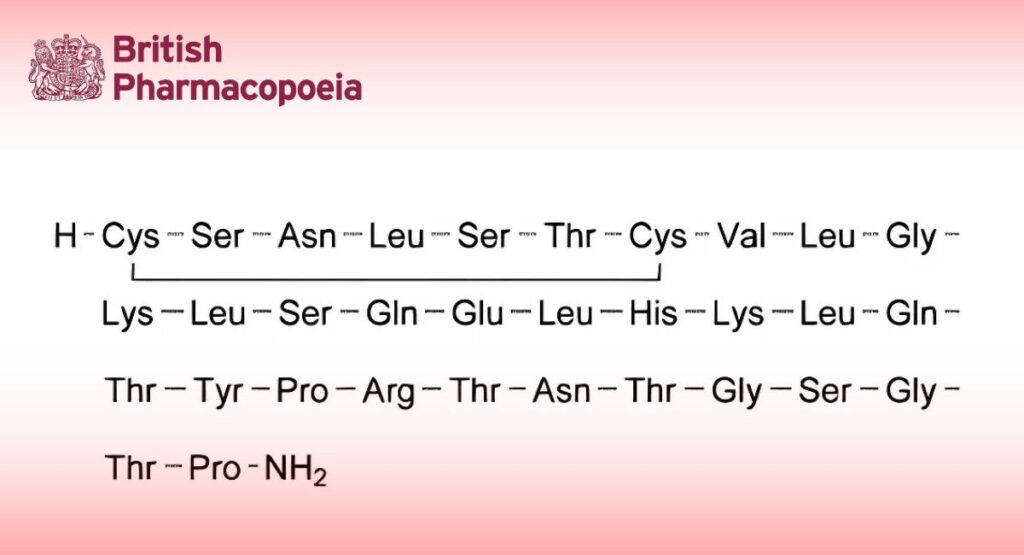
(Ph. Eur. monograph 0471)
C145H240N44O48S2 3432
Action and use
Hormone.
Preparation
Calcitonin (Salmon) Injection
DEFINITION
Polypeptide having the structure determined for salmon calcitonin I. It lowers the calcium concentration in plasma of mammals by diminishing the rate of bone resorption. It is obtained by chemical synthesis or by a method based on recombinant DNA (rDNA) technology. It is available as an acetate.
Content
90.0 per cent to 105.0 per cent of the peptide C145H240N44O48S2 (anhydrous and acetic acid-free substance).
By convention, for the purpose of labelling calcitonin (salmon) preparations, 1 mg of calcitonin (salmon) (C145H240N44O48S2) is equivalent to 6000 IU of biological activity.
PRODUCTION
The following requirements apply only to calcitonin (salmon) produced by a method based on rDNA technology.
Prior to release, the following tests are carried out on each batch of calcitonin (salmon), unless exemption has been granted by the competent authority.
Host-cell-derived proteins
The limit is approved by the competent authority.
Host-cell or vector-derived DNA
The limit is approved by the competent authority.
CHARACTERS
Appearance
White or almost white powder.
Solubility
Freely soluble in water.
IDENTIFICATION
A. Examine the chromatograms obtained in the assay.
Results: The principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with the test solution is similar in retention time and size to the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with the reference solution.
The following requirement applies only to calcitonin (salmon) obtained by chemical synthesis.
B. Amino acid analysis (2.2.56).
Express the content of each amino acid in moles. Calculate the relative proportions of the amino acids taking as equivalent to 1 the sum, divided by 20, of the number of moles of aspartic acid, glutamic acid, proline, glycine, valine, leucine, histidine, arginine and lysine. The values fall within the following limits: aspartic acid: 1.8 to 2.2; glutamic acid: 2.7 to 3.3; proline: 1.7 to 2.3; glycine: 2.7 to 3.3; valine: 0.9 to 1.1; leucine: 4.5 to 5.3; histidine: 0.9 to 1.1; arginine: 0.9 to 1.1; lysine: 1.8 to 2.2; serine: 3.2 to 4.2; threonine: 4.2 to 5.2; tyrosine: 0.7 to 1.1; half-cystine: 1.4 to 2.1. The following requirement applies only to calcitonin (salmon) produced by a method based on rDNA technology.
C. Peptide mapping (2.2.55).
SELECTIVE CLEAVAGE OF THE PEPTIDE BONDS
Test solution: Prepare a 1 mg/mL solution of the substance to be examined. Transfer 1.0 mL to a clean tube. Add 100 μL of 1 M tris-hydrochloride buffer solution pH 8.0 R and 20 μL of a freshly prepared 1.0 mg/mL solution of trypsin for peptide mapping R. Allow to stand at 2-8 °C for 16-20 h. Stop the reaction by adding 10 μL of a 50 per cent V/V solution of trifluoroacetic acid R. Cap the vial and mix. Centrifuge the vials to remove air bubbles.
