(Ph. Eur. monograph 0466)
1405-89-6
Action and use
Polypeptide antibacterial.
Preparation
Polymyxin and Bacitracin Ointment
DEFINITION
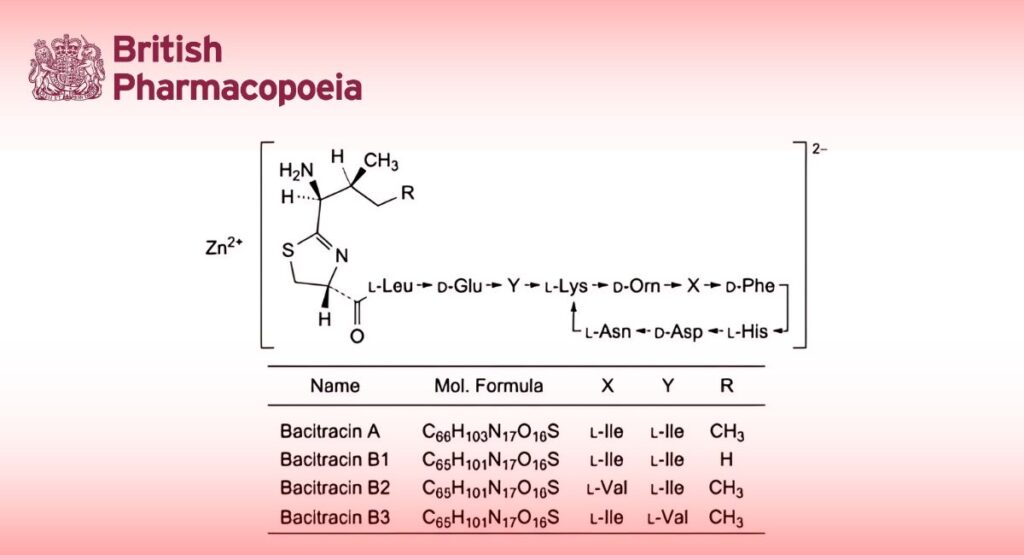
Zinc complex of bacitracin, which consists of a mixture of antimicrobial polypeptides produced by certain strains of Bacillus licheniformis or Bacillus subtilis, the main components being:
— 4,10-anhydro[N-[[(4R)-2-[(1S,2S)-1-amino-2-methylbutyl]-4,5-dihydro-1,3-thiazol-4-yl]carbonyl]-L-leucyl-D-α- glutamyl-L-isoleucyl-L-lysyl-D-ornithyl-L-isoleucyl-D-phenylalanyl-L-histidyl-D-α-aspartyl-L-asparagine] (bacitracin A);
— 4,10-anhydro[N-[[(4R)-2-[(1S)-1-amino-2-methylpropyl]-4,5-dihydro-1,3-thiazol-4-yl]carbonyl]-L-leucyl-D-α-glutamyl-L -isoleucyl-L-lysyl-D-ornithyl-L-isoleucyl-D-phenylalanyl-L-histidyl-D-α-aspartyl-L-asparagine] (bacitracin B1);
— 4,10-anhydro[N-[[(4R)-2-[(1S,2S)-1-amino-2-methylbutyl]-4,5-dihydro-1,3-thiazol-4-yl]carbonyl]-L-leucyl-D-α- glutamyl-L-isoleucyl-L-lysyl-D-ornithyl-L-valyl-D-phenylalanyl-L-histidyl-D-α-aspartyl-L-asparagine] (bacitracin B2);
— 4,10-anhydro[N-[[(4R)-2-[(1S,2S)-1-amino-2-methylbutyl]-4,5-dihydro-1,3-thiazol-4-yl]carbonyl]-L-leucyl-D-α- glutamyl-L-valyl-L-lysyl-D-ornithyl-L-isoleucyl-D-phenylalanyl-L-histidyl-D-α-aspartyl-L-asparagine] (bacitracin B3).
Content
Minimum 60 IU/mg (dried substance).
CHARACTERS
Appearance
White or light yellowish-grey, hygroscopic powder.
Solubility
Slightly soluble in water and in ethanol (96 per cent).
IDENTIFICATION
First identification: B, C.
Second identification: A, C.
A. Thin-layer chromatography (2.2.27).
Test solution: Dissolve 10 mg of the substance to be examined in 0.5 mL of dilute hydrochloric acid R and dilute to 1.0 mL with water R.
Reference solution: Dissolve 10 mg of bacitracin zinc CRS in 0.5 mL of dilute hydrochloric acid R and dilute to 1.0 mL with water R.
Plate: TLC silica gel plate R.
