(Ph. Eur. monograph 0974)
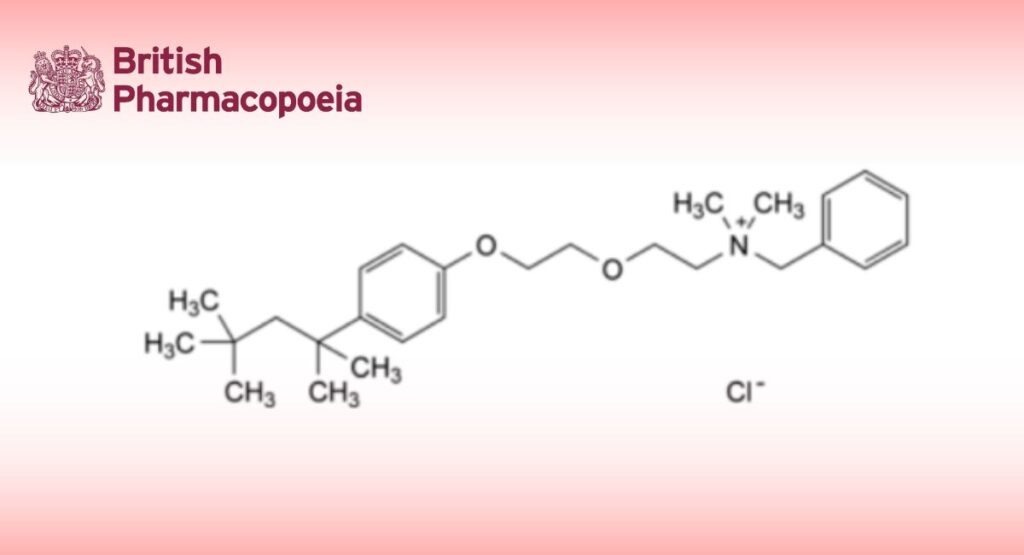
C27H42ClNO2 448.1 121-54-0
Action and use
Antiseptic.
DEFINITION
N-Benzyl-N,N-dimethyl-2-[2-[4-(1,1,3,3-tetramethylbutyl)phenoxy]ethoxy]ethanaminium chloride.
Content
97.0 per cent to 103.0 per cent (dried substance).
CHARACTERS
Appearance
White or yellowish-white powder.
Solubility
Very soluble in water and in ethanol (96 per cent), freely soluble in methylene chloride.
An aqueous solution froths copiously when shaken.
IDENTIFICATION
A. Melting point (2.2.14): 158 °C to 164 °C, after drying at 105 °C for 4 h.
B. Thin-layer chromatography (2.2.27).
Test solution: Dissolve 25 mg of the substance to be examined in water R and dilute to 5 mL with the same solvent.
Reference solution: Dissolve 25 mg of benzethonium chloride CRS in water R and dilute to 5 mL with the same solvent.
Plate: TLC silica gel F254 plate R.
Mobile phase glacial acetic acid R, water R, methanol R (5:5:100 V/V/V).
Application: 20 μL.
Development: Over a path of 12 cm.
Drying In: a current of warm air.
Detection: Examine in ultraviolet light at 254 nm.
Results: The principal spot in the chromatogram obtained with the test solution is similar in position and size to the principal spot in the chromatogram obtained with the reference solution.
C. To 5 mL of dilute sodium hydroxide solution R add 0.1 mL of bromophenol blue solution R1 and 5 mL of methylene chloride R and shake. The lower layer is colourless. Add 0.1 mL of solution S (see Tests) and shake. A blue colour develops in the lower layer.
D. To 2 mL of solution S add 1 mL of dilute nitric acid R. A white precipitate is formed which dissolves upon addition of 5 mL of ethanol (96 per cent) R. The solution gives reaction (a) of chlorides (2.3.1).
TESTS
Solution S
Dissolve 5.0 g in carbon dioxide-free water R and dilute to 50 mL with the same solvent.
Appearance of solution
Solution S is clear (2.2.1) and not more intensely coloured than reference solution Y6 (2.2.2, Method II).
Acidity or alkalinity
To 25 mL of solution S add 0.1 mL of phenolphthalein solution R. The solution is colourless. Add 0.3 mL of 0.01 M sodium hydroxide. The solution is pink. Add 0.1 mL of methyl red solution R and 0.5 mL of 0.01 M hydrochloric acid. The solution is orange-red.
Volatile bases and salts of volatile bases (2.4.1, Method B)
Maximum 50 ppm, determined on 0.20 g.
Prepare the standard using 0.1 mL of ammonium standard solution (100 ppm NH4) R. Replace heavy magnesium oxide by 2.0 mL of strong sodium hydroxide solution R.
Loss on drying (2.2.32)
Maximum 5.0 per cent, determined on 1.000 g by drying in an oven at 105 °C for 4 h.
Sulfated ash (2.4.14)
Maximum 0.1 per cent, determined on 1.0 g.
ASSAY
Dissolve 2.000 g in water R and dilute to 100.0 mL with the same solvent. Transfer 25.0 mL of the solution to a separating funnel, add 10 mL of a 4 g/L solution of sodium hydroxide R, 10.0 mL of a freshly prepared 50 g/L solution of potassium iodide R and 25 mL of methylene chloride R. Shake vigorously, allow to separate and discard the lower layer. Shake the upper layer with 3 quantities, each of 10 mL, of methylene chloride R and discard the lower layers. To the upper layer add 40 mL of hydrochloric acid R, allow to cool and titrate with 0.05 M potassium iodate until the deep brown colour is almost discharged. Add 4 mL of methylene chloride R and continue the titration, shaking vigorously, until the lower layer is no longer brown. Carry out a blank titration using a mixture of 10.0 mL of a freshly prepared 50 g/L solution of potassium iodide R, 20 mL of water R and 40 mL of hydrochloric acid R.
1 mL of 0.05 M potassium iodate is equivalent to 44.81 mg of C27H42ClNO2.
STORAGE
Protected from light.