Edition: BP 2025 (Ph. Eur. 11.6 update)
Action and use
Adrenoceptor agonist + local anaesthetic.
DEFINITION
Adrenaline and Cocaine Intranasal Solution contains Adrenaline Acid Tartrate and Cocaine Hydrochloride in a suitable vehicle.
The intranasal solution complies with the requirements stated under Nasal Preparations and with the following requirements. Where appropriate, the intranasal solution also complies with the requirements stated under Unlicensed Medicines.
Content of adrenaline, C9H13NO3
95.0 to 105.0% of the stated amount.
Content of cocaine hydrochloride, C17H21NO4,HCl
95.0 to 105.0% of the stated amount.
IDENTIFICATION
A. In the Assay for adrenaline, the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with solution (1) has the same retention time as that in the chromatogram obtained with solution (2).
B. In the Assay for cocaine hydrochloride, the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with solution (1) has the same retention time as that in the chromatogram obtained with solution (2).
C. To 10 ml of the intranasal solution add 2 mL of a 10% w/v solution of disodium hydrogen orthophosphate and sufficient iodinated potassium iodide solution to produce a brown colour and remove excess iodine by adding 0.1M sodium thiosulfate drop wise. A red colour is produced.
D. Yields reaction A characteristic of chlorides, Appendix VI.
TESTS
Acidity
pH, 2.0 to 4.0, Appendix V L.
Related substances (for cocaine hydrochloride)
Carry out the method for liquid chromatography, Appendix III D, using the following solutions.
(1) Dilute a volume of the intranasal solution with sufficient mobile phase to produce a solution containing 0.04% w/v of Cocaine Hydrochloride.
(2) 0.0008% w/v of benzoylecgonine hydrate in the mobile phase.
(3) 0.0008% w/v of benzoic acid in the mobile phase.
(4) 0.0008% w/v of each of benzoylecgonine hydrate and benzoic acid in solution (1).
CHROMATOGRAPHIC CONDITIONS
(a) Use a stainless steel column (25 cm × 4.6 mm) packed with octadecylsilyl silica gel for chromatography (10 μm) (Partisil 10 ODS is suitable).
(b) Use isocratic elution and the mobile phase described below.
(c) Use a flow rate of 2 mL per minute.
(d) Use an ambient column temperature.
(e) Use a detection wavelength of 240 nm.
(f) Inject 20 μL of each solution.
MOBILE PHASE
1 volume of 9M perchloric acid, 35 volumes of methanol and 64 volumes of water.
SYSTEM SUITABILITY
The test is not valid unless, in the chromatogram obtained with solution (4), the resolution between the peaks corresponding to benzoylecgonine and benzoic acid is at least 2.0.
LIMITS
In the chromatogram obtained with solution (1):
the area of any peak corresponding to benzoylecgonine is not greater than the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with solution (2) (2%);
the area of any peak corresponding to benzoic acid is not greater than the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with solution (3) (2%).
The total impurity content is not greater than 2%.
ASSAY
For adrenaline
Carry out the method for liquid chromatography, Appendix III D, using the following solutions.
(1) Dilute a suitable volume of the intranasal solution with sufficient mobile phase to produce a solution containing the equivalent of 0.011% w/v of adrenaline.
(2) 0.02% w/v of adrenaline acid tartrate BPCRS in the mobile phase.
(3) 0.02% w/v of adrenaline acid tartrate BPCRS and 0.02% w/v of noradrenaline acid tartrate in the mobile phase.
CHROMATOGRAPHIC CONDITIONS
(a) Use a stainless steel column (10 cm × 4.6 mm) packed with end-capped octadecylsilyl silica gel for chromatography (5 μm) (Nucleosil C18 is suitable).
(b) Use isocratic elution and the mobile phase described below.
(c) Use a flow rate of 2 mL per minute.
(d) Use an ambient column temperature.
(e) Use a detection wavelength of 205 nm.
(f) Inject 20 μL of each solution.
Dissolve 4.0 g of tetramethylammonium hydrogen sulfate, 1.1 g of sodium heptanesulfonate and 2 mL of 0.1M disodium edetate in a mixture of 950 mL of water and 50 mL of methanol and adjust the pH to 3.5 with 1M sodium hydroxide.
SYSTEM SUITABILITY
The assay is not valid unless, in the chromatogram obtained with solution (3), the resolution between the two principal peaks is at least 2.0.
DETERMINATION OF CONTENT
Calculate the content of C9H13NO3 in the intranasal solution from the chromatograms obtained and using the declared content of C9H13NO3 in adrenaline acid tartrate BPCRS.
For cocaine hydrochloride
Carry out the method for liquid chromatography, Appendix III D, using the following solutions.
(1) Dilute a volume of the intranasal solution containing 40 mg of Cocaine Hydrochloride with sufficient water to produce 100 mL.
(2) 0.04% w/v of cocaine hydrochloride BPCRS in water.
(3) 0.0008% w/v of each of benzoylecgonine hydrate and benzoic acid in solution (1).
CHROMATOGRAPHIC CONDITIONS
(a) Use a stainless steel column (25 cm × 4.6 mm) packed with octadecylsilyl silica gel for chromatography (10 μm) (Partisil 10 ODS is suitable).
(b) Use isocratic elution and the mobile phase described below.
(c) Use a flow rate of 2 mL per minute.
(d) Use an ambient column temperature.
(e) Use a detection wavelength of 240 nm.
(f) Inject 20 μL of each solution.
MOBILE PHASE
1 volume of 9M perchloric acid, 35 volumes of methanol and 64 volumes of water.
SYSTEM SUITABILITY
The test is not valid unless, in the chromatogram obtained with solution (3), the resolution between the peaks corresponding to benzoylecgonine and benzoic acid is at least 2.0.
