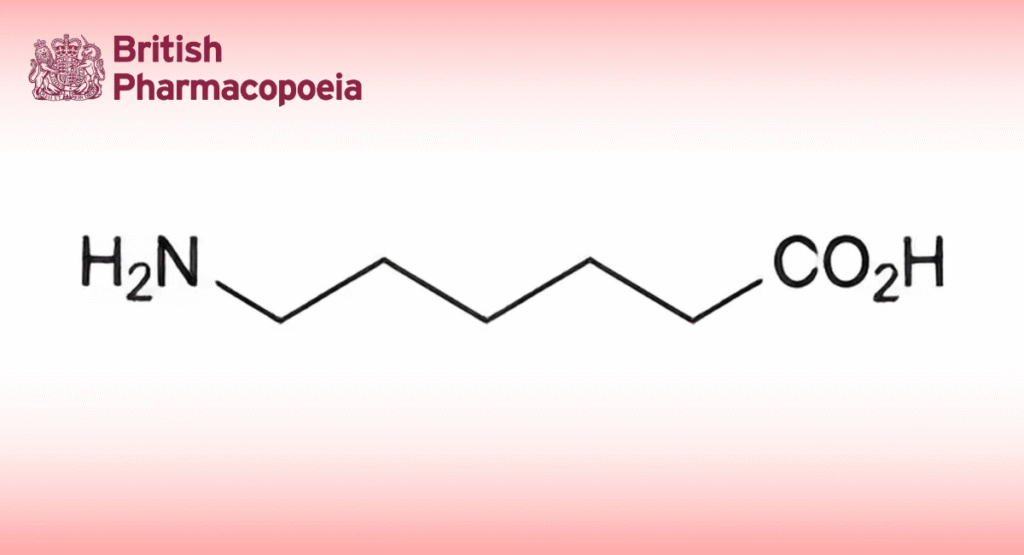
(Ph. Eur. monograph 0874)
C6H13NO2 131.2 60-32-2
Action and use
Antifibrinolytic.
DEFINITION
Aminocaproic acid contains not less than 98.5 per cent and not more than the equivalent of 101.0 per cent of 6- aminohexanoic acid, calculated with reference to the dried substance.
CHARACTERS
A white or almost white, crystalline powder or colourless crystals, freely soluble in water, slightly soluble in ethanol (96 per cent).
It melts at about 205 °C with decomposition.
IDENTIFICATION
First identification: A.
Second identification: B, C, D.
A. Examine by infrared absorption spectrophotometry (2.2.24), comparing with the spectrum obtained with aminocaproic acid CRS. Examine the substances prepared as discs.
B. Examine the chromatograms obtained in the test for ninhydrin-positive substances. The principal spot in the chromatogram obtained with the test solution (b) is similar in position, colour and size to the principal spot in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a).
C. Dissolve 0.5 g in 4 mL of a mixture of equal volumes of dilute hydrochloric acid R and water R. Evaporate to dryness by heating on a water-bath. Dry the residue in a desiccator. Dissolve the residue in about 2 mL of boiling ethanol R. Allow to cool and maintain at 4 °C to 8 °C for 3 h. Filter under reduced pressure. The residue washed with about 10 mL of acetone R and dried at 60 °C for 30 min, melts (2.2.14) at 131 °C to 133 °C.
D. Dissolve about 5 mg in 0.5 mL of distilled water R. Add 3 mL of dimethylformamide R and 2 mL of ascorbic acid solution R. Heat on a water-bath. An orange colour develops.
TESTS
Solution S
Dissolve 10.0 g in carbon dioxide-free water R and dilute to 50.0 mL with the same solvent.
Appearance of solution
Solution S is colourless (2.2.2, Method II) and remains clear (2.2.1) on standing for 24 h.
pH (2.2.3)
The pH of solution S is 7.5 to 8.0.
Absorbance (2.2.25)
A. The absorbance of solution S at 287 nm is not more than 0.10 and at 450 nm is not more than 0.03.
B. Place 2.0 g in an even layer in a shallow dish 9 cm in diameter, cover and allow to stand at 98 °C to 102 °C for 72 h.
Dissolve in water R and dilute to 10.0 mL with the same solvent. The absorbance of the solution at 287 nm is not more than 0.15 and at 450 nm is not more than 0.03.
Ninhydrin-positive substances
Examine by thin-layer chromatography (2.2.27), using a suitable silica gel as the coating substance.
Test solution (a): Dissolve 0.10 g of the substance to be examined in water R and dilute to 10 mL with the same solvent.
Test solution (b): Dilute 1 mL of test solution (a) to 50 mL with water R.
Reference solution (a): Dissolve 10 mg of aminocaproic acid CRS in water R and dilute to 50 mL with the same solvent.
Reference solution (b): Dilute 5 mL of test solution (b) to 20 mL with water R.
Reference solution (c): Dissolve 10 mg of aminocaproic acid CRS and 10 mg of leucine CRS in water R and dilute to 25 mL with the same solvent.
Apply separately to the plate 5 μL of each solution. Allow the plate to dry in air. Develop over a path of 15 cm using a mixture of 20 volumes of glacial acetic acid R, 20 volumes of water R and 60 volumes of butanol R. Dry the plate in a current of warm air. Spray with ninhydrin solution R and heat at 100 °C to 105 °C for 15 min. Any spot in the chromatogram obtained with the test solution (a), apart from the principal spot, is not more intense than the spot in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b) (0.5 per cent). The test is not valid unless the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (c) shows two clearly separated principal spots.
Loss on drying (2.2.32)
Not more than 0.5 per cent, determined on 1.000 g by drying in an oven at 105 °C.
Sulfated ash (2.4.14)
Not more than 0.1 per cent, determined on 1.0 g.
ASSAY
Dissolve 0.100 g in 20 mL of anhydrous acetic acid R. Using 0.1 mL of crystal violet solution R as indicator, titrate with 0.1 M perchloric acid until the colour changes from bluish-violet to bluish-green.
1 mL of 0.1 M perchloric acid is equivalent to 13.12 mg of C6H13NO2.