(Ph. Eur. monograph 0808)
C21H28ClN3O7S 502.0 37661-08-8
Action and use
Penicillin antibacterial.
DEFINITION
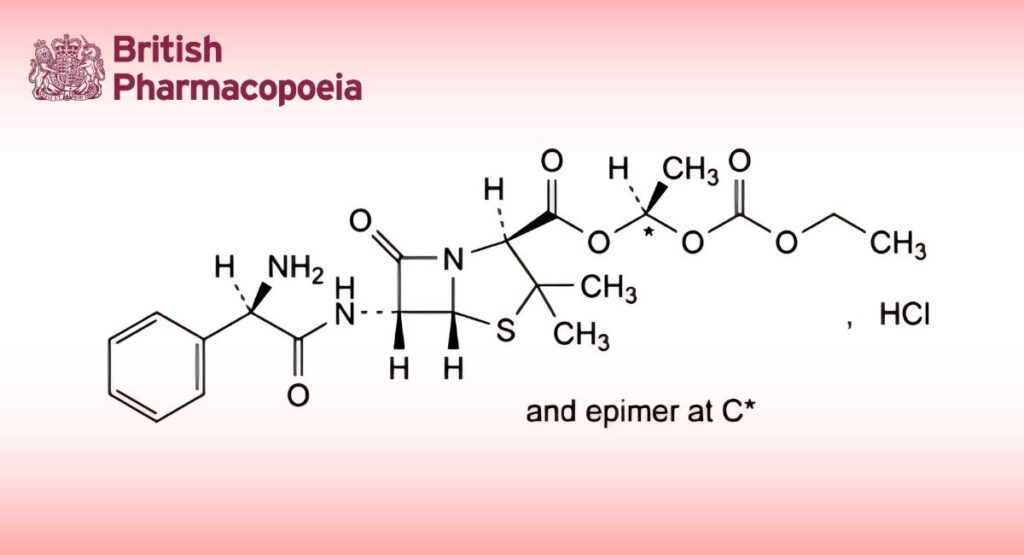
(1RS)-1-[(Ethoxycarbonyl)oxy]ethyl (2S,5R,6R)-6-[[(2R)-2-amino-2-phenylacetyl]amino]-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-4-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylate hydrochloride.
Semi-synthetic product derived from a fermentation product.
Content
95.0 per cent to 102.0 per cent (anhydrous substance).
CHARACTERS
Appearance
White or almost white powder or granules, hygroscopic.
Solubility
Soluble in water, freely soluble in ethanol (96 per cent), soluble in methylene chloride.
IDENTIFICATION
First identification: A, D.
Second identification: B, C, D.
A. Infrared absorption spectrophotometry (2.2.24).
Comparison: bacampicillin hydrochloride CRS.
B. Thin-layer chromatography (2.2.27).
Test solution: Dissolve 10 mg of the substance to be examined in 2 mL of methanol R.
Reference solution (a): Dissolve 10 mg of bacampicillin hydrochloride CRS in 2 mL of methanol R.
Reference solution (b): Dissolve 10 mg of bacampicillin hydrochloride CRS, 10 mg of talampicillin hydrochloride CRS and 10 mg of pivampicillin CRS in 2 mL of methanol R.
Plate: TLC silanised silica gel plate R.
Mobile phase: Mix 10 volumes of a 272 g/L solution of sodium acetate R adjusted to pH 5.0 with glacial acetic acid R, 40 volumes of water R and 50 volumes of ethanol (96 per cent) R.
Application: 1 μL.
Development: Over a path of 15 cm.
Drying: In a current of warm air.
Detection: Spray with ninhydrin solution R1 and heat at 60 °C for 10 min.
System suitability: Reference solution (b):
— the chromatogram shows 3 clearly separated spots.
Results: The principal spot in the chromatogram obtained with the test solution is similar in position, colour and size to the principal spot in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a).
C. Place about 2 mg in a test-tube about 150 mm long and 15 mm in diameter. Moisten with 0.05 mL of water R and add 2 mL of sulfuric acid-formaldehyde reagent R. Mix the contents of the tube by swirling; the solution is practically colourless.
