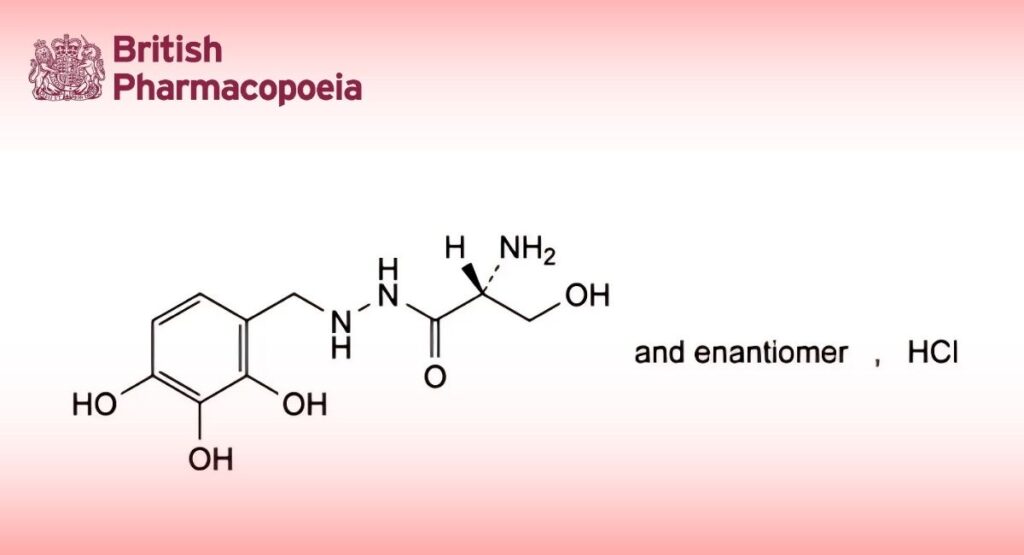
(Ph. Eur. monograph 1173)
C10H16ClN3O5 293.7 14919-77-8
Action and use
Dopa decarboxylase inhibitor.
Preparations
Co-beneldopa Capsules
Co-beneldopa Dispersible Tablets
Co-beneldopa Prolonged-release Capsules
DEFINITION
(2RS)-2-Amino-3-hydroxy-N′-[(2,3,4-trihydroxyphenyl)methyl]propanehydrazide hydrochloride.
Content
98.5 per cent to 101.0 per cent (anhydrous substance).
CHARACTERS
Appearance
White or yellowish-white or orange-white, crystalline powder.
Solubility
Freely soluble in water, very slightly soluble in anhydrous ethanol, practically insoluble in acetone.
It shows polymorphism (5.9).
IDENTIFICATION
A. Infrared absorption spectrophotometry (2.2.24).
Comparison: benserazide hydrochloride CRS.
If the spectra obtained show differences, dissolve the substance to be examined and the reference substance separately in hot methanol R, evaporate to dryness and record new spectra using the residues.
B. Dissolve 16 mg in 2 mL of methanol R. The solution gives reaction (a) of chlorides (2.3.1).
TESTS
Solution S
Dissolve 1.0 g in carbon dioxide-free water R and dilute to 100 mL with the same solvent.
Appearance of solution
Solution S is clear (2.2.1) and not more intensely coloured than reference solution BY6 (2.2.2, Method II).
pH (2.2.3)
4.0 to 5.0 for solution S.
Related substances
Liquid chromatography (2.2.29). All solutions must be injected immediately or stored at 4 °C.
Test solution: Dissolve 0.100 g of the substance to be examined in methanol R and dilute to 50.0 mL with the same solvent.
Reference solution (a): Dilute 1.0 mL of the test solution to 100.0 mL with methanol R. Dilute 1.0 mL of this solution to 10.0 mL with methanol R.
Reference solution (b): Dissolve 5.0 mg of benserazide impurity A CRS and 5.0 mg of benserazide impurity C CRS in methanol R and dilute to 50.0 mL with the same solvent. Dilute 1.0 mL of the solution to 10.0 mL with methanol R.
Reference solution (c): Dissolve 5 mg of benserazide for peak identification A CRS (containing impurity B) in 5 mL of reference solution (b).
