(Ph. Eur. monograph 1071)
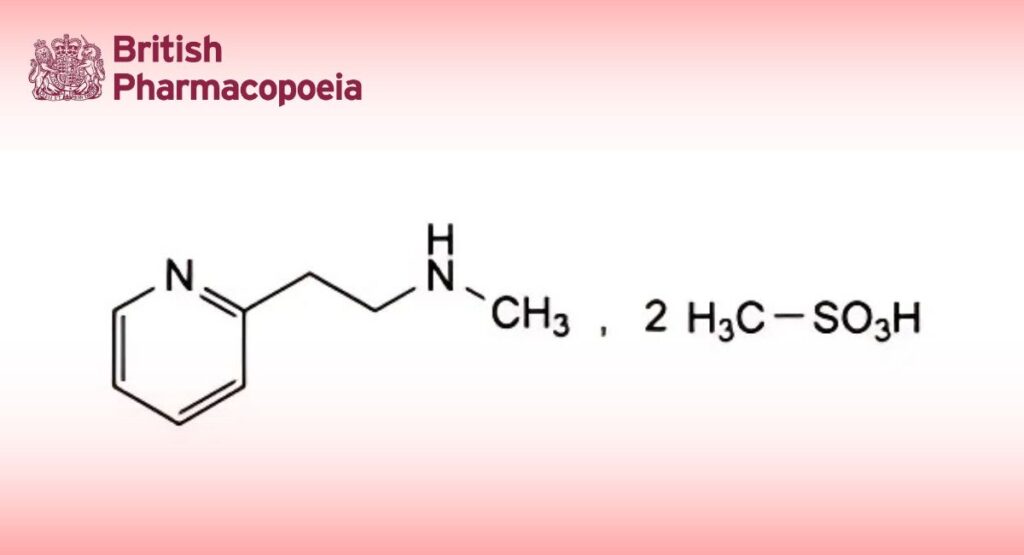
C10H20N2O6S2 328.4 54856-23-4
Action and use
Histamine H1 receptor antagonist; antihistamine.
DEFINITION
N-Methyl-2-(pyridin-2-yl)ethanamine bis(methanesulfonate).
Content
98.0 per cent to 101.0 per cent (anhydrous substance).
PRODUCTION
It is considered that alkyl methanesulfonate esters are genotoxic and are potential impurities in betahistine mesilate. The manufacturing process should be developed taking into consideration the principles of quality risk management, together with considerations of the quality of starting materials, process capability and validation. The general methods 2.5.37. Methyl, ethyl and isopropyl methanesulfonate in methanesulfonic acid, 2.5.38. Methyl, ethyl and isopropyl methanesulfonate in active substances and 2.5.39. Methanesulfonyl chloride in methanesulfonic acid are available to assist manufacturers.
CHARACTERS
Appearance
White or almost white, crystalline powder, very hygroscopic.
Solubility
Very soluble in water, freely soluble in ethanol (96 per cent), very slightly soluble in 2-propanol.
IDENTIFICATION
First identification: B.
Second identification: A, C, D.
A. Melting point (2.2.14): 108 °C to 112 °C.
B. Infrared absorption spectrophotometry (2.2.24).
Comparison: betahistine mesilate CRS.
C. Thin-layer chromatography (2.2.27).
Test solution: Dissolve 10 mg of the substance to be examined in ethanol (96 per cent) R and dilute to 2 mL with the same solvent.
Reference solution: Dissolve 10 mg of betahistine mesilate CRS in ethanol (96 per cent) R and dilute to 2 mL with the same solvent.
Plate: TLC silica gel F254 plate R.
Mobile phase: concentrated ammonia R, ethyl acetate R, methanol R (0.75:15:30 V/V/V).
Application: 2 μL.
Development: Over 3/4 of the plate.
Drying: At 110 °C for 10 min.
Detection: Examine in ultraviolet light at 254 nm.
Results: The principal spot in the chromatogram obtained with the test solution is similar in position and size to the principal spot in the chromatogram obtained with the reference solution.
D. To 0.1 g add 5 mL of dilute hydrochloric acid R and shake for about 5 min. Add 1 mL of barium chloride solution R1.
The solution remains clear. To a further 0.1 g add 0.5 g of anhydrous sodium carbonate R, mix and ignite until a white residue is obtained. Allow to cool and dissolve the residue in 7 mL of water R. The solution gives reaction (a) of sulfates (2.3.1).
TESTS
Solution S
Dissolve 5.0 g in carbon dioxide-free water R prepared from distilled water R, and dilute to 50 mL with the same solvent.
Appearance of solution
Solution S is clear (2.2.1) and colourless (2.2.2, Method II).
pH (2.2.3)
2.0 to 3.0 for solution S.
Related substances
Liquid chromatography (2.2.29).
Test solution: Dissolve 50 mg of the substance to be examined in the mobile phase and dilute to 10.0 mL with the mobile phase.
Reference solution (a): Dissolve 10 mg of betahistine mesilate CRS and 10 mg of 2-vinylpyridine R (impurity A) in the mobile phase and dilute to 50.0 mL with the mobile phase. Dilute 2.0 mL of this solution to 50.0 mL with the mobile phase.
Reference solution (b): Dilute 1.0 mL of the test solution to 100.0 mL with the mobile phase.
Reference solution (c): Dilute 2.0 mL of reference solution (b) to 10.0 mL with the mobile phase.
Column:
— size: l = 0.25 m, Ø = 4.6 mm;
— stationary phase: octadecylsilyl silica gel for chromatography R (5 μm).
Mobile phase: Dissolve 2.0 g of sodium dodecyl sulfate R in a mixture of 15 volumes of a 10 per cent V/V solution of sulfuric acid R, 35 volumes of a 17 g/L solution of tetrabutylammonium hydrogen sulfate R and 650 volumes of water R; adjust to pH 3.3 using dilute sodium hydroxide solution R and mix with 300 volumes of acetonitrile R.
Flow rate: 1 mL/min.
Detection: Spectrophotometer at 260 nm.
Injection: 20 μL.
Run time: mes the retention time of betahistine mesilate.
Retention time: Betahistine mesilate = about 8 min.
System suitability: Reference solution (a):
— resolution: minimum 3.5 between the peaks due to impurity A and betahistine mesilate.
Limits:
— impurity A: not more than the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (c) (0.2 per cent);
— unspecified impurities: for each impurity, not more than 0.1 times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b) (0.10 per cent);
— total: not more than 0.5 times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b) (0.5 per cent);
— disregard limit: 0.05 times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b) (0.05 per cent).
2-Propanol (2.4.24)
Maximum 0.5 per cent.
Chlorides (2.4.4)
Maximum 35 ppm.
To 14 mL of solution S add 1 mL of water R.
Sulfates (2.4.13)
Maximum 250 ppm.
Dilute 6 mL of solution S to 15 mL with distilled water R.
Water (2.5.12)
Maximum 2.0 per cent, determined on 0.50 g.
ASSAY
Dissolve 0.140 g in 50 mL of a mixture of 1 volume of anhydrous acetic acid R and 7 volumes of acetic anhydride R.
Titrate with 0.1 M perchloric acid, determining the end-point potentiometrically (2.2.20).
1 mL of 0.1 M perchloric acid is equivalent to 16.42 mg of C10H20N2O6S2.
STORAGE
In an airtight container.
IMPURITIES
Specified impurities A.
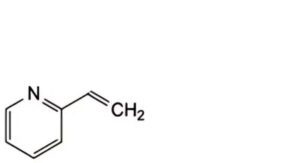
A. 2-ethenylpyridine (2-vinylpyridine).