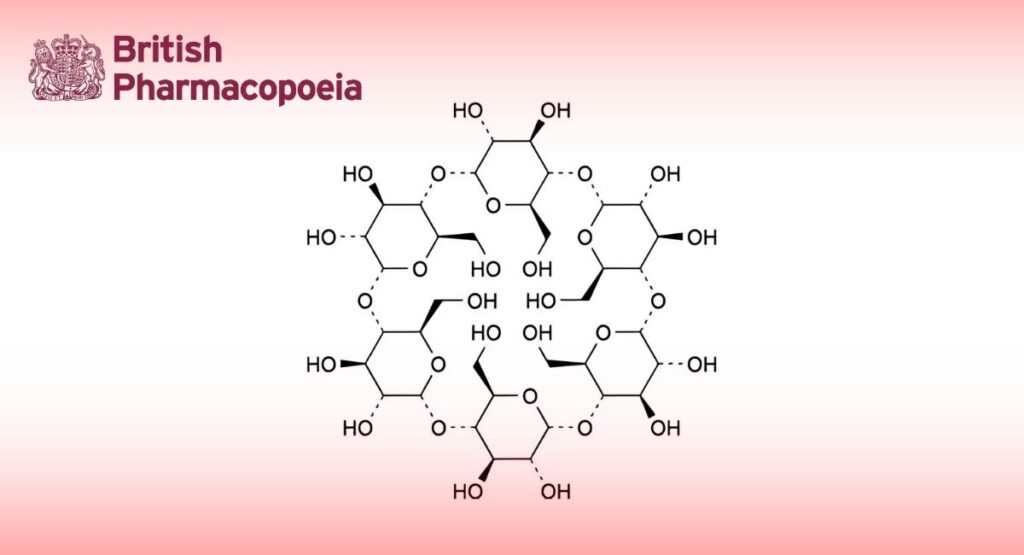
Alphacyclodextrin
(Ph. Eur. monograph 1487)
[C6H10O5]6 973 10016-20-3Action and use
Cyclodextran; carrier molecule for drug delivery systems.
DEFINITION
Cyclohexakis-(1→4)-(α-D-glucopyranosyl) (cyclomaltohexaose, α-cyclodextrin).
Content
97.0 per cent to 102.0 per cent (dried substance).
CHARACTERS
Appearance
White or almost white, amorphous or crystalline, hygroscopic powder.
Solubility
Alfadex
Freely soluble in water, slightly soluble in propylene glycol, practically insoluble in anhydrous ethanol and in methylene chloride.
IDENTIFICATION
A. Specific optical rotation (2.2.7): + 147 to + 152 (dried substance), determined on solution S (see Tests).
B. Examine the chromatograms obtained in the assay.
Results The principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with test solution (b) is similar in retention time and size to the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (c).
C. Dissolve 0.2 g in 2 mL of iodine solution R4 by warming on a water-bath, and allow to stand at room temperature; a yellowish-brown precipitate is formed.
TESTS
Solution S
Dissolve 1.000 g in carbon dioxide-free water R and dilute to 100.0 mL with the same solvent.
Appearance of solution
Solution S is clear (2.2.1).
pH (2.2.3)
5.0 to 8.0.
Mix 1 mL of a 223.6 g/L solution of potassium chloride R and 30 mL of solution S.
Reducing sugars
Maximum 0.2 per cent.
Test solution To 1 mL of solution S add 1 mL of cupri-tartaric solution R4. Heat on a water-bath for 10 min, cool to room temperature. Add 10 mL of ammonium molybdate reagent R1 and allow to stand for 15 min.
Reference solution Prepare a reference solution at the same time and in the same manner as the test solution, using 1 mL of a 0.02 g/L solution of glucose R.
Measure the absorbance (2.2.25) of the test solution and the reference solution at the absorption maximum at 740 nm using water R as the compensation liquid. The absorbance of the test solution is not greater than that of the reference solution.
Light-absorbing impurities
Examine solution S between 230 nm and 750 nm. Between 230 nm and 350 nm, the absorbance (2.2.25) is not greater than 0.10. Between 350 nm and 750 nm, the absorbance (2.2.25) is not greater than 0.05.
Related substances
Liquid chromatography (2.2.29).
Test solution (a) Dissolve 0.250 g of the substance to be examined in water R with heating, cool and dilute to 25.0 mL with the same solvent.
Test solution (b) Dilute 5.0 mL of test solution (a) to 50.0 mL with water R.
Reference solution (a) Dissolve 25.0 mg of betadex CRS (impurity A), 25.0 mg of gammacyclodextrin CRS (impurity B) and 50.0 mg of alfadex CRS in water R, then dilute to 50.0 mL with the same solvent.
Reference solution (b) Dilute 5.0 mL of reference solution (a) to 100.0 mL with water R.
Reference solution (c) Dissolve 25.0 mg of alfadex CRS in water R and dilute to 25.0 mL with the same solvent.
Column:
— size: l = 0.25 m, Ø = 4.6 mm;
— stationary phase: end-capped octadecylsilyl silica gel for chromatography R (5 μm).
Mobile phase methanol R, water for chromatography R (10:90 V/V).
Flow rate 1.5 mL/min.
Detection Differential refractometer.
Equilibration With the mobile phase for about 3 h.
Injection 50 μL of test solution (a) and reference solutions (a) and (b).
Run time 3.5 times the retention time of alfadex.
Identification of impurities Use the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a) to identify the peaks due to impurities A and B.
Relative retention With reference to alfadex (retention time = about 6 min): impurity B = about 0.7; impurity A = about 1.7.
System suitability Reference solution (a):
— resolution: minimum 1.5 between the peaks due to impurity B and alfadex; if necessary, adjust the concentration of methanol in the mobile phase.
Calculation of percentage contents:
— for impurities A and B, use the concentration of the corresponding impurity in reference solution (b);
— for impurities other than A and B, use the concentration of alfadex in reference solution (b).
Limits:
— impurities A, B: for each impurity, maximum 0.25 per cent;
— sum of impurities other than A and B: maximum 0.5 per cent;
— reporting threshold: 0.15 per cent.
Loss on drying (2.2.32)
Maximum 11 per cent, determined on 1.000 g by drying in an oven at 120 °C for 2 h.
Sulfated ash (2.4.14)
Maximum 0.1 per cent, determined on 1.0 g.
ASSAY
Liquid chromatography (2.2.29) as described in the test for related substances with the following modifications.
Injection Test solution (b) and reference solutions (a) and (c).
System suitability:
— repeatability: maximum relative standard deviation of 2.0 per cent for the peak due to alfadex determined on 5 injections of reference solution (a).
Calculate the percentage content of [C6H10O5]6 using the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (c) and taking into account the assigned content of alfadex CRS.
STORAGE
In an airtight container.
IMPURITIES
Specified impurities A, B.
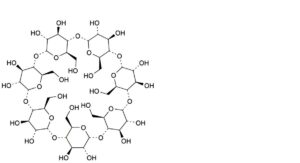
A. cycloheptakis-(1→4)-(α-D-glucopyranosyl) (betadex, cyclomaltoheptaose, β-cyclodextrin),
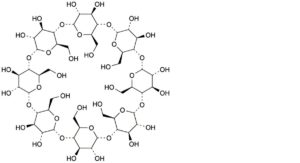
B. cyclooctakis-(1→4)-(α-D-glucopyranosyl) (gammadex, cyclomaltooctaose, γ-cyclodextrin).