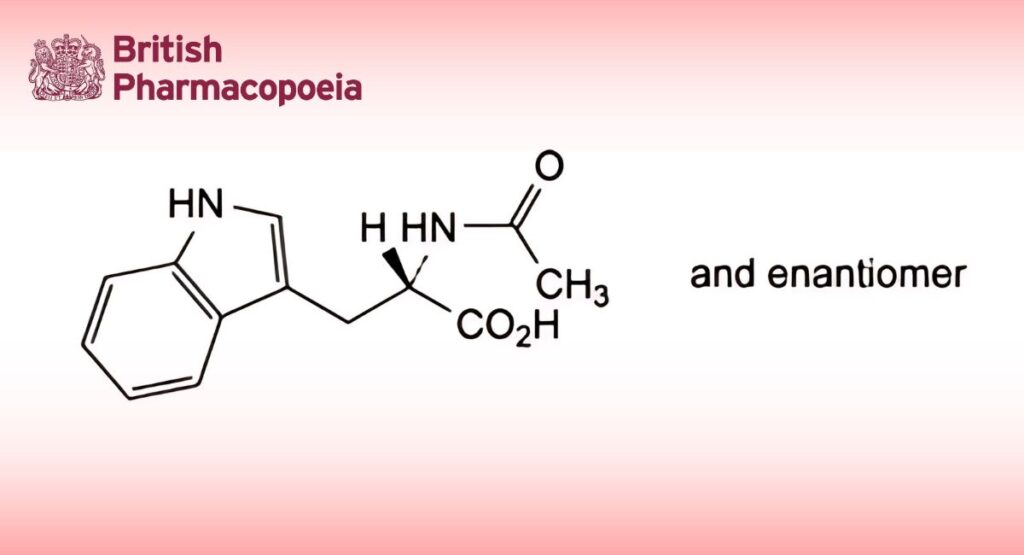
(N-Acetyltryptophan, Ph. Eur. monograph 1383)
C13H14N2O3 246.3 87-32-1
DEFINITION
(RS)-2-Acetylamino-3-(1H-indol-3-yl)propanoic acid.
Content
99.0 per cent to 101.0 per cent (dried substance).
PRODUCTION
Tryptophan used for the production of N-acetyltryptophan complies with the test for impurity A and other related substances in the monograph on Tryptophan (1272).
CHARACTERS
Appearance
White or almost white, crystalline powder, or colourless crystals.
Solubility
Slightly soluble in water, very soluble in ethanol (96 per cent). It dissolves in dilute solutions of alkali hydroxides.
mp
About 205 °C.
IDENTIFICATION
First identification: A, B.
Second identification: A, C, D, E.
A. Optical rotation (see Tests).
B. Infrared absorption spectrophotometry (2.2.24).
Comparison N-acetyltryptophan CRS.
C. Thin-layer chromatography (2.2.27).
Test solution: Dissolve 50 mg of the substance to be examined in 0.2 mL of concentrated ammonia R and dilute to 10 mL with water R.
Reference solution (a): Dissolve 50 mg of N-acetyltryptophan CRS in 0.2 mL of concentrated ammonia R and dilute to 10 mL with water R.
Reference solution (b): Dissolve 10 mg of tryptophan R in the test solution and dilute to 2 mL with the test solution.
Plate: TLC silica gel F254 plate R.
Mobile phase: glacial acetic acid R, water R, butanol R (25:25:40 V/V/V).
Application: 2 μL.
Development: Over a path of 10 cm.
Drying: In an oven at 100-105 °C for 15 min.
Detection: Examine in ultraviolet light at 254 nm.
System suitability: Reference solution (b):
— the chromatogram shows 2 clearly separated spots.
Results: The principal spot in the chromatogram obtained with the test solution is similar in position and size to the principal spot in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a).
D. Dissolve about 2 mg in 2 mL of water R. Add 2 mL of dimethylaminobenzaldehyde solution R6. Heat on a water-bath. A blue or greenish-blue colour develops.