Reference solution: Prepare at the same time and in the same manner as for the test solution but using calcitonin (salmon) CRS instead of the substance to be examined.
CHROMATOGRAPHIC SEPARATION
Liquid chromatography (2.2.29).
Column:
— size: l = 0.25 m, Ø = 4.6 mm;
— stationary phase: octadecylsilyl silica gel for chromatography R (5 μm) with a pore size of 30 nm.
Mobile phase:
— mobile phase A: mix 1 mL of trifluoroacetic acid R and 1000 mL of water R; filter and degas;
— mobile phase B: mix 0.850 mL of trifluoroacetic acid R, 200 mL of water R and 800 mL of acetonitrile for
chromatography R; filter and degas;
| Time
(min) |
Mobile phase A
(per cent V/V) |
Mobile phase B
(per cent V/V) |
| 0 – 50 | 100 → 65 | 0 → 35 |
| 50 – 60 | 65 → 40 | 35 → 60 |
| 60 – 60.1 | 40 → 0 | 60 → 100 |
| 60.1 – 65.1 | 0 | 100 |
| 65.1 – 65.2 | 0 → 100 | 100 → 0 |
| 65.2 – 80.2 | 100 | 0 |
Flow rate: 1.2 mL/min.
Detection: Spectrophotometer at 214 nm.
Equilibration: At initial conditions for at least 15 min. Carry out a blank run using the above-mentioned gradient.
Injection: 20 μL.
System suitability: The chromatogram obtained with the reference solution is qualitatively similar to the chromatogram of calcitonin (salmon) digest supplied with calcitonin (salmon) CRS.
Results: The profile of the chromatogram obtained with the test solution corresponds to that of the chromatogram obtained with the reference solution: the retention times of the fragment peaks in the chromatogram obtained with the test solution are within 5 per cent of the retention times of the fragments obtained with the reference solution; the peak area ratios of the fragment peaks in the chromatogram obtained with the test solution, normalised to the area of peak T2, are within 5 per cent of the corresponding peak ratios in the chromatogram obtained with the reference solution.
TESTS
Acetic acid (2.5.34)
4.0 per cent to 15.0 per cent.
Test solution: Dissolve 10.0 mg of the substance to be examined in a mixture of 5 volumes of mobile phase B and 95 volumes of mobile phase A and dilute to 10.0 mL with the same mixture of mobile phases.
Related substances
Liquid chromatography (2.2.29): use the normalisation procedure.
The following requirement applies to calcitonin (salmon), whether obtained by chemical synthesis or by a method based on rDNA technology.
A. Test solution. Prepare a 1.0 mg/mL solution of the substance to be examined in mobile phase A.
Reference solution: Dissolve the contents of a vial of calcitonin (salmon) CRS in mobile phase A to obtain a concentration of 1.0 mg/mL.
Resolution solution: Dissolve the contents of a vial of N-acetyl-Cys -calcitonin CRS in 400 μL of mobile phase A and add 100 μL of the test solution.
Column:
— size: l = 0.25 m, Ø = 4.6 mm;
— stationary phase: octadecylsilyl silica gel for chromatography R (5 μm);
— temperature: 65 °C.
Mobile phase:
— mobile phase A: dissolve 3.26 g of tetramethylammonium hydroxide R in 900 mL of water R, adjust to pH 2.5 with phosphoric acid R and mix with 100 mL of acetonitrile for chromatography R; filter and degas;
— mobile phase B: dissolve 1.45 g of tetramethylammonium hydroxide R in 400 mL of water R, adjust to pH 2.5 with phosphoric acid R and mix with 600 mL of acetonitrile for chromatography R; filter and degas;
| Time
(min) |
Mobile phase A
(per cent V/V) |
Mobile phase B
(per cent V/V) |
| 0 – 30 | 72 → 48 | 28 → 52 |
| 30 – 32 | 48 → 72 | 35 → 60 |
| 32 – 55 | 72 | 28 |
Flow rate: 1.0 mL/min.
Detection: Spectrophotometer at 220 nm.
Injection: 20 μL.
Relative retention: With reference to calcitonin (salmon) (retention time = about 20 min): impurity B = about 0.8; impurity C = about 0.9; impurity D = about 1.05; impurity A = about 1.15.
System suitability Resolution solution:
— resolution: minimum 5.0 between the peaks due to calcitonin (salmon) and impurity A,
— symmetry factor: maximum 2.5 for the peak due to impurity A.
