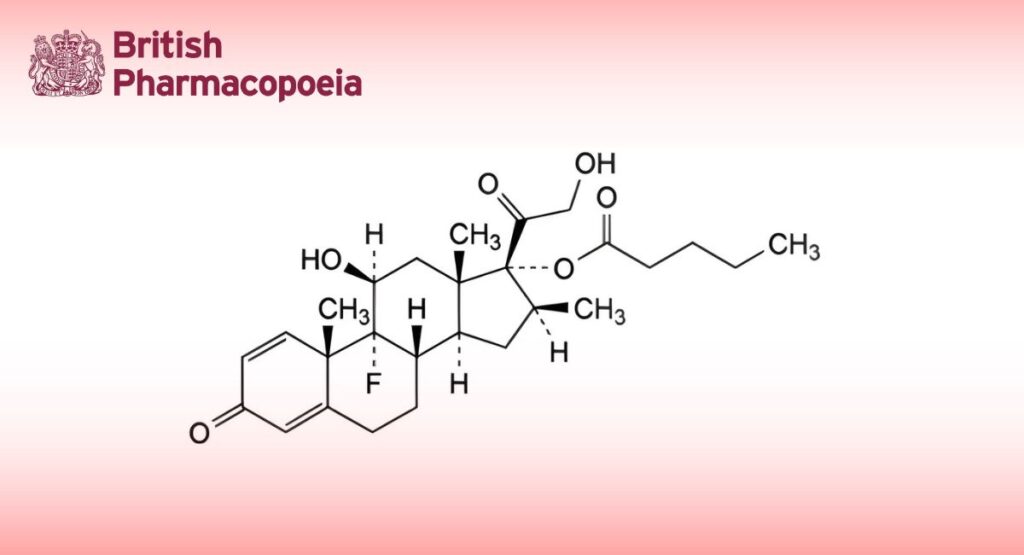
(Ph. Eur. monograph 0811)
C27H37FO6 476.6 2152-44-5
Action and use
Glucocorticoid.
Preparations
Betamethasone and Clioquinol Cream
Betamethasone and Clioquinol Ointment
Betamethasone Valerate and Coal Tar Paste
Betamethasone Valerate Cream
Betamethasone Valerate Lotion
Betamethasone Valerate Ointment
Betamethasone Valerate Scalp Application
DEFINITION
9-Fluoro-11β,21-dihydroxy-16β-methyl-3,20-dioxopregna-1,4-dien-17-yl pentanoate.
Content
97.0 per cent to 103.0 per cent (dried substance).
CHARACTERS
Appearance
White or almost white, crystalline powder.
Solubility
Practically insoluble in water, freely soluble in acetone and in methylene chloride, soluble in ethanol (96 per cent).
mp
About 192 °C, with decomposition.
IDENTIFICATION
First identification: A, C.
Second identification: B, D.
A. Infrared absorption spectrophotometry (2.2.24).
Comparison betamethasone 17-valerate CRS.
If the spectra obtained in the solid state show differences, dissolve the substance to be examined and the reference substance separately in the minimum volume of methylene chloride R, evaporate to dryness on a water-bath and record new spectra using the residues.
B. Thin-layer chromatography (2.2.27).
Test solution: Dissolve 10 mg of the substance to be examined in the mobile phase and dilute to 10.0 mL with the mobile phase.
Reference solution: Dissolve 10 mg of betamethasone 17-valerate CRS in the mobile phase and dilute to 10.0 mL with the mobile phase.
Plate: TLC silica gel F254 plate R.
Mobile phase methanol R, methylene chloride R (10:90 V/V).
Application: 5 μL.
Development: Over 3/4 of the plate.
Drying: In air.
Detection: Spray with a solution prepared as follows: dissolve 0.25 g of 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde R in glacial acetic acid R, dilute to 50 mL with the same solvent and add a mixture of 12.5 mL of sulfuric acid R and 37.5 mL of glacial acetic acid R; heat the plate at 90 °C for 35 min or until the spots appear, allow to cool and examine in daylight and in ultraviolet light at 365 nm.
Results The principal spot in the chromatogram obtained with the test solution is similar in position, colour and size to the principal spot in the chromatogram obtained with the reference solution.
C. Examine the chromatograms obtained in the test for related substances.
Results: The principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with the test solution is similar in retention time and size to the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b).
D. Add about 2 mg to 2 mL of sulfuric acid R and shake to dissolve. Within 5 min, a deep reddish-brown colour develops. Add this solution to 10 mL of water R and mix; the colour is discharged.
TESTS
Specific optical rotation (2.2.7)
+ 77 to + 83 (dried substance).
Dissolve 0.250 g in anhydrous ethanol R and dilute to 25.0 mL with the same solvent.
Related substances
Liquid chromatography (2.2.29). Carry out the test protected from light. Prepare the solutions immediately before use.
Solvent mixture glacial acetic acid R, mobile phase (1:1000 V/V).
