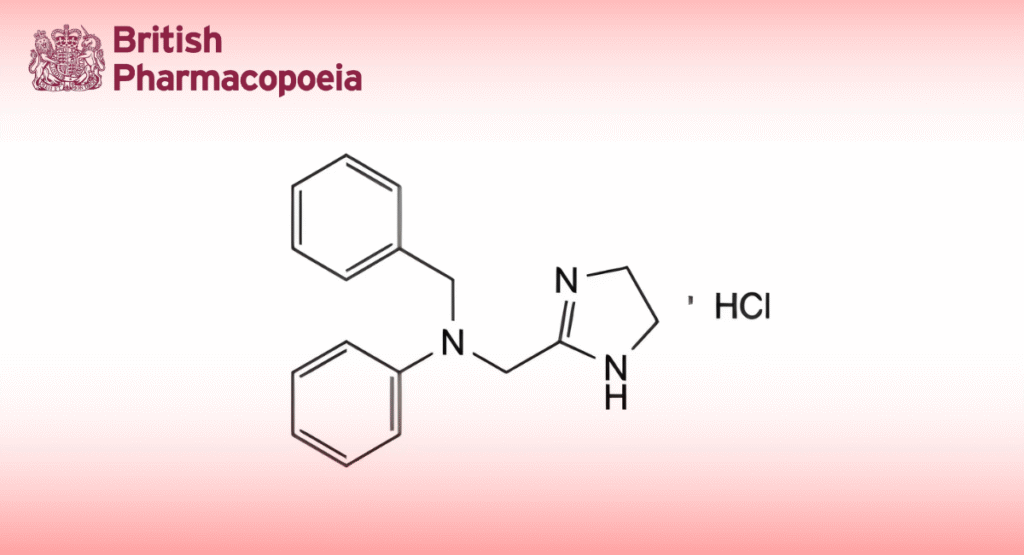
(Ph. Eur. monograph 0972)
C17H20ClN3 301.8 2508-72-7
Action and use
Histamine H1 receptor antagonist; antihistamine.
DEFINITION
Antazoline hydrochloride contains not less than 99.0 per cent and not more than the equivalent of 101.0 per cent of N-benzyl-N-[(4,5-dihydro-1H-imidazol-2-yl)methyl]aniline hydrochloride, calculated with reference to the dried substance.
CHARACTERS
A white or almost white, crystalline powder, sparingly soluble in water, soluble in ethanol (96 per cent), slightly soluble in methylene chloride.
It melts at about 240 °C, with decomposition.
IDENTIFICATION
First identification: A, D.
Second identification: B, C, D.
A. Examine by infrared absorption spectrophotometry (2.2.24), comparing with the spectrum obtained with antazoline hydrochloride CRS. Examine the substances as discs prepared using potassium chloride R.
B. Examine the chromatograms obtained in the test for related substances in daylight after spraying. The principal spot in the chromatogram obtained with test solution (b) is similar in position, colour and size to the principal spot in the
chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b).
C. To 5 mL of solution S (see Tests) add, drop by drop, dilute sodium hydroxide solution R until an alkaline reaction is produced. Filter. The precipitate, washed with two quantities, each of 10 mL, of water R and dried in a desiccator under
reduced pressure, melts (2.2.14) at 119 °C to 123 °C.
D. It gives reaction (a) of chlorides (2.3.1).
TESTS
Solution S
Dissolve 2.0 g in carbon dioxide-free water R prepared from distilled water R, heating at 60 °C if necessary. Allow to cool and dilute to 100 mL with the same solvent.
Appearance of solution
Solution S is clear (2.2.1) and not more intensely coloured than reference solution Y7 (2.2.2, Method II).
Acidity or alkalinity
To 10 mL of solution S add 0.2 mL of methyl red solution R. Not more than 0.1 mL of 0.01 M hydrochloric acid or 0.01 M sodium hydroxide is required to change the colour of the indicator.
Related substances
Examine by thin-layer chromatography (2.2.27), using silica gel GF254 R as the coating substance. Heat the plate at 110 °C for 15 min before using.
Test solution (a): Dissolve 0.10 g of the substance to be examined in methanol R and dilute to 5 mL with the same solvent.
Test solution (b): Dilute 1 mL of test solution (a) to 5 mL with methanol R.
Reference solution (a): Dilute 0.5 mL of test solution (a) to 100 mL with methanol R.
Reference solution (b): Dissolve 20 mg of antazoline hydrochloride CRS in methanol R and dilute to 5 mL with the same solvent.
Reference solution (c): Dissolve 20 mg of xylometazoline hydrochloride CRS in 1 mL of test solution (a) and dilute to 5 mL with methanol R.
Apply to the plate 5 μL of each solution. Develop over a path of 15 cm using a mixture of 5 volumes of diethylamine R, 10 volumes of methanol R and 85 volumes of ethyl acetate R. Dry the plate in a current of warm air for 15 min. Examine in ultraviolet light at 254 nm. The test is not valid unless the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (c) shows two clearly separated principal spots. Spray with a mixture of equal volumes of a 200 g/L solution of ferric chloride R and a 5 g/L solution of potassium ferricyanide R. Examine immediately in daylight. Any spot in the chromatogram obtained with test solution (a), apart from the principal spot, is not more intense than the spot in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a) (0.5 per cent).
Loss on drying (2.2.32)
Not more than 0.5 per cent, determined on 1.000 g by drying in an oven at 105 °C for 3 h.
Sulfated ash (2.4.14)
Not more than 0.1 per cent, determined on the residue obtained in the test for loss on drying.
ASSAY
Dissolve 0.250 g in 100 mL of alcohol R. Add 0.1 mL of phenolphthalein solution R1. Titrate with 0.1 M alcoholic potassium hydroxide.
1 mL of 0.1 M alcoholic potassium hydroxide is equivalent to 30.18 mg of C17H20ClN3.
IMPURITIES
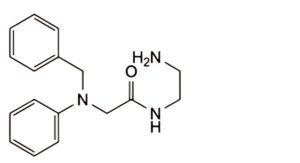
A. N-(2-aminoethyl)-2-(benzylphenylamino)acetamide.