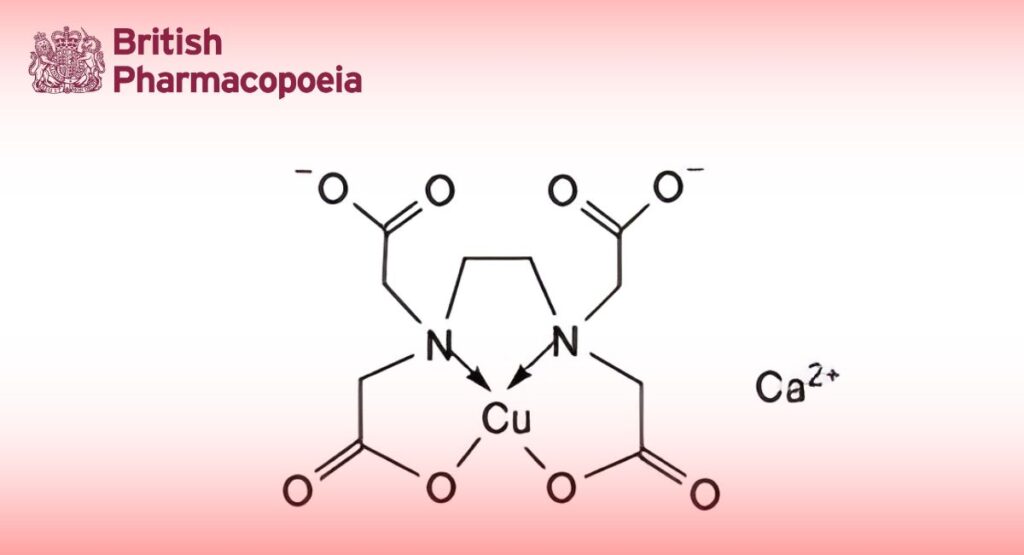
C10H12CaCuN2O8,2H2O 427.6
Action and use
Used in the treatment of copper deficiency.
Preparation
Calcium Copperedetate Injection
DEFINITION
Calcium Copperedetate is the dihydrate of calcium [ethylenediaminetetra-acetato(4-)-N,N′,O,O′]copper(II). It contains not less than 9.1% and not more than 9.7% of calcium, Ca, and not less than 14.4% and not more than 15.3% of copper, Cu, both calculated with reference to the dried substance.
CHARACTERISTICS
A blue, crystalline powder.
Freely soluble in water, the solution gradually precipitating the tetrahydrate; practically insoluble in ethanol (96%).
IDENTIFICATION
A. Dissolve 0.2 g in 5 mL of water and add 1 mL of 6M acetic acid and 2 mL of dilute potassium iodide solution. The solution remains clear and deep blue.
B. Ignite 0.2 g, dissolve the residue in 3 mL of 2M hydrochloric acid, neutralise the solution with 5M ammonia and add 1 mL of 6M acetic acid and 2 mL of dilute potassium iodide solution. A white precipitate is produced and iodine is liberated, colouring the supernatant liquid brown.
C. Dissolve 0.5 g in 10 mL of water, acidify with 2M hydrochloric acid, add 25 mL of a 10% v/v solution of mercaptoacetic acid and filter. Make the filtrate alkaline with 5M ammonia and add 5 mL of a 2.5% w/v solution of ammonium oxalate. A white precipitate is produced which is soluble in hydrochloric acid but only sparingly soluble in 6M acetic acid.
TESTS
Lead
Not more than 25 ppm of Pb when determined by the following method. Dissolve 1.25 g in 10 mL of hydrochloric acid, dilute to 25 mL with water and determine by atomic absorption spectrophotometry, Appendix II D, measuring at 283.3 nm and using a lead hollow-cathode lamp as the radiation source and lead standard solution (100 ppm Pb), diluted if necessary with water, to prepare the standard solutions.
Zinc
Not more than 200 ppm of Zn when determined by the following method. Dissolve 1.0 g in 20 mL of hydrochloric acid, dilute to 200 mL with water and determine by atomic absorption spectrophotometry, Appendix II D, measuring at 213.9 nm and using a zinc hollow-cathode lamp as the radiation source and zinc standard solution (5 mg/mL Zn) diluted if necessary with water, to prepare the standard solutions.
Loss on drying
When dried to constant weight at 105°, loses not more than 2.0% of its weight. Use 1 g.
ASSAY
For copper
Ignite 4 g at 600° to 700°, cool and heat the residue with 12 mL of a mixture of equal volumes of hydrochloric acid and water on a water bath for 15 minutes. Add 10 mL of water, filter and dilute the filtrate to 100 mL with water (solution A); reserve a portion for the Assay for calcium. To 25 mL of solution A add 25 mL of water and 10 mL of bromine solution, boil to remove the bromine, cool and add dilute sodium carbonate solution until a faint permanent precipitate is produced. Add 3 g of potassium iodide and 5 mL of 6M acetic acid and titrate the liberated iodine with 0.1M sodium thiosulfate VS, using starch mucilage as indicator, until only a faint blue colour remains; add 2 g of potassium thiocyanate and continue the titration until the blue colour disappears. Each mL of 0.1M sodium thiosulfate VS is equivalent to 6.354 mg of Cu.
For calcium
To 5 mL of solution A add 10 mL of water and 10 mL of a 10% v/v solution of mercaptoacetic acid, allow to stand until the precipitate has coagulated, dilute to 100 mL with water, add 5 mL of 5M sodium hydroxide and titrate with 0.05M disodium edetate VS, using methyl thymol blue mixture as indicator, until the solution becomes a full purple colour, adding the titrant slowly as the end point is approached. Each mL of 0.05M disodium edetate VS is equivalent to 2.004 mg of Ca.