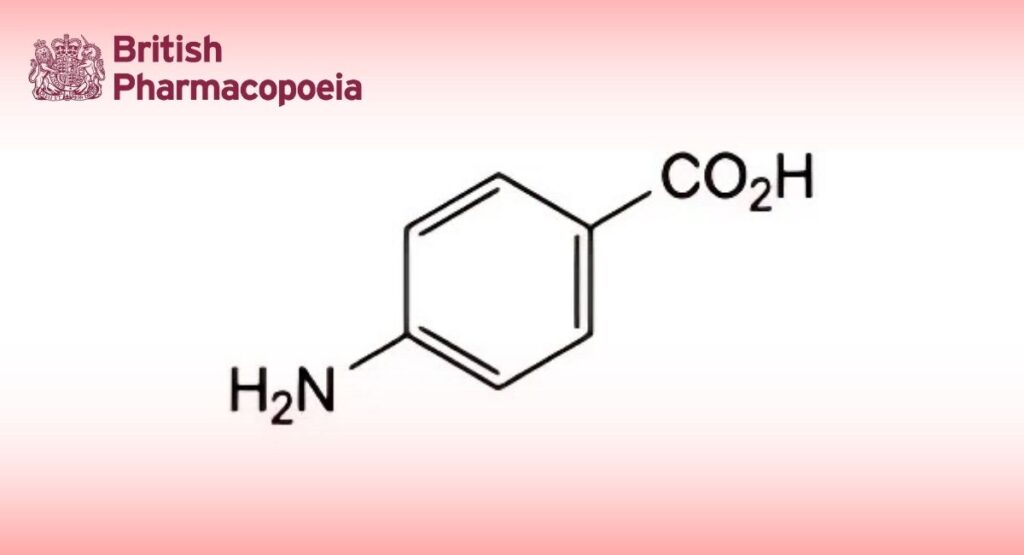
(4-Aminobenzoic Acid, Ph. Eur. monograph 1687)
C7H7NO2 137.1 150-13-0
Action and use
Skin protective.
DEFINITION
4-Aminobenzoic acid.
Content
99.0 per cent to 101.0 per cent (anhydrous substance).
CHARACTERS
Appearance
White or slightly yellow, crystalline powder.
Solubility
Slightly soluble in water, freely soluble in ethanol (96 per cent). It dissolves in dilute solutions of alkali hydroxides.
IDENTIFICATION
First identification: B.
Second identification: A, C.
A. Melting point (2.2.14): 186 °C to 189 °C.
B. Infrared absorption spectrophotometry (2.2.24).
Comparison 4-aminobenzoic acid CRS.
C. Thin-layer chromatography (2.2.27).
Test solution: Dissolve 20 mg of the substance to be examined in methanol R and dilute to 20 mL with the same solvent.
Reference solution (a): Dissolve 20 mg of 4-aminobenzoic acid CRS in methanol R and dilute to 20 mL with the same solvent.
Reference solution (b): Dissolve 10 mg of 4-nitrobenzoic acid R in 10 mL of reference solution (a).
Plate: Suitable silica gel with a fluorescent indicator having an optimal intensity at 254 nm as the coating substance.
Mobile phase: glacial acetic acid R, hexane R, methylene chloride R (5:20:75 V/V/V).
Application: 1 μL.
Development: Over a path of 10 cm.
Drying: In air.
Detection: Examine in ultraviolet light at 254 nm.
System suitability: The chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b) shows 2 clearly separated spots.
Results: The principal spot in the chromatogram obtained with the test solution is similar in position and size to the principal spot in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a).
TESTS
Appearance of solution
The solution is clear (2.2.1) and not more intensely coloured than reference solution B5 (2.2.2, Method II).
Dissolve 1.0 g in ethanol (96 per cent) R and dilute to 20 mL with the same solvent.
Related substances
Liquid chromatography (2.2.29).
Test solution: Dissolve 25.0 mg of the substance to be examined in the mobile phase and dilute to 100.0 mL with the mobile phase.
Reference solution: Dissolve 25.0 mg of 4-nitrobenzoic acid R and 25.0 mg of benzocaine R in methanol R and dilute to 100.0 mL with the same solvent. Dilute 1.0 mL to 50.0 mL with the mobile phase. Dilute 1.0 mL of this solution to 10.0 mL with the mobile phase.
Column:
— size: l = 0.12 m, Ø = 4.0 mm,
— stationary phase: octylsilyl silica gel for chromatography R (5 μm).
Mobile phase: Mix 20 volumes of a mixture of 70 volumes of acetonitrile R and 80 volumes of methanol R, and 80 volumes of a solution containing 1.5 g/L of potassium dihydrogen phosphate R and 2.5 g/L of sodium octanesulfonate R adjusted to pH 2.2 with phosphoric acid R.
Flow rate: 1.0 mL/min.
