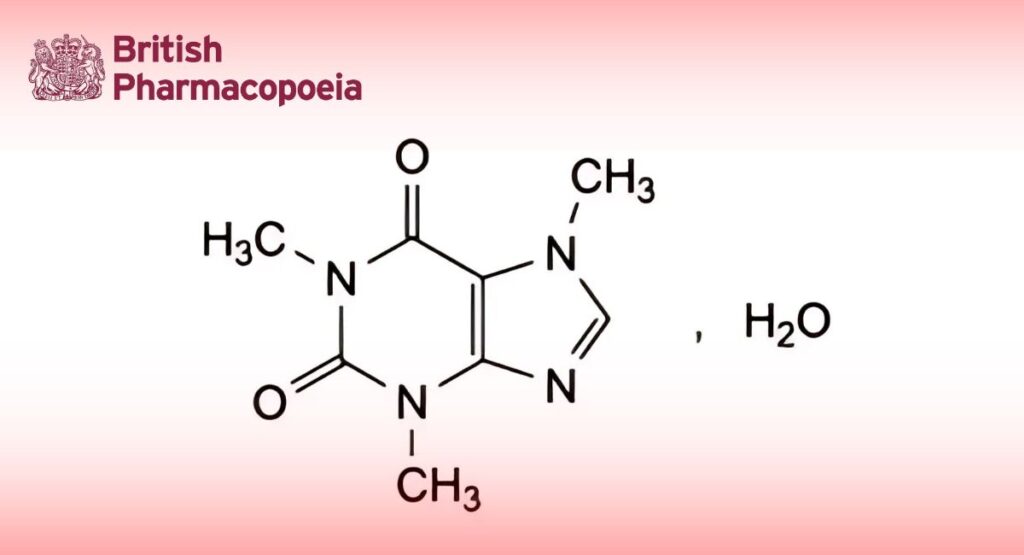
(Caffeine Monohydrate, Ph. Eur. monograph 0268)
C8H10N4O2,H2O 212.2 5743-12-4
Action and use
Central nervous system stimulant.
DEFINITION
1,3,7-Trimethyl-3,7-dihydro-1H-purine-2,6-dione monohydrate.
Content
98.5 per cent to 101.5 per cent (dried substance).
CHARACTERS
Appearance
White or almost white, crystalline powder or silky crystals.
Solubility
Sparingly soluble in water, freely soluble in boiling water, slightly soluble in ethanol (96 per cent). It dissolves in concentrated solutions of alkali benzoates or salicylates.
It sublimes readily.
IDENTIFICATION
First identification: A, B, E.
Second identification: A, C, D, E, F.
A. Melting point (2.2.14): 234 °C to 239 °C, determined after drying at 100-105 °C.
B. Infrared absorption spectrophotometry (2.2.24).
Preparation: Dry the substance to be examined at 100-105 °C before use.
Comparison: caffeine CRS.
C. To 2 mL of a saturated solution add 0.05 mL of iodinated potassium iodide solution R; the solution remains clear. Add 0.1 mL of dilute hydrochloric acid R; a brown precipitate is formed. Neutralise with dilute sodium hydroxide solution R; the precipitate dissolves.
D. In a glass-stoppered tube, dissolve about 10 mg in 0.25 mL of a mixture of 0.5 mL of acetylacetone R and 5 mL of dilute sodium hydroxide solution R. Heat in a water-bath at 80 °C for 7 min. Cool and add 0.5 mL of dimethylaminobenzaldehyde solution R2. Heat again in a water-bath at 80 °C for 7 min. Allow to cool and add 10 mL of water R; an intense blue colour develops.
E. Loss on drying (see Tests).
F. It gives the reaction of xanthines (2.3.1).
TESTS
Solution S
Dissolve 0.5 g with heating in 30 mL of carbon dioxide-free water R prepared from distilled water R, cool, and dilute to 50 mL with the same solvent.
Appearance of solution
Solution S is clear (2.2.1) and colourless (2.2.2, Method II).
Acidity
To 10 mL of solution S add 0.05 mL of bromothymol blue solution R1; the solution is green or yellow. Not more than 0.2 mL of 0.01 M sodium hydroxide is required to change the colour of the indicator to blue.
Related substances
Liquid chromatography (2.2.29).
Test solution: Dissolve 0.110 g of the substance to be examined in the mobile phase and dilute to 50.0 mL with the mobile phase. Dilute 1.0 mL of this solution to 10.0 mL with the mobile phase.
