(Ph. Eur. monograph 1183)
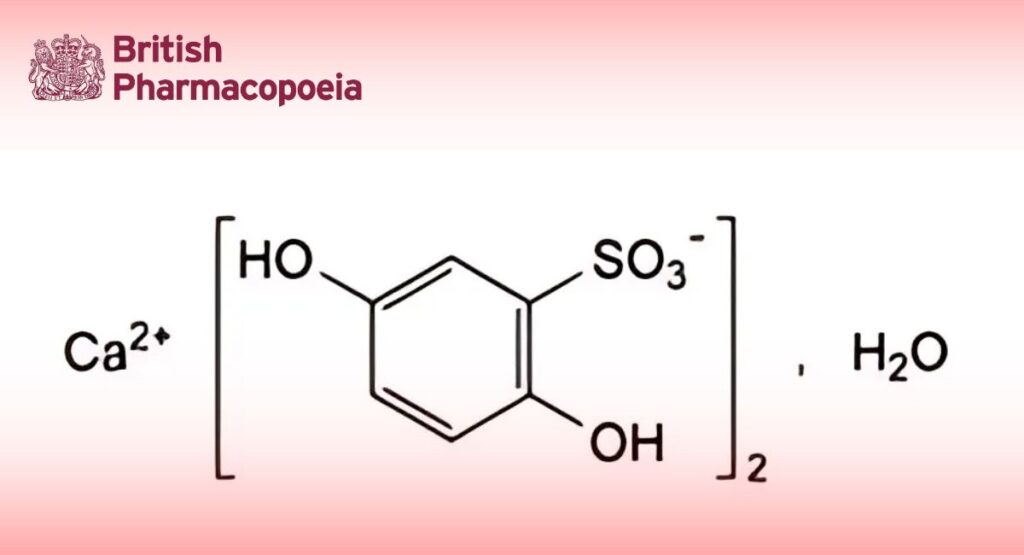
C12H10CaO10S2,H2O 436.4
Anhydrous calcium dobesilate 20123-80-2
DEFINITION
Calcium bis(2,5-dihydroxybenzene-1-sulfonate) monohydrate.
Content
99.0 per cent to 101.0 per cent (anhydrous substance).
CHARACTERS
Appearance
White or almost white, hygroscopic powder.
Solubility
Very soluble in water, freely soluble in anhydrous ethanol, very slightly soluble in 2-propanol, practically insoluble in methylene chloride.
IDENTIFICATION
A. Ultraviolet and visible absorption spectrophotometry (2.2.25).
Test solution: Dissolve 0.100 g in water R and dilute to 200.0 mL with the same solvent. Dilute 5.0 mL of this solution to 100.0 mL with water R.
Spectral range: 210-350 nm.
Absorption maxima: At 221 nm and 301 nm.
Specific absorbance at the absorption maximum at 301 nm: 174 to 181.
B. Mix 1 mL of ferric chloride solution R2, 1 mL of a freshly prepared 10 g/L solution of potassium ferricyanide R and 0.1 mL of nitric acid R. To this mixture add 5 mL of freshly prepared solution S (see Tests): a blue colour and a precipitate are immediately produced.
C. 2 mL of freshly prepared solution S gives reaction (b) of calcium (2.3.1).
TESTS
Solution S
Dissolve 10.0 g in carbon dioxide-free water R and dilute to 100 mL with the same solvent.
Appearance of solution
Solution S, when freshly prepared, is clear (2.2.1) and colourless (2.2.2, Method II).
pH (2.2.3)
4.5 to 6.0 for solution S.
Related substances
Liquid chromatography (2.2.29). Keep all solutions at 2-8 °C.
Buffer solution: Dissolve 1.2 g of anhydrous sodium dihydrogen phosphate R in 900 mL of water for chromatography R, adjust to pH 6.5 with disodium hydrogen phosphate solution R and dilute to 1000 mL with water for chromatography R.
Test solution: Dissolve 0.100 g of the substance to be examined in water R and dilute to 10.0 mL with the same solvent.
Reference solution (a): Dilute 1.0 mL of the test solution to 100.0 mL with water R. Dilute 1.0 mL of this solution to 10.0 mL with water R.
Reference solution (b): Dissolve 10 mg of the substance to be examined and 10 mg of hydroquinone R (impurity A) in water R and dilute to 10 mL with the same solvent. Dilute 1 mL of this solution to 100 mL with water R.
Column:
— size: l = 0.25 m, Ø = 4.6 mm;
— stationary phase: spherical end-capped octadecylsilyl silica gel for chromatography R (5 μm).
Mobile phase: acetonitrile R1, buffer solution (10:90 V/V).
Flow rate: 0.8 mL/min.
Detection: Spectrophotometer at 220 nm.
Injection: 10 μL.
Run time: 2.5 times the retention time of dobesilic acid.
Relative retention: With reference to dobesilic acid (retention time = about 6 min): impurity A = about 1.7.
System suitability: Reference solution (b):
— resolution: minimum 8.0 between the peaks due to dobesilic acid and impurity A.
Limits:
— correction factor: for the calculation of content, multiply the peak area of impurity A by 0.6;
— impurity A: not more than the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a) (0.1 per cent);
— unspecified impurities: for each impurity, not more than the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a) (0.10 per cent);
— total: not more than twice the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a) (0.2 per cent);
— disregard limit: 0.5 times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a) (0.05 per cent).
Iron (2.4.9)
Maximum 10 ppm, determined on 10 mL of solution S.
Water (2.5.12)
4.0 per cent to 6.0 per cent, determined on 0.500 g.
ASSAY
Dissolve 0.200 g in a mixture of 10 mL of water R and 40 mL of dilute sulfuric acid R. Titrate with 0.1 M cerium sulfate, determining the end-point potentiometrically (2.2.20).
1 mL of 0.1 M cerium sulfate is equivalent to 10.45 mg of C12H10CaO10S2.
STORAGE
In an airtight container, protected from light.
IMPURITIES
Specified impurities A.
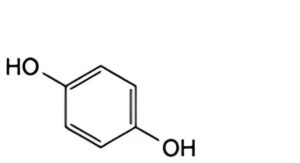
A. benzene-1,4-diol (hydroquinone).