Mobile phase: glacial acetic acid R, water R, butanol R (14:29:57 V/V/V).
Application: 10 μL.
Development: Over half of the plate.
Drying: At 100-105 °C.
Detection: Spray with ninhydrin solution R1 and heat at 110 °C for 5 min.
Results: The spots in the chromatogram obtained with the test solution are similar in position, size and colour to the spots in the chromatogram obtained with the reference solution.
B. Composition (see Tests).
C. Ignite about 0.15 g, allow to cool and dissolve the residue in 1 mL of dilute hydrochloric acid R. Add 4 mL of water R.
The solution gives the reaction of zinc (2.3.1).
TESTS
pH (2.2.3)
6.0 to 7.5.
Shake 1.0 g for about 1 min with 10 mL of carbon dioxide-free water R and filter.
Composition
Liquid chromatography (2.2.29): use the normalisation procedure. Prepare the solutions immediately before use.
Solution A: 40 g/L solution of sodium edetate R adjusted to pH 7.0 with dilute sodium hydroxide solution R.
Solution B: In a volumetric flask, dissolve 54.4 g of potassium dihydrogen phosphate R in water for chromatography R and dilute to 2000 mL with the same solvent. Adjust to pH 6.0 with a 34.8 g/L solution of dipotassium hydrogen phosphate R and filter through a membrane filter (nominal pore size 0.45 μm).
Test solution: Dissolve 0.100 g of the substance to be examined in solution A and dilute to 50.0 mL with the same solution.
Reference solution (a): Dissolve 20.0 mg of bacitracin for system suitability CRS in solution A and dilute to 10.0 mL with the same solution.
Reference solution (b): Dilute 5.0 mL of reference solution (a) to 100.0 mL with solution A. Dilute 1.0 mL of this solution to 10.0 mL with solution A.
Reference solution (c): In order to prepare impurities E, F, G and H in situ, heat about 4 mL of reference solution (a) in a water-bath for 30 min. Cool to room temperature.
Column:
— size: l = 0.15 m, Ø = 4.6 mm;
— stationary phase: base-deactivated end-capped octadecylsilyl silica gel for chromatography R (3 μm);
— temperature: 28 ± 2 °C.
Mobile phase: acetonitrile R, solution B, water for chromatography R, methanol R (43:100:300:557 V/V/V/V).
Flow rate: 1.0 mL/min.
Detection: Spectrophotometer at 254 nm.
Injection: 100 μL of the test solution and reference solutions (a) and (b).
Run time: 3 times the retention time of bacitracin A.
Identification of peaks: Use the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a) to identify the peaks due to impurity M and bacitracins A, B1, B2 and B3 (see Figure 0466.-1).
Relative retention: With reference to bacitracin A (retention time = about 20 min): impurity A = about 0.44; impurity B = about 0.52; impurity C = about 0.55; bacitracin B1 = about 0.65; bacitracin B2 = about 0.67; bacitracin B3 = about 0.81; impurity M = about 0.87; impurity N = about 0.90; impurity L = about 0.93; impurity O = about 1.2; impurities P and Q = about 1.3; impurity F = about 1.6; impurity G = about 1.8; impurity H = about 2.1; impurity E = about 2.8.
If necessary, adjust the composition of the mobile phase by changing the amount of organic modifier whilst keeping the ratio constant between methanol and acetonitrile.
System suitability:
— peak-to-valley ratio: minimum 1.2, where Hp = height above the baseline of the peak due to bacitracin B2 and Hv = height above the baseline of the lowest point of the curve separating this peak from the peak due to bacitracin B1 in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a);
— peak-to-valley ratio: minimum 1.1, where Hp = height above the baseline of the peak due to impurity M and Hv = height above the baseline of the lowest point of the curve separating this peak from the peak due to bacitracin B3 in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a);
— signal-to-noise ratio: minimum 50 for the peak due to bacitracin A in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b).
Limits:
— bacitracin A: minimum 45.0 per cent;
— sum of bacitracins A, B1, B2 and B3: minimum 77.0 per cent;
— reporting threshold: 0.25 per cent.
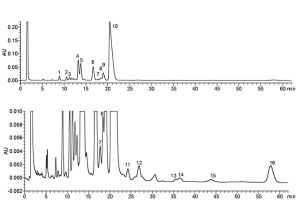
1. impurity A 5. bacitracin B2 9. impurity L 13. impurity F
2. impurity B 6. bacitracin B3 10. bacitracin A 14. impurity G
3. impurity C 7. impurity M 11. impurity O 15. impurity H
4. bacitracin B1 8. impurity N 12. impurities P and Q 16. impurity E
Figure 0466.-1. – Chromatogram for the test for composition of bacitracin zinc: test solution
Related substances
Liquid chromatography (2.2.29) as described in the test for composition with the following modifications. Use the normalisation procedure.