Reference solution (a): Dilute 2.0 mL of the test solution to 100.0 mL with the mobile phase. Dilute 1.0 mL of this solution to 10.0 mL with the mobile phase.
Reference solution (b): Dissolve 5 mg of caffeine for system suitability CRS (containing impurities A, C, D and F) in the mobile phase and dilute to 5 mL with the mobile phase. Dilute 2 mL of this solution to 10 mL with the mobile phase.
Column:
— size: l = 0.15 m, Ø = 4.6 mm;
— stationary phase: end-capped amidohexadecylsilyl silica gel for chromatography R (5 μm).
Mobile phase: Mix 20 volumes of tetrahydrofuran R, 25 volumes of acetonitrile R and 955 volumes of a solution containing 0.82 g/L of anhydrous sodium acetate R previously adjusted to pH 4.5 with glacial acetic acid R.
Flow rate: 1.0 mL/min.
Detection: Spectrophotometer at 275 nm.
Injection: 10 μL.
Run time: 1.5 times the retention time of caffeine.
Identification of impurities: Use the chromatogram supplied with caffeine for system suitability CRS and the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b) to identify the peaks due to impurities A, C, D and F.
Relative retention: With reference to caffeine (retention time = about 8 min): impurity C = about 0.38; impurity D = about 0.42; impurity F = about 0.6; impurity A = about 0.7.
System suitability: Reference solution (b):
— resolution: minimum 2.0 between the peaks due to impurities C and D; minimum 2.5 between the peaks due to impurities F and A.
Limits:
— unspecified impurities: for each impurity, not more than 0.5 times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a) (0.10 per cent);
— total: not more than 0.5 times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a) (0.10 per cent);
— disregard limit: 0.25 times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a) (0.05 per cent).
Sulfates (2.4.13)
Maximum 500 ppm, determined on 15 mL of solution S.
Prepare the standard using a mixture of 7.5 mL of sulfate standard solution (10 ppm SO4) R and 7.5 mL of distilled water R.
Loss on drying (2.2.32)
5.0 per cent to 9.0 per cent, determined on 1.000 g by drying in an oven at 105 °C for 1 h.
Sulfated ash (2.4.14)
Maximum 0.1 per cent, determined on 1.0 g.
ASSAY
Dissolve 0.170 g, previously dried at 100-105 °C, with heating in 5 mL of anhydrous acetic acid R. Allow to cool, and add 10 mL of acetic anhydride R and 20 mL of toluene R. Titrate with 0.1 M perchloric acid, determining the end-point potentiometrically (2.2.20).
1 mL of 0.1 M perchloric acid is equivalent to 19.42 mg of C8H10N4O2.
IMPURITIES
Other detectable impurities (the following substances would, if present at a sufficient level, be detected by one or other of the tests in the monograph. They are limited by the general acceptance criterion for other/unspecified impurities and/or by the general monograph Substances for pharmaceutical use (2034). It is therefore not necessary to identify these impurities for demonstration of compliance. See also 5.10. Control of impurities in substances for pharmaceutical use) A, B, C, D, E, F.
A. 1,3-dimethyl-3,7-dihydro-1H-purine-2,6-dione (theophylline),
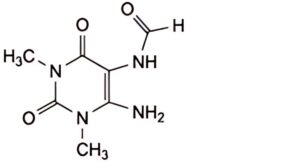
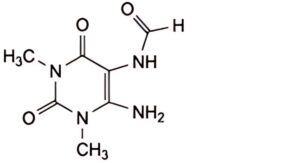
B. N-(6-amino-1,3-dimethyl-2,4-dioxo-1,2,3,4-tetrahydropyrimidin-5-yl)formamide,
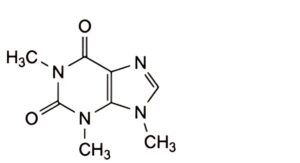
C. 1,3,9-trimethyl-3,9-dihydro-1H-purine-2,6-dione (isocaffeine),
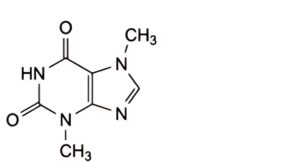
D. 3,7-dimethyl-3,7-dihydro-1H-purine-2,6-dione (theobromine),
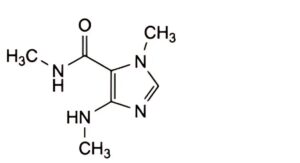
E. N,1-dimethyl-4-(methylamino)-1H-imidazole-5-carboxamide (caffeidine),

F. 1,7-dimethyl-3,7-dihydro-1H-purine-2,6-dione.