbon dioxide-free water R prepared from distilled water R and dilute to 100 mL with the same solvent.
Appearance of solution
Solution S is clear (2.2.1) and not more intensely coloured than reference solution Y6 (2.2.2, Method II).
pH (2.2.3)
6.0 to 8.0 for solution S.
Reducing sugars
Maximum 1 per cent, expressed as glucose.
Dissolve 1.0 g in 5 mL of water R with the aid of gentle heat. Cool and add 20 mL of cupri-citric solution R and a few glass beads. Heat so that boiling begins after 4 min and maintain boiling for 3 min. Cool rapidly and add 100 mL of a 2.4 per cent V/V solution of glacial acetic acid R and 20.0 mL of 0.025 M iodine. With continuous shaking, add 25 mL of a mixture
of 6 volumes of hydrochloric acid R and 94 volumes of water R until the precipitate dissolves, titrate the excess of iodine with 0.05 M sodium thiosulfate using 1 mL of starch solution R added towards the end of the titration, as indicator. Not less than 12.6 mL of 0.05 M sodium thiosulfate is required.
Cyanide
Dissolve 5.0 g in 50 mL of water R and add 2.0 g of tartaric acid R. Place this solution in a distillation apparatus (2.2.11).
The plain bend adapter attached to the end of the condenser has a vertical part that is long enough to extend to 1 cm from the bottom of a 50 mL test-tube used as a receiver. Place 10 mL of water R and 2 mL of 0.1 M sodium hydroxide into the receiver. Distil, collect 25 mL of distillate and dilute to 50 mL with water R. To 25 mL of this solution add 25 mg of ferrous
sulfate R and boil for a short time. After cooling to about 70 °C add 10 mL of hydrochloric acid R1. After 30 min, filter the solution and wash the filter. A yellow spot appears on the filter; there is no blue or green spot.
Chlorides (2.4.4)
Maximum 100 ppm.
To 5 mL of solution S, add 10 mL of water R.
Sulfates (2.4.13)
Maximum 100 ppm, determined on solution S.
Iron (2.4.9)
Maximum 40 ppm.
Dilute 2.5 mL of solution S to 10 mL with water R.
Loss on drying (2.2.32)
Maximum 5.0 per cent, determined on 1.000 g by drying in an oven at 105 °C for 3 h.
Bacterial endotoxins (2.6.14)
Less than 167 IU/g, if intended for use in the manufacture of parenteral preparations without a further appropriate procedure for the removal of bacterial endotoxins.
ASSAY
Dissolve 0.800 g in a mixture of 2 mL of 3 M hydrochloric acid R and 150 mL of water R. While stirring, add 12.5 mL of
0.1 M sodium edetate, 15 mL of 1 M sodium hydroxide and 0.3 g of hydroxynaphthol blue, sodium salt R. Titrate with 0.1 M sodium edetate until the colour changes from violet to pure blue.
1 mL of 0.1 M sodium edetate is equivalent to 49.04 mg of C14H26CaO16.
STORAGE
In an airtight container. If the substance is sterile, store in a sterile, airtight, tamper-evident container.