Injection: Test solution and reference solutions (a), (b) and (c).
Identification of impurities: Use the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a) to identify the peaks due to impurities A, B, C, L, M, N, O, P and Q (see Figure 0466.-1); use the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (c) to identify the peaks due to impurities E, F, G, and H (see Figure 0466.-2).
Limits:
— sum of impurities L and N: maximum 8.0 per cent;
— impurity E: maximum 4.0 per cent;
— impurity A: maximum 3.5 per cent;
— impurities B, M: for each impurity, maximum 3.0 per cent;
— impurity C: maximum 2.5 per cent;
— sum of impurities O, P and Q: maximum 2.5 per cent;
— sum of impurities F and G: maximum 2.0 per cent;
— impurity H: maximum 1.0 per cent;
— any other impurity: for each impurity, maximum 2.0 per cent;
— total: maximum 23.0 per cent;
— reporting threshold: 0.25 per cent.
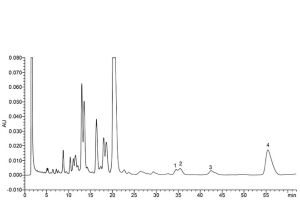
1. impurity F 2. impurity G 3. impurity H 4. impurity E
Figure 0466.-2. – Chromatogram for the test for related substances of bacitracin zinc: reference solution (c)
Zinc
3.5 per cent to 5.5 per cent (dried substance).
Dissolve 0.200 g in a mixture of 2.5 mL of dilute acetic acid R and 2.5 mL of water. Add 50 mL of water R, 50 mg of xylenol orange triturate R and sufficient hexamethylenetetramine R to produce a red colour. Add 2 g of hexamethylenetetramine R in excess. Titrate with 0.01 M sodium edetate until a yellow colour is obtained.
1 mL of 0.01 M sodium edetate is equivalent to 0.654 mg of Zn.
Loss on drying (2.2.32)
Maximum 5.0 per cent, determined on 1.000 g by drying in vacuo at 60 °C at a pressure not exceeding 0.1 kPa for 3 h.
ASSAY
Suspend 50.0 mg in 5 mL of water R, add 0.5 mL of dilute hydrochloric acid R and dilute to 100.0 mL with water R. Allow the solution to stand for 30 min. Carry out the microbiological assay of antibiotics (2.7.2). Use bacitracin zinc CRS as the chemical reference substance.
STORAGE
In an airtight container. If the substance is sterile, the container is also sterile and tamper-evident.
IMPURITIES
Specified impurities: A, B, C, E, F, G, H, L, M, N, O, P, Q.
Other detectable impurities (the following substances would, if present at a sufficient level, be detected by one or other of the tests in the monograph. They are limited by the general acceptance criterion for other/unspecified impurities. It is therefore not necessary to identify these impurities for demonstration of compliance. See also 5.10. Control of impurities in substances for pharmaceutical use) D, I, J, K.