Detection: Spectrophotometer at 270 nm.
Injection: 20 μL.
Run time: 11 times the retention time of 4-aminobenzoic acid.
Relative retention: With reference to 4-aminobenzoic acid (retention time = about 3 min): impurity A = about 4; impurity B = about 9.
Limits:
— impurity A: not more than the area of the corresponding peak in the chromatogram obtained with the reference solution (0.2 per cent),
— impurity B: not more than the area of the corresponding peak in the chromatogram obtained with the reference solution (0.2 per cent),
— any other impurity: not more than 0.5 times the area of the peak due to impurity A in the chromatogram obtained with the reference solution (0.1 per cent),
— total: not more than 2.5 times the area of the peak due to impurity A in the chromatogram obtained with the
reference solution (0.5 per cent),
— disregard limit: 0.1 times the area of the peak due to impurity A in the chromatogram obtained with the reference solution (0.02 per cent).
Impurity C and impurity D
Gas chromatography (2.2.28).
Internal standard solution: Dissolve 20.0 mg of lauric acid R in methylene chloride R and dilute to 100.0 mL with the same solvent.
Test solution: Dissolve 1.000 g of the substance to be examined in 10.0 mL of an 84 g/L solution of sodium hydroxide R and extract with 2 quantities, each of 10 mL, of methylene chloride R. Combine and wash with 5 mL of water R; filter through anhydrous sodium sulfate R. Wash the filter with methylene chloride R. Evaporate in a water-bath at 50-60 °C to obtain a volume of about 1-5 mL. Add 1.0 mL of the internal standard solution and dilute to 10.0 mL with methylene chloride R.
Reference solution (a): Dissolve 20.0 mg of aniline R in methylene chloride R and dilute to 100.0 mL with the same solvent.
Reference solution (b): Dissolve 20.0 mg of p-toluidine R in methylene chloride R and dilute to 100.0 mL with the same solvent.
Reference solution (c): Dilute 0.50 mL of reference solution (a), 0.50 mL of reference solution (b) and 10.0 mL of the internal standard solution to 100.0 mL with methylene chloride R.
Column:
— material: fused silica,
— size: l = 30 m, Ø = 0.32 mm,
— stationary phase: phenyl(5)methyl(95)polysiloxane R (film thickness 0.5 μm).
Carrier gas helium for chromatography R.
Flow rate: 1.0 mL/min.
Split ratio: 1:10.
Temperature:
| Time
(min) |
Temperature
(°C) |
|
| Column | 0 – 4 | 130 |
| 4 – 6.5 | 130 → 180 | |
| 6.5 – 11.5 | 180 | |
| Injection port | 280 | |
| Detector | 300 |
Detection: Flame ionisation.
Injection: 2 μL; inject the test solution and reference solution (c).
Retention time Internal standard = about 9.5 min.
Limits:
— impurity C: calculate the ratio (R) of the area of the peak due to impurity C to the area of the peak due to the internal standard from the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (c); calculate the ratio of the area of the peak due to impurity C to the area of the peak due to the internal standard from the chromatogram obtained with the test solution: this ratio is not greater than R (10 ppm),
— impurity D: calculate the ratio (R) of the area of the peak due to impurity D to the area of the peak due to the
internal standard from the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (c); calculate the ratio of the area of the peak due to impurity D to the area of the peak due to the internal standard from the chromatogram obtained with the test solution: this ratio is not greater than R (10 ppm).
Iron (2.4.9)
Maximum 40 ppm.
Dissolve 0.250 g in 3 mL of ethanol (96 per cent) R and dilute to 10.0 mL with water R.
Water (2.5.12)
Maximum 0.2 per cent, determined on 1.00 g.
Sulfated ash (2.4.14)
Maximum 0.1 per cent, determined on 1.0 g.
ASSAY
Dissolve 0.100 g with heating in 50 mL of carbon dioxide-free water R. Titrate with 0.1 M sodium hydroxide determining the end-point potentiometrically (2.2.20).
1 mL of 0.1 M sodium hydroxide is equivalent to 13.71 mg of C7H7NO2.
STORAGE
Protected from light.
IMPURITIES
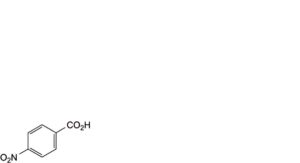
A. 4-nitrobenzoic acid,
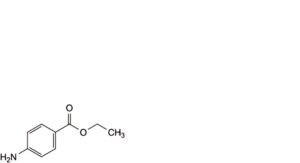
B. ethyl 4-aminobenzoate (benzocaine),

C. aniline,
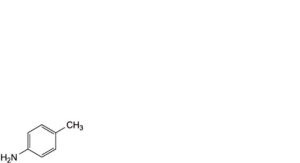
D. 4-methylaniline (p-toluidine).