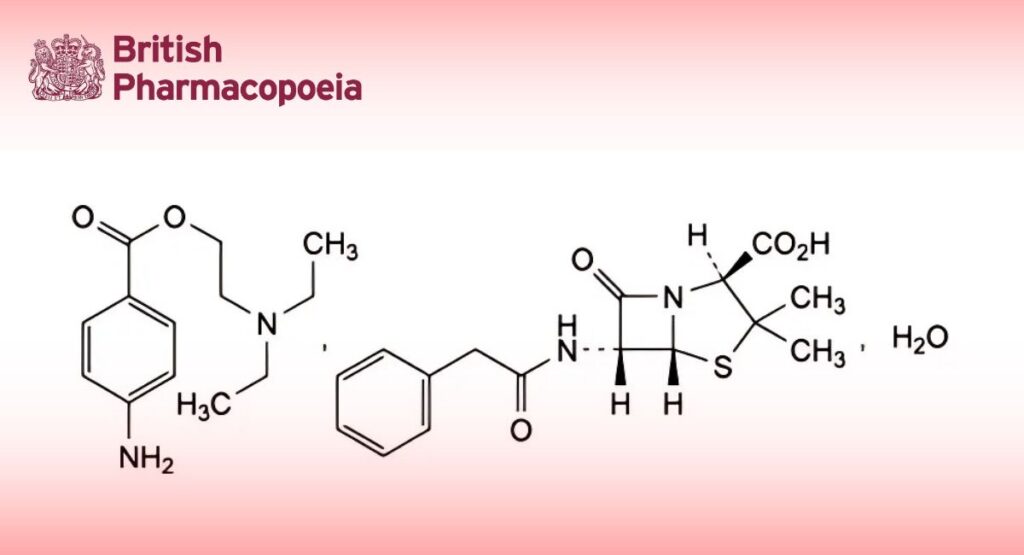
(Ph. Eur. monograph 0115)
C29H38N4O6S,H2O 588.7 6130-64-9
Action and use
Penicillin antibacterial.
Preparation
Procaine Benzylpenicillin Injection
DEFINITION
2-(Diethylamino)ethyl 4-aminobenzoate (2S,5R,6R)-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-6-[(phenylacetyl)amino]-4-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylic acid monohydrate.
Salt obtained from Benzylpenicillin sodium (0114) or Benzylpenicillin potassium (0113) produced by the growth of certain strains of Penicillium notatum or related micro-organisms.
Content
— procaine benzylpenicillin: 96.0 per cent to 102.0 per cent (anhydrous substance) without correction for dispersing or suspending agents;
— procaine (C13H20N2O2; Mr 236.3): 39.0 per cent to 42.0 per cent (anhydrous substance).
Dispersing or suspending agents (for example, lecithin and polysorbate 80) may be added.
CHARACTERS
Appearance
White or almost white, slightly hygroscopic, crystalline powder.
Solubility
Slightly soluble in water, sparingly soluble in ethanol (96 per cent).
IDENTIFICATION
First identification: A.
Second identification: B, C, D.
A. Infrared absorption spectrophotometry (2.2.24).
Comparison procaine benzylpenicillin CRS.
B. Thin-layer chromatography (2.2.27).
Test solution: Dissolve 25 mg of the substance to be examined in 5 mL of acetone R.
Reference solution: Dissolve 25 mg of procaine benzylpenicillin CRS in 5 mL of acetone R.
Plate: TLC silanised silica gel plate R.
Mobile phase: Mix 30 volumes of acetone R and 70 volumes of a 154 g/L solution of ammonium acetate R previously adjusted to pH 7.0 with ammonia R.
Application: 1 μL.
Development: Over 2/3 of the plate.
Drying: In air.
Detection: Expose to iodine vapour until the spots appear and examine in daylight.
System suitability: Reference solution:
— the chromatogram shows 2 clearly separated spots.
Results: The 2 principal spots in the chromatogram obtained with the test solution are similar in position, colour and size to the 2 principal spots in the chromatogram obtained with the reference solution.
