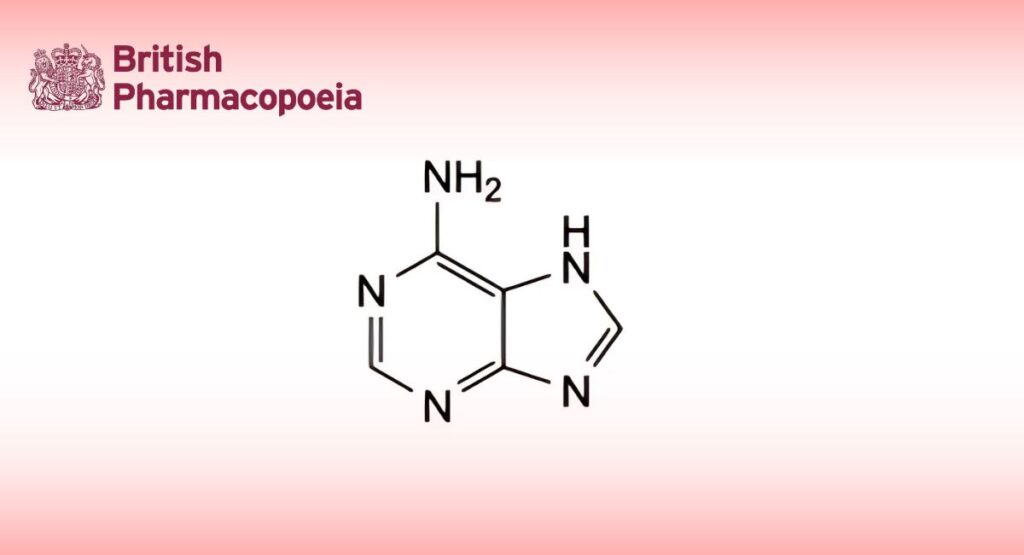
(Ph. Eur. monograph 0800)
C5H5N5 135.1 73-24-5
Action and use
Constituent of anticoagulant and preservative solutions for blood.
DEFINITION
Adenine contains not less than 98.5 per cent and not more than the equivalent of 101.0 per cent of 7H-purin-6-amine, calculated with reference to the dried substance.
CHARACTERS
A white or almost white powder, very slightly soluble in water and in ethanol (96 per cent). It dissolves in dilute mineral acids and in dilute solutions of alkali hydroxides.
IDENTIFICATION
First identification: A.
Second identification: B, C.
A. Examine by infrared absorption spectrophotometry (2.2.24), comparing with the spectrum obtained with adenine CRS. Examine the substances prepared as discs.
B. Examine the chromatograms obtained in the test for related substances. The principal spot in the chromatogram obtained with test solution (b) is similar in position and size to the principal spot in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a).
C. To 1 g add 3.5 mL of propionic anhydride R and boil for 15 min with stirring. Cool. To the resulting crystalline mass add 15 mL of light petroleum R and heat to boiling with vigorous stirring. Cool and filter. Wash the precipitate with two quantities, each of 5 mL, of light petroleum R. Dissolve the precipitate in 10 mL of water R and boil for 1 min. Filter the mixture at 30 °C to 40 °C. Allow to cool. Filter, and dry the precipitate at 100 °C to 105 °C for 1 h. The melting point (2.2.14) of the precipitate is 237 °C to 241 °C.
TESTS
Solution S
Suspend 2.5 g in 50 mL of distilled water R and boil for 3 min. Cool and dilute to 50 mL with distilled water R. Filter. Use the filtrate as solution S.
Appearance of solution
Dissolve 0.5 g in dilute hydrochloric acid R and dilute to 50 mL with the same acid. The solution is clear (2.2.1) and colourless (2.2.2, Method II).
Acidity or alkalinity
To 10 mL of solution S add 0.1 mL of bromothymol blue solution R1 and 0.2 mL of 0.01 M sodium hydroxide. The solution is blue. Add 0.4 mL of 0.01 M hydrochloric acid. The solution is yellow.
Related substances
Examine by thin-layer chromatography (2.2.27), using silica gel GF254 R as the coating substance.
Test solution (a): Dissolve 0.10 g of the substance to be examined in dilute acetic acid R, with heating if necessary, and dilute to 10 mL with the same acid.
Test solution (b): Dilute 1 mL of test solution (a) to 10 mL with dilute acetic acid R.
Reference solution (a): Dissolve 10 mg of adenine CRS in dilute acetic acid R, with heating if necessary, and dilute to 10 mL with the same acid.
Reference solution (b): Dilute 1 mL of test solution (b) to 20 mL with dilute acetic acid R.
Reference solution (c): Dissolve 10 mg of adenine CRS and 10 mg of adenosine R in dilute acetic acid R, with heating if necessary, and dilute to 10 mL with the same acid.
Apply to the plate 5 μL of each solution. Develop over a path of 12 cm using a mixture of 20 volumes of concentrated ammonia R, 40 volumes of ethyl acetate R and 40 volumes of propanol R. Dry the plate in a current of warm air and examine in ultraviolet light at 254 nm. Any spot in the chromatogram obtained with test solution (a), apart from the principal spot, is not more intense than the spot in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b) (0.5 per cent). The test is not valid unless the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (c) shows two clearly separated spots.
Chlorides (2.4.4)
To 10 mL of solution S add 1 mL of concentrated ammonia R and 3 mL of silver nitrate solution R2. Filter. Wash the precipitate with a little water R and dilute the filtrate to 15 mL with water R. The solution complies with the limit test for chlorides (100 ppm). When carrying out the test, add 2 mL of dilute nitric acid R instead of 1 mL of dilute nitric acid R.
Sulfates (2.4.13)
Dilute 10 mL of solution S to 15 mL with distilled water R. The solution complies with the limit test for sulfates (300 ppm).
Ammonium
Prepare a cell consisting of two watch-glasses 60 mm in diameter placed edge to edge. To the inner wall of the upper watch-glass stick a piece of red litmus paper R 5 mm square and wetted with a few drops of water R. Finely powder the substance to be examined, place 0.5 g in the lower watch-glass and suspend in 0.5 mL of water R. To the suspension add 0.30 g of heavy magnesium oxide R. Briefly triturate with a glass rod. Immediately close the cell by putting the two watch – glasses together. Heat at 40 °C for 15 min. The litmus paper is not more intensely blue coloured than a standard prepared at the same time and in the same manner using 0.05 mL of ammonium standard solution (100 ppm NH4) R, 0.5 mL of water R and 0.30 g of heavy magnesium oxide R (10 ppm).
Loss on drying (2.2.32)
Not more than 0.5 per cent, determined on 1.000 g by drying in an oven at 105 °C.
Sulfated ash (2.4.14)
Not more than 0.1 per cent, determined on 1.0 g.
ASSAY
Dissolve 0.100 g in a mixture of 20 mL of acetic anhydride R and 30 mL of anhydrous acetic acid R. Titrate with 0.1 M perchloric acid, determining the end-point potentiometrically (2.2.20).
1 mL of 0.1 M perchloric acid is equivalent to 13.51 mg of C5H5N5.