Limits:
— impurities A, B, C, D: for each impurity, maximum 3.0 per cent; other unidentified, specified impurities may occur that co-elute with impurities A, B, C and D; the acceptance criterion applies irrespective of whether these impurities co-elute;
— total: maximum 5.0 per cent;
— disregard limit: 0.1 per cent.
The following requirement applies only to calcitonin (salmon) produced by a method based on rDNA technology.
B. Test solution. Prepare a 0.5 mg/mL solution of the substance to be examined. To 1.0 mL of this solution add 100 μL of 0.25 M citrate buffer solution pH 3.0 R.
Resolution solution: Prepare a 1 mg/mL solution of the substance to be examined. Mix 1 volume of the solution and 1 volume of calcitonin-Gly CRS. To 1.0 mL of this mixture add 100 μL of 0.25 M citrate buffer solution pH 3.0 R.
Column:
— size: l = 0.20 m, Ø = 4.6 mm;
— stationary phase: a suitable polysulfoethylaspartamide ion-exchange gel (5 μm).
Mobile phase:
— mobile phase A: mix 15 volumes of acetonitrile for chromatography R and 85 volumes of a 2.72 g/L solution of potassium dihydrogen phosphate R adjusted to pH 5.0 with a 600 g/L solution of potassium hydroxide R;
— mobile phase B: mix 15 volumes of acetonitrile for chromatography R and 85 volumes of a solution containing 2.72 g/L of potassium dihydrogen phosphate R and 29.22 g/L of sodium chloride R adjusted to pH 4.6 with a 600 g/L solution of potassium hydroxide R;
| Time
(min) |
Mobile phase A
(per cent V/V) |
Mobile phase B
(per cent V/V) |
| 0 – 10 | 100 → 0 | 0 → 100 |
| 10 – 15 | 0 | 100 |
| 15 – 15.1 | 0 → 100 | 100 → 0 |
| 15.1 – 22.1 | 100 | 0 |
Flow rate: 1.2 mL/min.
Detection: Spectrophotometer at 220 nm.
Injection: 50 μL; rinse the injector with a 40 per cent V/V solution of acetonitrile for chromatography R.
Relative retention: With reference to calcitonin (salmon) (retention time = about 9 min): impurity G = about 0.4; impurity F = about 0.6; impurity E = about 0.9.
System suitability: Resolution solution:
— resolution: minimum 3.0 between the peaks due to impurity E and calcitonin (salmon).
Limits:
— impurity E: maximum 0.6 per cent;
— impurities F, G: for each impurity, maximum 0.2 per cent.
Water (2.5.32)
Maximum 10.0 per cent.
Acetic acid and water
Maximum 20 per cent, calculated by adding together the percentage contents of acetic acid and water determined by the methods described above.
Bacterial endotoxins (2.6.14)
Less than 25 IU/mg, if intended for use in the manufacture of parenteral preparations without a further appropriate procedure for the removal of bacterial endotoxins.
ASSAY
Liquid chromatography (2.2.29) as described in the test for related substances. Use method A for calcitonin (salmon) obtained by chemical synthesis and method B for calcitonin (salmon) obtained by a method based on rDNA technology.
Calculate the content of calcitonin (salmon) (C145H240N44O48S2) from the area of the principal peak in each of the chromatograms obtained with the test solution and the reference solution and the declared content of C145H240N44O48S2 in calcitonin (salmon) CRS. Proceed with tangential integration of the peak areas.
STORAGE
Protected from light at a temperature between 2 °C and 8 °C. If the substance is sterile, store in a sterile, airtight, tamper-evident container.
LABELLING
The label states:
— the calcitonin peptide content (C145H240N44O48S2);
— the origin: synthetic or rDNA technology.
IMPURITIES
Specified impurities A, B, C, D, E, F, G.

A. acetylcalcitonin (salmon),

B. [9-D-leucine]calcitonin (salmon),

C. des-22-tyrosine-calcitonin (salmon),
D. O-acetylated calcitonin (salmon),
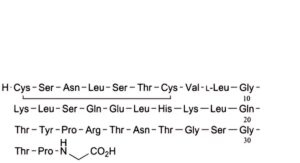
E. salmon calcitoninylglycine,

F. [1,7-bis(3-sulfo-L-alanine)]calcitonin (salmon),
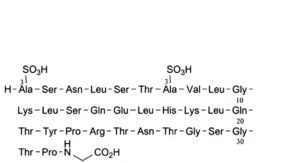
G. [1,7-bis(3-sulfo-L-alanine)]calcitoninylglycine (salmon).