C. Place about 2 mg in a test-tube about 150 mm long and 15 mm in diameter. Moisten with 0.05 mL of water R and add 2 mL of sulfuric acid-formaldehyde reagent R. Mix the contents of the tube by swirling; the solution is practically colourless. Place the test-tube on a water-bath for 1 min; a reddish-brown colour develops.
D. Dissolve 0.1 g in 2 mL of dilute hydrochloric acid R. The solution, which may be turbid, gives the reaction of primary aromatic amines (2.3.1).
TESTS
pH (2.2.3)
5.0 to 7.5.
Dissolve 50 mg in carbon dioxide-free water R and dilute to 15 mL with the same solvent. Shake until dissolution is complete.
Related substances
Liquid chromatography (2.2.29). Prepare the test solutions immediately before use.
Solvent mixture methanol R, water R (50:50 V/V).
Test solution (a): Dissolve 50.0 mg of the substance to be examined in 25 mL of methanol R and dilute to 50.0 mL with water R.
Test solution (b): Dissolve 0.100 g of the substance to be examined in 10 mL of methanol R and dilute to 20.0 mL with water R.
Reference solution (a): Dissolve 50.0 mg of procaine benzylpenicillin CRS in 25 mL of methanol R and dilute to 50.0 mL with water R.
Reference solution (b): Dissolve 12.0 mg of 4-aminobenzoic acid R (impurity A) in water R and dilute to 100.0 mL with the same solvent. Dilute 1.0 mL of the solution to 100.0 mL with water R.
Reference solution (c): Dissolve 10 mg of procaine benzylpenicillin for peak identification A CRS (containing impurities B, C, D, E, G, H, I and J) in 1 mL of methanol R and add 1 mL of water R.
Reference solution (d): Dissolve the contents of a vial of procaine benzylpenicillin impurity F CRS in 1 mL of reference solution (c).
Reference solution (e): Dilute 1.0 mL of reference solution (a) to 20.0 mL with the solvent mixture.
Reference solution (f): Dilute 1.0 mL of reference solution (e) to 20.0 mL with the solvent mixture.
Column:
— size: l = 0.15 m, Ø = 4.6 mm;
— stationary phase: end-capped octadecylsilyl silica gel for chromatography R (3 μm);
— temperature: 50 °C.
Mobile phase:
— mobile phase A: mix 10 volumes of a 68 g/L solution of potassium dihydrogen phosphate R adjusted to pH 3.4 with a 500 g/L solution of phosphoric acid R, 30 volumes of methanol R1 and 60 volumes of water for chromatography R;
— mobile phase B: mix 10 volumes of a 68 g/L solution of potassium dihydrogen phosphate R adjusted to pH 3.4 with a 500 g/L solution of phosphoric acid R, 35 volumes of water for chromatography R and 55 volumes of methanol R1;
| Time
(min) |
Mobile phase A
(per cent V/V) |
Mobile phase B
(per cent V/V) |
| 0 – 7 | 70 | 30 |
| 7 – 17 | 70 → 0 | 30 → 100 |
| 17 – 22 | 0 | 100 |
Flow rate: 1.5 mL/min.
Detection: Spectrophotometer at 225 nm.
Injection: 20 μL of test solution (b) and reference solutions (b), (d), (e) and (f).
Identification of impurities: Use the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b) to identify the peak due to impurity A; use the chromatogram supplied with procaine benzylpenicillin for peak identification A CRS and the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (d) to identify the peaks due to impurities B, C, D, E, F, G, H, I and J.
Relative retention: With reference to benzylpenicillin (retention time = about 7 min): procaine = about 0.19; impurity A = about 0.22; impurity D = about 0.33; impurity F = about 0.35; impurity B = about 0.48 and 0.55; impurity E = about 0.62; impurity C = about 0.81 and 0.83; impurity I = about 0.93; impurity G = about 1.47; impurity H = about 1.90; impurity J = about 2.37.
System suitability:
— resolution: minimum 1.0 between the peaks due to the epimers of impurity C and minimum 1.2 between the peaks due to impurities D and F in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (d);
— signal-to-noise ratio: minimum 10 for the peak due to benzylpenicillin in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (f).
