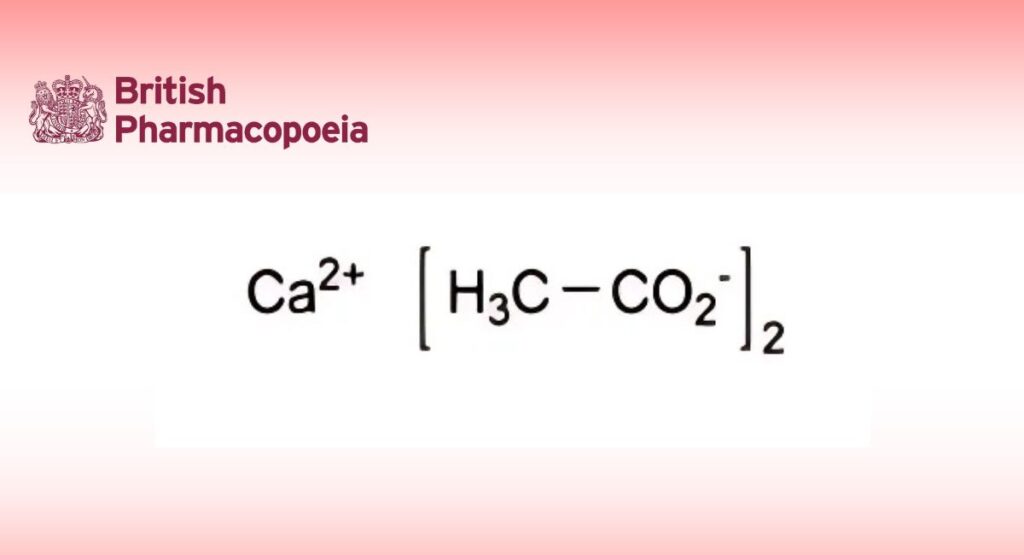
(Ph. Eur. monograph 2128)
C4H6CaO4 158.2 62-54-4
Action and use
Used in solutions for haemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis.
DEFINITION
Calcium diacetate.
Content
99.0 per cent to 101.0 per cent (anhydrous substance).
CHARACTERS
Appearance
White or almost white, hygroscopic powder.
Solubility
Freely soluble in water, slightly soluble in ethanol (96 per cent).
IDENTIFICATION
A. It gives reaction (b) of calcium (2.3.1).
B. It gives reaction (b) of acetates (2.3.1).
TESTS
Solution S
Dissolve 5.0 g in carbon dioxide-free water R and dilute to 50.0 mL with the same solvent.
Appearance of solution
Solution S is clear (2.2.1) and colourless (2.2.2, Method II).
pH (2.2.3)
7.2 to 8.2.
Dilute 5.0 mL of solution S to 10.0 mL with carbon dioxide-free water R.
Readily oxidisable substances
Dissolve 2.0 g in boiling water R and dilute to 100 mL with boiling water R. Add a few glass beads, 6 mL of 5 M sulfuric acid R and 0.3 mL of a 3.2 g/L solution of potassium permanganate R. Mix, boil gently for 5 min and allow the precipitate to settle. The pink colour in the supernatant is not completely discharged.
Chlorides, nitrates, sulfates
Liquid chromatography (2.2.29).
Test solution (a): Dissolve 5.00 g of the substance to be examined in 50 mL of water for chromatography R and dilute to 100.0 mL with the same solvent.
Test solution (b): Dilute 20.0 mL of test solution (a) to 100.0 mL with water for chromatography R.
Reference solution To 20.0 mL of test solution (a) add 8.0 mL of chloride standard solution (50 ppm Cl) R, 1.0 mL of nitrate standard solution (10 ppm NO3) R and 6.0 mL of sulfate standard solution (100 ppm SO4) R and dilute to 100.0 mL with water for chromatography R.
Blank solution water for chromatography R.
Pre-concentration column Connected with a suitable cation-exchange module. Use water for chromatography R to transfer the injected solution to the pre-concentration column.
— size: l = 0.013 m, Ø = 4 mm;
— stationary phase: strong anion-exchange polymethacrylate resin for chromatography R (65 μm).
Precolumn:
— size: l = 0.05 m, Ø = 4 mm;
— stationary phase: strong anion-exchange poly(vinyl alcohol) resin for chromatography R (5 μm);
— temperature: 40 °C.
Column:
— size: l = 0.25 m, Ø = 4 mm;
— stationary phase: strong anion-exchange poly(vinyl alcohol) resin for chromatography R (5 μm);
— temperature: 40 °C.
Mobile phase: Dissolve 0.382 g of anhydrous sodium carbonate R in water for chromatography R and dilute to 1000 mL with the same solvent.
Flow rate: 0.7 mL/min.
Detection: Conductivity detector equipped with a suitable anion suppressor.
Injection: 20 μL of test solution (b), the reference solution and the blank solution.
Run time: 1.3 times the retention time of sulfate.
Retention time: Chloride = about 12 min; nitrate = about 25 min; sulfate = about 33 min.