DETERMINATION OF CONTENT
Calculate the content of C17H21NO4,HCl in the intranasal solution from the chromatograms obtained and using the declared content of C17H21NO4,HCl in cocaine hydrochloride BPCRS.
STORAGE
Adrenaline and Cocaine Intranasal Solution should be protected from light.
LABELLING
The quantity of adrenaline acid tartrate is stated in terms of the equivalent amount of adrenaline (epinephrine).
IMPURITIES
The impurities limited by the requirements of this monograph include:
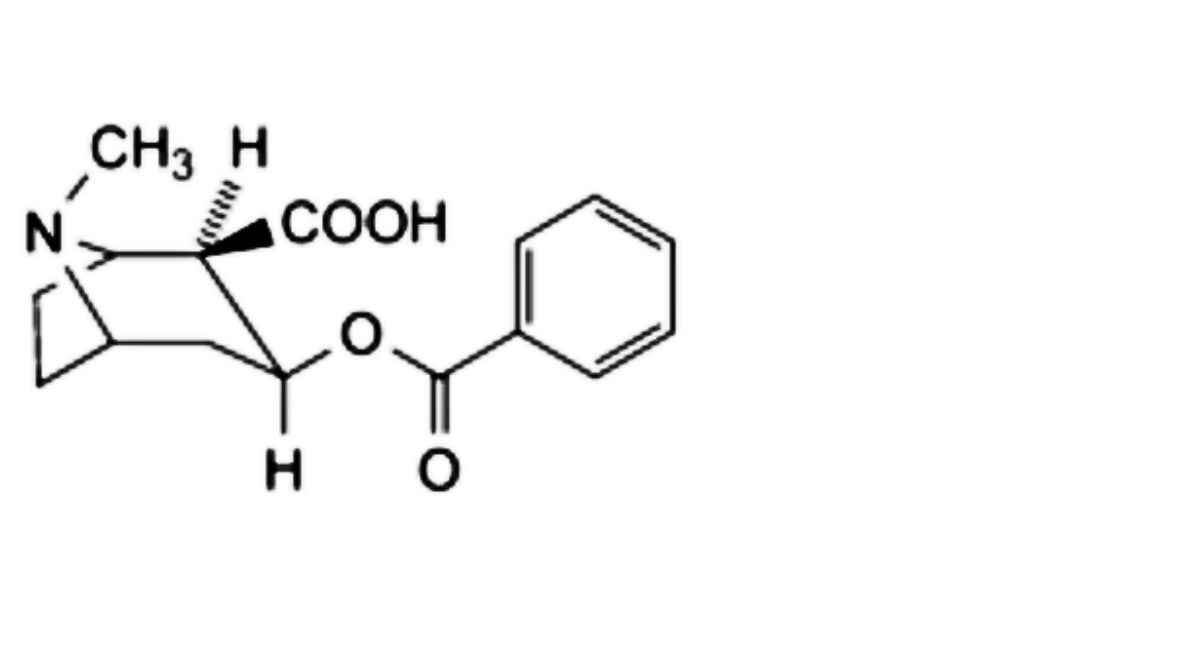
1. Benzoylecgonine,
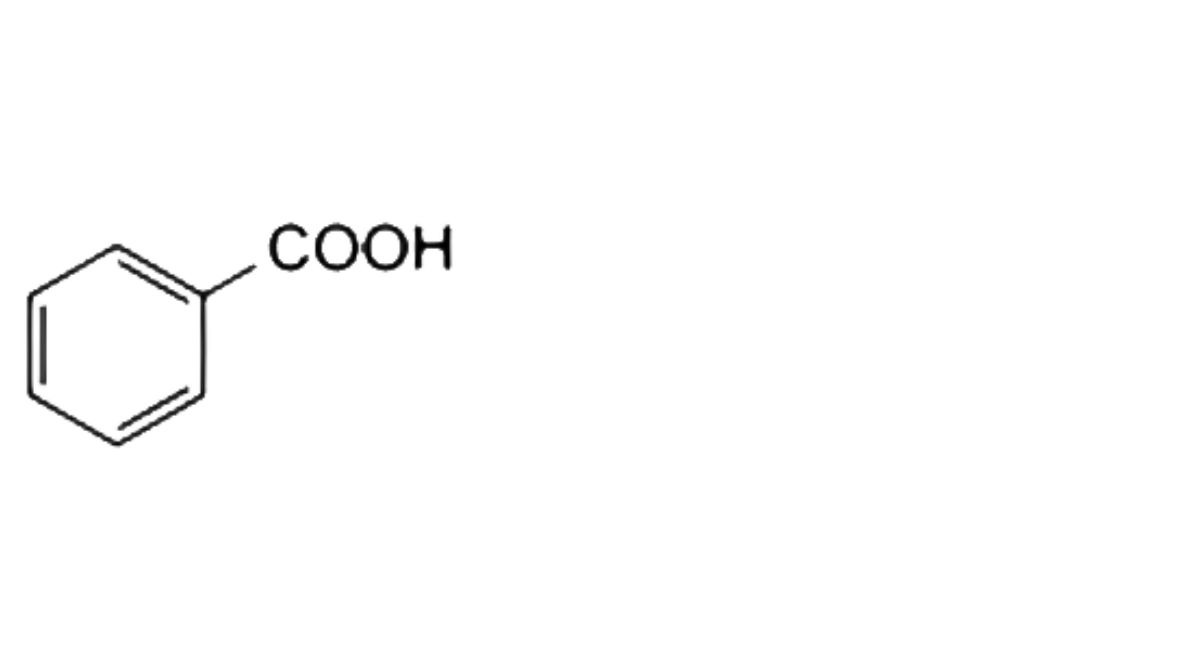
2. Benzoic acid.