E. It gives the reaction of acetyl (2.3.1). Proceed as described for substances hydrolysable only with difficulty.
TESTS
Appearance of solution
The solution is clear (2.2.1) and not more intensely coloured than reference solution Y7 or GY7 (2.2.2, Method II).
Dissolve 1.0 g in a 40 g/L solution of sodium hydroxide R and dilute to 100 mL with the same alkaline solution.
Optical rotation (2.2.7)
-0.1° to + 0.1°.
Dissolve 2.50 g in a 40 g/L solution of sodium hydroxide R and dilute to 25.0 mL with the same alkaline solution.
Related substances
Liquid chromatography (2.2.29). Prepare the test and reference solutions immediately before use.
Buffer solution: pH 2.3 Dissolve 3.90 g of sodium dihydrogen phosphate R in 1000 mL of water R. Add about 700 mL of a 2.9 g/L solution of phosphoric acid R and adjust to pH 2.3 with the same acid solution.
Solvent mixture: acetonitrile R, water R (10:90 V/V).
Test solution: Dissolve 0.10 g of the substance to be examined in a mixture of 50 volumes of acetonitrile R and 50 volumes of water R and dilute to 20.0 mL with the same mixture of solvents.
Reference solution (a): Dilute 1.0 mL of the test solution to 100.0 mL with the solvent mixture.
Reference solution (b): Dilute 4.0 mL of reference solution (a) to 100.0 mL with the solvent mixture.
Reference solution (c): Dissolve the contents of a vial of 1,1′-ethylidenebistryptophan CRS in 1 mL of reference solution (b).
Column:
— size: l = 0.25 m, Ø = 4.6 mm;
— stationary phase: octadecylsilyl silica gel for chromatography R (5 μm);
— temperature: 40 °C.
Mobile phase:
— mobile phase A: acetonitrile R, buffer solution pH 2.3 (115:885 V/V);
— mobile phase B: acetonitrile R, buffer solution pH 2.3 (350:650 V/V);
| Time (min) |
Mobile phase A (per cent V/V) |
Mobile phase B (per cent V/V) |
| 0 – 10 | 100 | 0 |
| 10 – 45 | 100 → 0 | 0 → 100 |
| 45 – 65 | 0 | 100 |
Flow rate: 0.7 mL/min.
Detection: Spectrophotometer at 220 nm.
Injection:20 μL of the test solution and reference solutions (a) and (c).
Retention time: N-acetyltryptophan = about 29 min; 1,1′-ethylidenebis(tryptophan) = about 34 min.
System suitability: Reference solution (c):
— resolution: minimum 8.0 between the peaks due to N-acetyltryptophan and 1,1′-ethylidenebis(tryptophan); if necessary, adjust the time programme for the elution gradient (an increase in the duration of elution with mobile phase A produces longer retention times and a better resolution);
— symmetry factor: maximum 3.5 for the peak due to 1,1′-ethylidenebistryptophan in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (c).
Limits:
— impurities A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H, I, J, K, L: for each impurity, not more than 0.25 times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a) (0.25 per cent);
— total: not more than 0.5 times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a) (0.5 per cent);
— disregard limit: 0.01 times the area of the principal peak the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a) (0.01 per cent).
Ammonium (2.4.1, Method B)
Maximum 200 ppm, determined on 0.10 g.
Prepare the standard using 0.2 mL of ammonium standard solution (100 ppm NH4) R.
Iron (2.4.9)
Maximum 10 ppm.
Dissolve 1.0 g in 50 mL of hydrochloric acid R1, with heating at 50 °C. Allow to cool. In a separating funnel, shake with 3 quantities, each of 10 mL, of methyl isobutyl ketone R1, shaking for 3 min each time. To the combined organic layers add 10 mL of water R and shake for 3 min. Examine the aqueous layer.
Loss on drying (2.2.32)
Maximum 0.5 per cent, determined on 1.000 g by drying in an oven at 105 °C.
Sulfated ash (2.4.14)
Maximum 0.1 per cent, determined on 1.0 g.