Test solution: Dissolve 50 mg of the substance to be examined in the solvent mixture and dilute to 20.0 mL with the solvent mixture.
Reference solution (a): Dilute 1.0 mL of the test solution to 100.0 mL with the solvent mixture. Dilute 1.0 mL of this solution to 10.0 mL with the solvent mixture.
Reference solution (b): Dissolve 12 mg of betamethasone valerate for system suitability CRS (containing impurities D and G) in 5 mL of the solvent mixture. Use 1 mL of this solution to dissolve the contents of a vial of betamethasone valerate impurity mixture CRS (containing impurities C, H and I).
Reference solution (c): Dissolve 6 mg of betamethasone CRS (impurity A) and 3 mg of betamethasone 21-valerate CRS (impurity E) in 30 mL of the solvent mixture. Dilute 1 mL of this solution to 10 mL with the solvent mixture.
Column:
— size: l = 0.25 m, Ø = 4.6 mm;
— stationary phase: end-capped octadecylsilyl silica gel for chromatography R (5 μm);
— temperature: 20 °C.
Mobile phase acetonitrile for chromatography R, water for chromatography R (50:50 V/V).
Flow rate: 1 mL/min.
Detection: Spectrophotometer at 239 nm.
Injection: 20 μL.
Run time: 2.5 times the retention time of betamethasone valerate.
Identification of impurities: Use the chromatogram supplied with betamethasone valerate for system suitability CRS and the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b) to identify the peaks due to impurities C, D, G, H and I; use the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (c) to identify the peaks due to impurities A and E.
Relative retention: With reference to betamethasone valerate (retention time = about 20 min): impurity A = about 0.3; impurity I = about 0.6; impurity C = about 0.8; impurity H = about 1.3; impurity D = about 1.4; impurity E = about 1.6; impurity G = about 2.0.
System suitability: Reference solution (b):
— resolution: minimum 1.7 between the peaks due to impurities H and D.
Limits:
— impurity A: not more than 7 times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a) (0.7 per cent);
— impurities E, G: for each impurity, not more than 3 times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram
obtained with reference solution (a) (0.3 per cent);
— impurities C, H, I: for each impurity, not more than 1.5 times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a) (0.15 per cent);
— unspecified impurities: for each impurity, not more than the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a) (0.10 per cent);
— total: not more than 15 times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference
solution (a) (1.5 per cent);
— disregard limit: 0.5 times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a) (0.05 per cent).
Loss on drying (2.2.32)
Maximum 0.5 per cent, determined on 1.000 g by drying in an oven at 105 °C.
ASSAY
Dissolve 50.0 mg in ethanol (96 per cent) R and dilute to 100.0 mL with the same solvent. Dilute 2.0 mL of this solution to 50.0 mL with ethanol (96 per cent) R. Measure the absorbance (2.2.25) at the absorption maximum at 240 nm.
Calculate the content of C27H37FO6 taking the specific absorbance to be 325.
STORAGE
Protected from light.
IMPURITIES
Specified impurities A, C, E, G, H, I.
Other detectable impurities (the following substances would, if present at a sufficient level, be detected by one or other of the tests in the monograph. They are limited by the general acceptance criterion for other/unspecified impurities and/or by the general monograph Substances for pharmaceutical use (2034). It is therefore not necessary to identify these impurities for demonstration of compliance. See also 5.10. Control of impurities in substances for pharmaceutical use) B, D, F.
A. 9-fluoro-11β,17,21-trihydroxy-16β-methylpregna-1,4-diene-3,20-dione (betamethasone),
B. 9-fluoro-11β,17-dihydroxy-16β-methylpregna-1,4-diene-3,20-dione (21-deoxy-betamethasone),
C. 9-fluoro-11β,21-dihydroxy-16α-methyl-3,20-dioxopregna-1,4-dien-17-yl pentanoate (dexamethasone 17-valerate),
D. 9-bromo-11β,21-dihydroxy-16β-methyl-3,20-dioxopregna-1,4-dien-17-yl pentanoate (9-bromo betamethasone valerate),
E. 9-fluoro-11β,17-dihydroxy-16β-methyl-3,20-dioxopregna-1,4-dien-21-yl pentanoate (betamethasone 21-valerate),
F. 21-hydroxy-16β-methyl-3,20-dioxopregna-1,4,9(11)-trien-17-yl pentanoate (betamethasone valerate δ-9(11)),
G. 6α-bromo-9-fluoro-11β,21-dihydroxy-16β-methyl-3,20-dioxopregna-1,4-dien-17-yl pentanoate (6α-bromo-
betamethasone valerate),
H. 9-chloro-11β,21-dihydroxy-16β-methyl-3,20-dioxopregna-1,4-dien-17-yl pentanoate (beclomethasone 17-valerate),
I. 9-fluoro-11β,21-dihydroxy-3,20-dioxopregna-1,4-dien-17-yl pentanoate (9-fluoro-prednisolone 17-valerate).