Calculation of percentage contents:
— correction factor: multiply the peak area of impurity D by 0.4;
— for impurity A, use the concentration of impurity A in reference solution (b);
— for impurities other than A, use the concentration of procaine benzylpenicillin monohydrate in reference solution (e) taking into account the area of the peak due to benzylpenicillin in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (e).
Limits:
— impurities F, G, H, I, J: for each impurity, maximum 0.5 per cent;
— impurities B (sum of isomers), C (sum of epimers): for each impurity, maximum 0.4 per cent;
— impurities E, D: for each impurity, maximum 0.2 per cent;
— impurity A: maximum 0.024 per cent;
— any other impurity: for each impurity, maximum 0.2 per cent;
— total: maximum 2.0 per cent;
— reporting threshold: 0.05 per cent; disregard the peak due to procaine.
Water (2.5.12)
2.8 per cent to 4.2 per cent, determined on 0.300 g.
ASSAY
Liquid chromatography (2.2.29) as described in the test for related substances with the following modifications.
Mobile phase: Mobile phase B, mobile phase A (30:70 V/V).
Injection: 10 μL of test solution (a) and reference solution (a).
Run time: 3 times the retention time of benzylpenicillin.
Calculate the percentage content of procaine (C13H20N2O2) taking into account the area of the peak due to procaine and the assigned content of procaine (C13H20N2O2) in procaine benzylpenicillin CRS.
Calculate the percentage content of procaine benzylpenicillin (C29H38N4O6S) taking into account the area of the peak due to benzylpenicillin and the assigned content of procaine benzylpenicillin (C29H38N4O6S) in procaine benzylpenicillin CRS.
STORAGE
In an airtight container. If the substance is sterile, the container is also sterile and tamper-evident.
IMPURITIES
Specified impurities A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H, I, J.
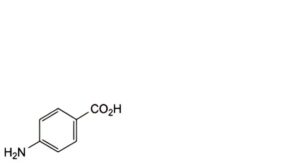
A. 4-aminobenzoic acid,
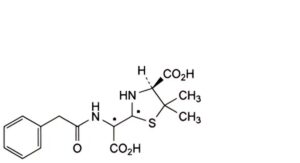
B. (2Ξ,4S)-2-[(Ξ)-carboxy(2-phenylacetamido)methyl]-5,5-dimethyl-1,3-thiazolidine-4-carboxylic acid (penicilloic acids of benzylpenicillin),
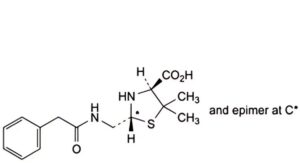
C. (2RS,4S)-5,5-dimethyl-2-[(2-phenylacetamido)methyl]-1,3-thiazolidine-4-carboxylic acid (penilloic acids of benzylpenicillin),
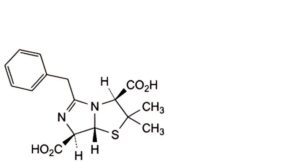
D. (3S,7R,7aR)-5-benzyl-2,2-dimethyl-2,3,7,7a-tetrahydroimidazo[5,1-b][1,3]thiazole-3,7-dicarboxylic acid (penillic acid of benzylpenicillin),
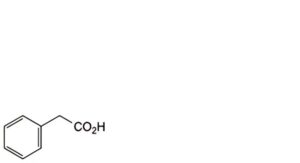
E. phenylacetic acid,
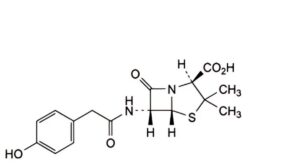
F. (2S,5R,6R)-6-[2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)acetamido]-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-4-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2- carboxylic acid,
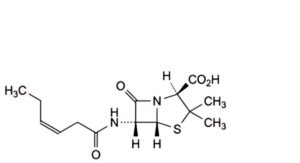
G. (2S,5R,6R)-6-[(3Z)-hex-3-enamido]-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-4-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylic acid (iso-penicillin F),
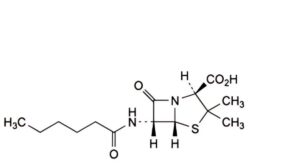
H. (2S,5R,6R)-6-hexanamido-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-4-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylic acid (dihydropenicillin F),
I. unknown structure,
J. unknown structure.