Place the test-tube on a water-bath for 1 min; a dark yellow colour develops.
D. Dissolve about 25 mg in 2 mL of water R. Add 2 mL of dilute sodium hydroxide solution R and shake. Wait a few minutes and add 3 mL of dilute nitric acid R and 0.5 mL of silver nitrate solution R1. A white precipitate is formed. Add 0.5 mL of concentrated ammonia R. The precipitate dissolves.
TESTS
Appearance of solution
Dissolve 0.200 g in 20 mL of water R; the solution is not more opalescent than reference suspension II (2.2.1). Dissolve 0.500 g in 10 mL of water R; the absorbance (2.2.25) of the solution at 430 nm is not greater than 0.10.
pH (2.2.3)
3.0 to 4.5.
Dissolve 1.0 g in carbon dioxide-free water R and dilute to 50 mL with the same solvent.
Specific optical rotation (2.2.7)
+ 175 to + 195 (anhydrous substance).
Dissolve 0.250 g in water R and dilute to 25.0 mL with the same solvent.
Related substances
Liquid chromatography (2.2.29). Prepare the test solution and reference solutions (a), (b) and (d) immediately before use.
Phosphate buffer A: Dissolve 1.4 g of sodium dihydrogen phosphate monohydrate R in water R and dilute to about 800 mL with the same solvent. Adjust to pH 3.0 with dilute phosphoric acid R and dilute to 1000.0 mL with water R.
Phosphate buffer B: Dissolve 2.75 g of sodium dihydrogen phosphate monohydrate R and 2.3 g of disodium hydrogen phosphate dihydrate R in water R and dilute to about 1800 mL with the same solvent. Adjust to pH 6.8, if necessary, using dilute phosphoric acid R or dilute sodium hydroxide solution R and dilute to 2000.0 mL with water R.
Test solution: Dissolve 30.0 mg of the substance to be examined in phosphate buffer A and dilute to 100.0 mL with phosphate buffer A.
Reference solution (a): Dissolve 30.0 mg of bacampicillin hydrochloride CRS in phosphate buffer A and dilute to 100.0 mL with phosphate buffer A.
Reference solution (b): Dilute 1.0 mL of reference solution (a) to 100.0 mL with phosphate buffer A.
Reference solution (c): Dissolve 30 mg of the substance to be examined in phosphate buffer B and dilute to 100 mL with phosphate buffer B. Heat at 80 °C for about 30 min.
Reference solution (d): Dissolve 20 mg of ampicillin trihydrate CRS (impurity I) in phosphate buffer A and dilute to 250 mL with phosphate buffer A. Dilute 5 mL of this solution to 100 mL with phosphate buffer A.
Column:
— size: l = 0.05 m, Ø = 3.9 mm;
— stationary phase: octadecylsilyl silica gel for chromatography R (5 μm).
Mobile phase: Mix 30 volumes of acetonitrile R1 and 70 volumes of a 0.06 per cent m/m solution of tetrahexylammonium hydrogen sulfate R in phosphate buffer B.
Flow rate: 1.0 mL/min.
Detection: Spectrophotometer at 220 nm.
Injection 20 μL of the test solution and reference solutions (b), (c) and (d).
Run time 3.5 times the retention time of bacampicillin.
System suitability:
— the peak due to impurity I is separated from the peaks due to the solvent in the chromatogram obtained with
reference solution (d);
— relative retention with reference to bacampicillin: degradation product eluting just after bacampicillin = 1.12 to 1.38 in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (c); if necessary, adjust the concentration of
tetrahexylammonium hydrogen sulfate in the mobile phase.
Limits:
— any impurity: for each impurity, not more than 1.5 times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b) (1.5 per cent);
— total: not more than 3 times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b) (3 per cent);
— disregard limit: 0.1 times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b) (0.1 per cent).
Butyl acetate and ethyl acetate (2.4.24, System A)
Maximum 2.0 per cent of butyl acetate, maximum 4.0 per cent of ethyl acetate and maximum 5.0 per cent for the sum of the contents.