A. 4,10-anhydro[N-[[(4R)-2-[(1S)-1-amino-2-methylpropyl]-4,5-dihydro-1,3-thiazol-4-yl]carbonyl]-L-leucyl-D-α-glutamyl-L- isoleucyl-L-lysyl-D-ornithyl-L-valyl-D-phenylalanyl-L-histidyl-D-α-aspartyl-L-asparagine] (bacitracin D1, bacitracin C2),
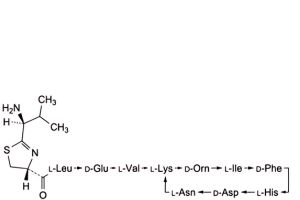
B. 4,10-anhydro[N-[[(4R)-2-[(1S)-1-amino-2-methylpropyl]-4,5-dihydro-1,3-thiazol-4-yl]carbonyl]-L-leucyl-D-α-glutamyl-L- valyl-L-lysyl-D-ornithyl-L-isoleucyl-D-phenylalanyl-L-histidyl-D-α-aspartyl-L-asparagine] (bacitracin D2, bacitracin C3),
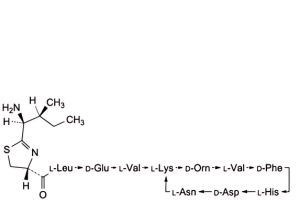
C. 4,10-anhydro[N-[[(4R)-2-[(1S,2S)-1-amino-2-methylbutyl]-4,5-dihydro-1,3-thiazol-4-yl]carbonyl]-L-leucyl-D-α-glutamyl-L -valyl-L-lysyl-D-ornithyl-L-valyl-D-phenylalanyl-L-histidyl-D-α-aspartyl-L-asparagine] (bacitracin D3, bacitracin C1a),
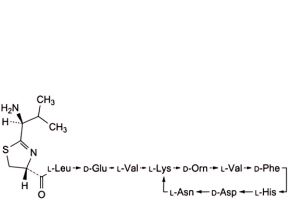
D. 4,10-anhydro[N-[[(4R)-2-[(1S)-1-amino-2-methylpropyl]-4,5-dihydro-1,3-thiazol-4-yl]carbonyl]-L-leucyl-D-α-glutamyl-L- valyl-L-lysyl-D-ornithyl-L-valyl-D-phenylalanyl-L-histidyl-D-α-aspartyl-L-asparagine] (bacitracin E),
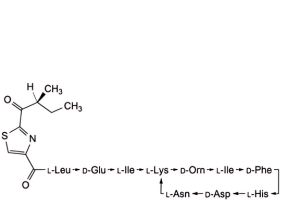
E. 4,10-anhydro[N-[[2-[(2S)-2-methyl-1-oxobutyl]-1,3-thiazol-4-yl]carbonyl]-L-leucyl-D-α-glutamyl-L-isoleucyl-L-lysyl-D-ornithyl-L-isoleucyl-D-phenylalanyl-L-histidyl-D-α-aspartyl-L-asparagine], (bacitracin F),
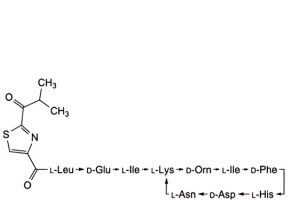
F. 4,10-anhydro[N-[[2-(2-methyl-1-oxopropyl)-1,3-thiazol-4-yl]carbonyl]-L-leucyl-D-α-glutamyl-L-isoleucyl-L-lysyl-D-ornithyl-L-isoleucyl-D-phenylalanyl-L-histidyl-D-α-aspartyl-L-asparagine] (bacitracin H1),
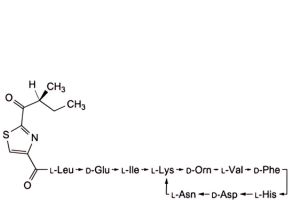
G. 4,10-anhydro[N-[[2-[(2S)-2-methyl-1-oxobutyl]-1,3-thiazol-4-yl]carbonyl]-L-leucyl-D-α-glutamyl-L-isoleucyl-L-lysyl-D-ornithyl-L-valyl-D-phenylalanyl-L-histidyl-D-α-aspartyl-L-asparagine] (bacitracin H2),
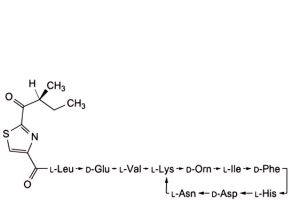
H. 4,10-anhydro[N-[[2-[(2S)-2-methyl-1-oxobutyl]-1,3-thiazol-4-yl]carbonyl]-L-leucyl-D-α-glutamyl-L-valyl-L-lysyl-D-ornithyl-L-isoleucyl-D-phenylalanyl-L-histidyl-D-α-aspartyl-L-asparagine] (bacitracin H3),
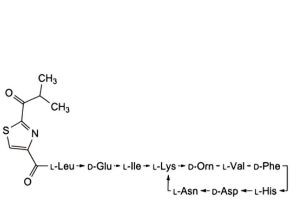