Column:
— size: l = 0.25 m, Ø = 4 mm;
— stationary phase: octylsilyl silica gel for chromatography R (5 μm);
— temperature: 30 °C.
Mobile phase:
— mobile phase A: dissolve 2.2 g of sodium heptanesulfonate monohydrate R and 6.8 g of potassium dihydrogen phosphate R in 900 mL of water for chromatography R, add 50 mL of methanol R2 and adjust to pH 3.5 with phosphoric acid R;
— mobile phase B: dissolve 2.2 g of sodium heptanesulfonate monohydrate R and 6.8 g of potassium dihydrogen phosphate R in 500 mL of water for chromatography R, adjust to pH 3.5 with phosphoric acid R and add 500 mL of methanol R2;
| Time
(min) |
Mobile phase A
(per cent V/V) |
Mobile phase B
(per cent V/V) |
| 0 – 15 | 100 → 0 | 0 → 100 |
| 15 – 25 | 0 | 100 |
Flow rate: 1.3 mL/min.
Detection: Spectrophotometer at 210 nm.
Injection: 5 μL.
Identification of impurities: Use the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b) to identify the peaks due to impurities A and C; use the chromatogram supplied with benserazide for peak identification A CRS and the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (c) to identify the peak due to impurity B; doubling of the peak due to impurity C, related to separation of the (EZ)-isomers, may be observed.
Relative retention: With reference to benserazide (retention time = about 9 min): impurity A = about 0.6; impurity C = about 1.2; impurity B = about 1.5.
System suitability: Reference solution (c):
— resolution: minimum 5.0 between the peaks due to benserazide and impurity C; use the 1 peak of impurity C if 2 peaks occur.
Limits:
— correction factor: for the calculation of content, multiply the peak area of impurity B by 0.7;
— impurity A: not more than the area of the corresponding peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b) (0.5 per cent);
— impurity B: not more than 5 times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a) (0.5 per cent);
— impurity C: not more than the area of the corresponding peak or pair of peaks in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b) (0.5 per cent);
— unspecified impurities: for each impurity, not more than the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a) (0.10 per cent);
— sum of impurities other than A: not more than 10 times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a) (1.0 per cent);
— disregard limit: 0.5 times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a) (0.05 per cent).
Water (2.5.12)
Maximum 1.0 per cent, determined on 0.500 g. Use as the solvent a solution containing 30 mL of formamide R, 30 mL of methanol R and 7.0 g of salicylic acid R (the salicylic acid R must be added to the solvent mixture in the titration vessel).
Sulfated ash (2.4.14)
Maximum 0.1 per cent, determined on 1.0 g.
ASSAY
In order to avoid overheating during the titration, mix thoroughly throughout and stop the titration immediately after the end-point has been reached.
Dissolve 0.250 g in 5 mL of anhydrous formic acid R. Add 70 mL of anhydrous acetic acid R. Titrate immediately with 0.1 M perchloric acid, determining the end-point potentiometrically (2.2.20).
1 mL of 0.1 M perchloric acid is equivalent to 29.37 mg of C10H16ClN3O5.
STORAGE
Protected from light.
IMPURITIES
Specified impurities A, B, C.
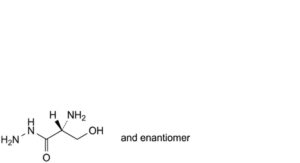
A. (2RS)-2-amino-3-hydroxypropanehydrazide,
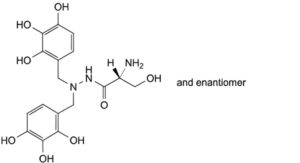
B. (2RS)-2-amino-3-hydroxy-N′,N′-bis[(2,3,4-trihydroxyphenyl)methyl]propanehydrazide,
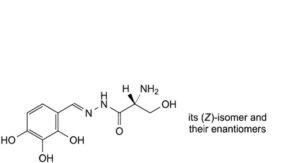
C. (2RS)-2-amino-3-hydroxy-N′-[(EZ)-(2,3,4-trihydroxyphenyl)methylidene]propanehydrazide.