Sample solution: Dissolve 50.0 mg of the substance to be examined in water R and dilute to 10.0 mL with the same solvent.
Use the method of standard additions.
Static head-space conditions that may be used:
— equilibration temperature: 60 °C;
— equilibration time: 20 min.
N,N-Dimethylaniline (2.4.26, Method A)
Maximum 20 ppm.
Water (2.5.12)
Maximum 0.8 per cent, determined on 0.300 g.
Sulfated ash (2.4.14)
Maximum 1.5 per cent, determined on 1.0 g.
ASSAY
Liquid chromatography (2.2.29) as described in the test for related substances with the following modifications.
Injection: Test solution and reference solution (a).
System suitability: Reference solution (a):
— repeatability: maximum relative standard deviation of 1.0 per cent after 6 injections.
Calculate the percentage content of C21H28ClN3O7S from the declared content of bacampicillin hydrochloride CRS.
STORAGE
In an airtight container.
IMPURITIES
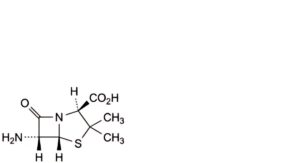
A. (2S,5R,6R)-6-amino-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-4-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylic acid (6-aminopenicillanic acid),
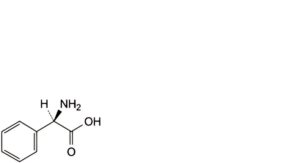
B. (2R)-2-amino-2-phenylacetic acid (D-phenylglycine),
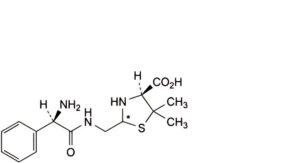
C. (2RS,4S)-2-[[[(2R)-2-amino-2-phenylacetyl]amino]methyl]-5,5-dimethylthiazolidine-4-carboxylic acid (penilloic acids of ampicillin),
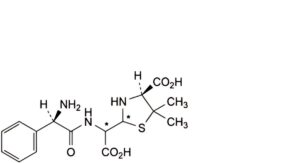
D. (4S)-2-[[[(2R)-2-amino-2-phenylacetyl]amino]carboxymethyl]-5,5-dimethylthiazolidine-4-carboxylic acid (penicilloic acids of ampicillin),
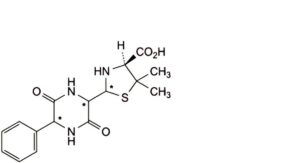
E. (4S)-2-(3,6-dioxo-5-phenylpiperazin-2-yl)-5,5-dimethylthiazolidine-4-carboxylic acid (diketopiperazines of ampicillin),
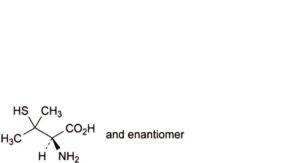
F. (2RS)-2-amino-3-methyl-3-sulfanylbutanoic acid (DL-penicillamine),
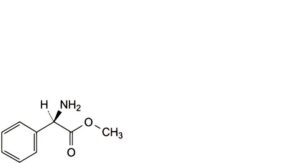
G. methyl (2R)-2-amino-2-phenylacetate (methyl D-phenylglycinate),
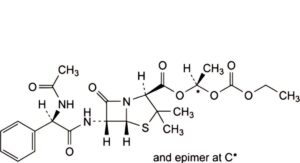
H. (1RS)-1-[(ethoxycarbonyl)oxy]ethyl (2S,5R,6R)-6-[[(2R)-2-(acetylamino)-2-phenylacetyl]amino]-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-4-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylate (N-acetylbacampicillin),
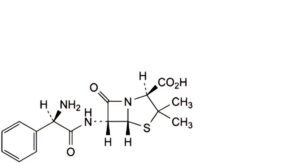
I. Axit (2S,5R,6R)-6-[[(2R)-2-amino-2-phenylacetyl]amino]-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-4-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylic (ampicillin).