I. 4,10-anhydro[N-[[2-(2-methyl-1-oxopropyl)-1,3-thiazol-4-yl]carbonyl]-L-leucyl-D-α-glutamyl-L-isoleucyl-L-lysyl-D-ornithyl-L-valyl-D-phenylalanyl-L-histidyl-D-α-aspartyl-L-asparagine] (bacitracin I1),
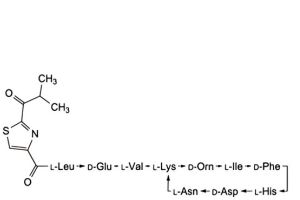
J. 4,10-anhydro[N-[[2-(2-methyl-1-oxopropyl)-1,3-thiazol-4-yl]carbonyl]-L-leucyl-D-α-glutamyl-L-valyl-L-lysyl-D-ornithyl-L-isoleucyl-D-phenylalanyl-L-histidyl-D-α-aspartyl-L-asparagine] (bacitracin I2),
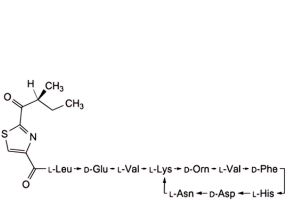
K. 4,10-anhydro[N-[[2-[(2S)-2-methyl-1-oxobutyl]-1,3-thiazol-4-yl]carbonyl]-L-leucyl-D-α-glutamyl-L-valyl-L-lysyl-D-ornithyl-L-valyl-D-phenylalanyl-L-histidyl-D-α-aspartyl-L-asparagine] (bacitracin I3),
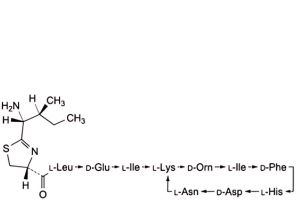
L. 4,10-anhydro[N-[[(4R)-2-[(1R,2S)-1-amino-2-methylbutyl]-4,5-dihydro-1,3-thiazol-4-yl]carbonyl]-L-leucyl-D-α-glutamyl-L-isoleucyl-L-lysyl-D-ornithyl-L-isoleucyl-D-phenylalanyl-L-histidyl-D-α-aspartyl-L-asparagine] (bacitracin X),
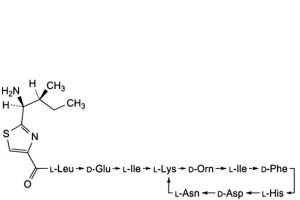
M. 4,10-anhydro[N-[[2-[(1S,2S)-1-amino-2-methylbutyl]-1,3-thiazol-4-yl]carbonyl]-L-leucyl-D-α-glutamyl-L-isoleucyl-L-lysyl-D-ornithyl-L-isoleucyl-D-phenylalanyl-L-histidyl-D-α-aspartyl-L-asparagine] (bacitracin Y),
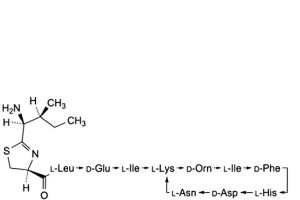
N. 4,10-anhydro[N-[[(4S)-2-[(1S,2S)-1-amino-2-methylbutyl]-4,5-dihydro-1,3-thiazol-4-yl]carbonyl]-L-leucyl-D-α-glutamyl-L-isoleucyl-L-lysyl-D-ornithyl-L-isoleucyl-D-phenylalanyl-L-histidyl-D-α-aspartyl-L-asparagine] (bacitracin Z),
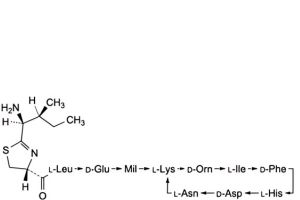
O. Mil = 5-methylene-L-isoleucine: 4,10-anhydro[N-[[(4R)-2-[(1S,2S)-1-amino-2-methylbutyl]-4,5-dihydro-1,3-thiazol-4-yl]carbonyl]-L-leucyl-D-α-glutamyl-5-methylene-L-isoleucyl-L-lysyl-D-ornithyl-L-isoleucyl-D-phenylalanyl-L-histidyl-D-α-aspartyl-L-asparagine] (bacitracin J1),
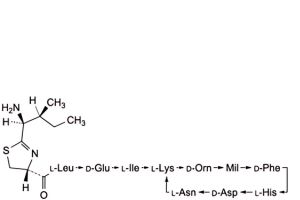
P. Mil = 5-methylene-L-isoleucine: 4,10-anhydro[N-[[(4R)-2-[(1S,2S)-1-amino-2-methylbutyl]-4,5-dihydro-1,3-thiazol-4-yl]carbonyl]-L-leucyl-D-α-glutamyl-L-isoleucyl-L-lysyl-D-ornithyl-5-methylene-L-isoleucyl-D-phenylalanyl-L-histidyl-D-α-aspartyl-L-asparagine] (bacitracin J2),
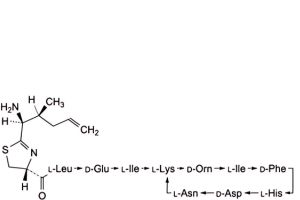
Q. 4,10-anhydro[N-[[(4R)-2-[(1S,2S)-1-amino-2-methylpent-4-en-1-yl]-4,5-dihydro-1,3-thiazol-4-yl]carbonyl]-L-leucyl-D-α-glutamyl-L-isoleucyl-L-lysyl-D-ornithyl-L-isoleucyl-D-phenylalanyl-L-histidyl-D-α-aspartyl-L-asparagine] (bacitracin J3).