System suitability: Reference solution:
— repeatability: maximum relative standard deviation of 5.0 per cent for the area of the peak due to nitrate determined on 5 injections;
— resolution: minimum 5.0 between the peaks due to nitrate and sulfate.
Calculation of contents:
— for chlorides, nitrates and sulfates, use the concentration of the corresponding ions in the reference solution;
correct the area of the peaks due to chloride, nitrate and sulfate in the chromatogram obtained with the reference
solution by subtracting the area of the corresponding peaks in the chromatogram obtained with test solution (b).
Limits:
— chlorides: maximum 330 ppm;
— nitrates: maximum 10 ppm;
— sulfates: maximum 600 ppm.
Fluorides
Maximum 50 ppm.
Potentiometry (2.2.36, Method I).
Test solution In a 50 mL volumetric flask, dissolve 0.200 g in a 10.3 g/L solution of hydrochloric acid R, add 5.0 mL of fluoride standard solution (1 ppm F) R and dilute to 50.0 mL with a 10.3 g/L solution of hydrochloric acid R. To 20.0 mL of the solution add 20.0 mL of total-ionic-strength-adjustment buffer R and 3 mL of an 82 g/L solution of anhydrous sodium acetate R. Adjust to pH 5.2 with ammonia R and dilute to 50.0 mL with distilled water R.
Reference solutions To 0.25 mL, 0.5 mL, 0.75 mL and 1.0 mL of fluoride standard solution (10 ppm F) R add 20.0 mL of total-ionic-strength-adjustment buffer R and dilute to 50.0 mL with distilled water R.
Indicator electrode Fluoride selective.
Reference electrode Silver-silver chloride.
Take into account the addition of fluoride to the test solution for the calculation.
Aluminium (2.4.17)
Maximum 1 ppm, if intended for use in the manufacture of peritoneal dialysis solutions, haemofiltration solutions or haemodialysis solutions.
Test solution: Dissolve 4.0 g of the substance to be examined in 100 mL of water R and add 10 mL of acetate buffer solution pH 6.0 R.
Reference solution: Mix 2 mL of aluminium standard solution (2 ppm Al) R, 10 mL of acetate buffer solution pH 6.0 R and 98 mL of water R.
Blank solution: Mix 10 mL of acetate buffer solution pH 6.0 R and 100 mL of water R.
Iron (2.4.9)
Maximum 20 ppm, if intended for use in the manufacture of parenteral preparations or haemodialysis solutions.
Dilute 5 mL of solution S to 10 mL of water R.
Magnesium
Maximum 500 ppm.
Atomic absorption spectrometry (2.2.23, Method II).
Test solution: Dissolve 50.0 mg of the substance to be examined in water R and dilute to 100.0 mL with the same solvent.
Reference solutions: Prepare the reference solutions using magnesium standard solution (0.1 per cent Mg) R, diluted as necessary with water R.
Source: Magnesium hollow-cathode lamp.
Wavelength 285.2 nm.
Atomisation device: Air-acetylene flame.
Potassium
Maximum 500 ppm, if intended for use in the manufacture of parenteral preparations or haemodialysis solutions.
Atomic emission spectrometry (2.2.22, Method II).
Test solution: Dissolve 1.00 g of the substance to be examined in water R and dilute to 25.0 mL with the same solvent.
Reference solutions: Prepare the reference solutions using potassium standard solution (0.2 per cent K) R, diluted as necessary with water R.
Wavelength 766.5 nm.
Sodium
Maximum 500 ppm, if intended for use in the manufacture of parenteral preparations or haemodialysis solutions.
Atomic emission spectrometry (2.2.22, Method II).
Test solution: Dissolve 1.00 g of the substance to be examined in water R and dilute to 100.0 mL with the same solvent.
Reference solutions: Prepare the reference solutions using sodium standard solution (200 ppm Na) R, diluted as
necessary with water R.
Wavelength: 589 nm.
Strontium
Maximum 500 ppm, if intended for use in the manufacture of parenteral preparations or haemodialysis solutions.
Atomic emission spectrometry (2.2.22, Method II).
Test solution Dissolve 2.00 g of the substance to be examined in water R and dilute to 100.0 mL with the same solvent.
Reference solutions Prepare the reference solutions using strontium standard solution (1.0 per cent Sr) R, diluted as necessary with water R.
Wavelength 460.7 nm.
Water (2.5.12)
Maximum 7.0 per cent, determined on 0.100 g. Add 2 mL of anhydrous acetic acid R to the titration vessel in addition to the methanol. Clean the titration vessel after each determination.
ASSAY
Dissolve 0.150 g in 100 mL of water R and carry out the complexometric titration of calcium (2.5.11).
1 mL of 0.1 M sodium edetate is equivalent to 15.82 mg of C4H6CaO4.
STORAGE
In an airtight container.
LABELLING
The label states, where applicable, that the substance is suitable for use in the manufacture of parenteral preparations, peritoneal dialysis solutions, haemofiltration solutions or haemodialysis solutions.