ASSAY
Dissolve 0.200 g in 5 mL of methanol R. Add 50 mL of anhydrous ethanol R. Titrate with 0.1 M sodium hydroxide, determining the end-point potentiometrically (2.2.20).
1 mL of 0.1 M sodium hydroxide is equivalent to 24.63 mg of C13H14N2O3
STORAGE
Protected from light.
IMPURITIES
Specified impurities A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H, I, J, K, L.
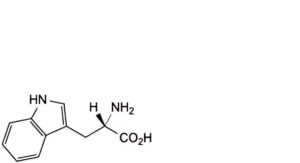
A. (S)-2-amino-3-(1H-indol-3-yl)propanoic acid (tryptophan),
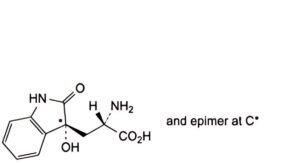
B. (S)-2-amino-3-[(3RS)-3-hydroxy-2-oxo-2,3-dihydro-1H-indol-3-yl]propanoic acid (dioxyindolylalanine),
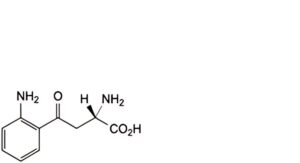
C. (S)-2-amino-4-(2-aminophenyl)-4-oxobutanoic acid (kynurenine),
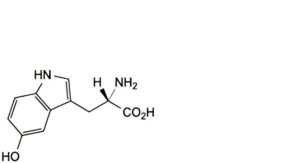
D. (S)-2-amino-3-(5-hydroxy-1H-indol-3-yl)propanoic acid (5-hydroxytryptophan),
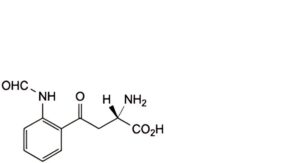
E. (S)-2-amino-4-[2-(formylamino)phenyl]-4-oxobutanoic acid (N-formylkynurenine),
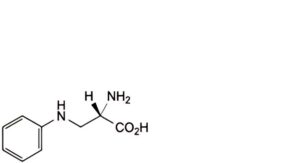
F. (S)-2-amino-3-(phenylamino)propanoic acid (3-phenylaminoalanine),
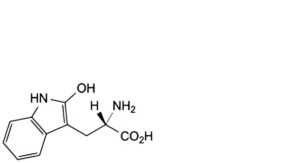
G. (S)-2-amino-3-(2-hydroxy-1H-indol-3-yl)propanoic acid (2-hydroxytryptophan),
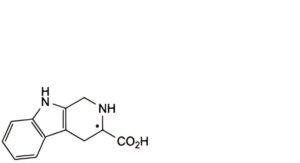
H. (3RS)-1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-9H-β-carboline-3-carboxylic acid,
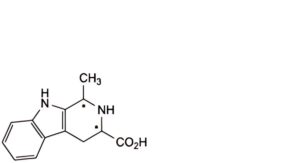
I. 1-methyl-1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-9H-β-carboline-3-carboxylic acid,
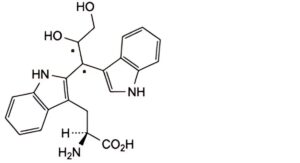
J. (S)-2-amino-3-[2-[2,3-dihydroxy-1-(1H-indol-3-yl)propyl]-1H-indol-3-yl]propanoic acid,
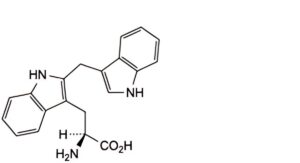
K. (S)-2-amino-3-[2-(1H-indol-3-ylmethyl)-1H-indol-3-yl]propanoic acid,
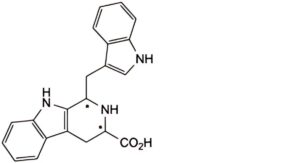
L. 1-(1H-indol-3-ylmethyl)-1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-9H-β-carboline-3-carboxylic acid.