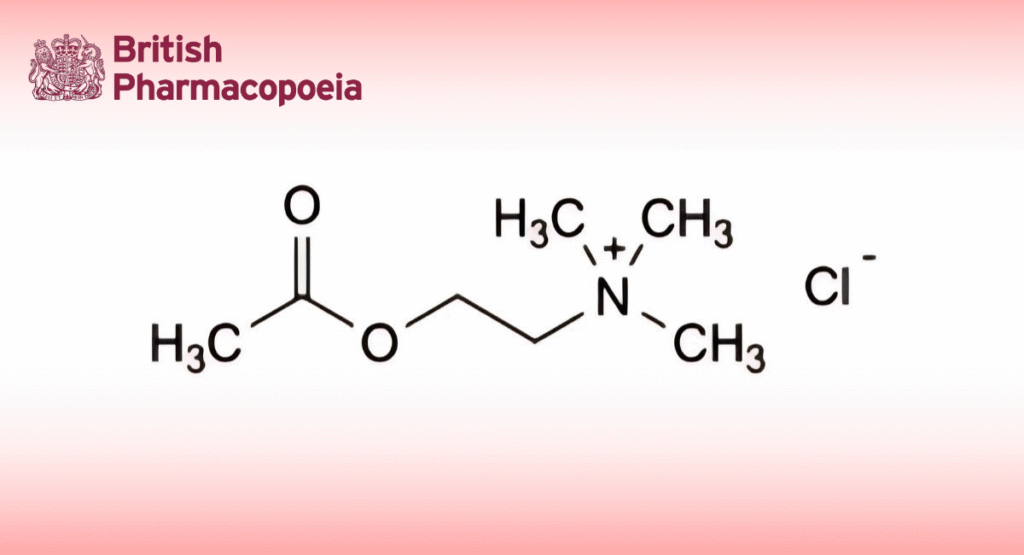
(Ph. Eur. monograph 1485)
C7H16ClNO2 181.7 60-31-1
Action and use
Cholinoceptor agonist.
DEFINITION
2-(Acetyloxy)-N,N,N-trimethylethanaminium chloride.
Content
98.5 per cent to 101.5 per cent (dried substance).
CHARACTERS
Appearance
White or almost white crystalline powder or colourless crystals, very hygroscopic.
Solubility
Very soluble in water, freely soluble in ethanol (96 per cent), slightly soluble in methylene chloride.
IDENTIFICATION
First identification: B, E.
Second identification: A, C, D, E.
A. Melting point (2.2.14): 149 °C to 152 °C.
Introduce the substance to be examined into a capillary tube. Dry in an oven at 100-105 °C for 3 h. Seal the tube and determine the melting point.
B. Infrared absorption spectrophotometry (2.2.24).
Comparison acetylcholine chloride CRS.
C. Examine the chromatograms obtained in the test for related substances.
Results The principal zone in the chromatogram obtained with test solution (b) is similar in position, colour and size to the principal zone in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b).
D. To 15 mg add 10 mL of dilute sodium hydroxide solution R, 2 mL of 0.02 M potassium permanganate and heat. The vapours formed change the colour of red litmus paper R to blue.
E. 0.5 mL of solution S (see Tests) gives reaction (a) of chlorides (2.3.1).
TESTS
Solution S
Dissolve 5.0 g in carbon dioxide-free water R and dilute to 50 mL with the same solvent.
Appearance of solution
Solution S is clear (2.2.1) and not more intensely coloured than reference solution Y6 or BY6 (2.2.2, Method II).
Acidity Dilute 1 mL of solution S to 10 mL with carbon dioxide-free water R. Add 0.05 mL of phenolphthalein solution R. Not more than 0.4 mL of 0.01 M sodium hydroxide is required to change the colour of the indicator to pink.
Related substances
Thin-layer chromatography (2.2.27). Prepare the solutions immediately before use.
Test solution (a): Dissolve 0.30 g of the substance to be examined in methanol R and dilute to 3.0 mL with the same solvent.
Test solution (b): Dilute 1 mL of test solution (a) to 10 mL with methanol R.
Reference solution (a): Dilute 1 mL of test solution (a) to 100 mL with methanol R.
Reference solution (b): Dissolve 20.0 mg of acetylcholine chloride CRS in methanol R and dilute to 2.0 mL with the same solvent.
Reference solution (c): Dissolve 20 mg of choline chloride R in methanol R, add 0.4 mL of test solution (a) and dilute to 2.0 mL with methanol R.
Plate: TLC silica gel plate R.
Mobile phase: Mix 20 volumes of a 40 g/L solution of ammonium nitrate R, 20 volumes of methanol R and 60 volumes of acetonitrile R.
Application: 5 μL as bands of 10 mm by 2 mm.
Development: Over 2/3 of the plate.
Detection: Spray with potassium iodobismuthate solution R3.
System suitability: The chromatogram obtained with reference solution (c) shows 2 clearly separated zones.
Limits:
— any impurity: any zones in the chromatogram obtained with test solution (a), apart from the principal zone, are not more intense than the principal zone in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a) (1 per cent).
Trimethylamine
Dissolve 0.1 g in 10 mL of sodium carbonate solution R and heat to boiling. No vapours appear which turn red litmus paper R blue.
Loss on drying (2.2.32)
Maximum 1.0 per cent, determined on 1.000 g by drying in an oven at 105 °C for 3 h.
Sulfated ash (2.4.14)
Maximum 0.1 per cent, determined on the residue obtained in the test for loss on drying.
ASSAY
Dissolve 0.200 g in 20 mL of carbon dioxide-free water R. Neutralise with 0.01 M sodium hydroxide using 0.15 mL of phenolphthalein solution R as indicator. Add 20.0 mL of 0.1 M sodium hydroxide and allow to stand for 30 min. Titrate with 0.1 M hydrochloric acid.
1 mL of 0.1 M sodium hydroxide is equivalent to 18.17 mg of C7H16ClNO2
STORAGE
In ampoules, protected from light.
IMPURITIES
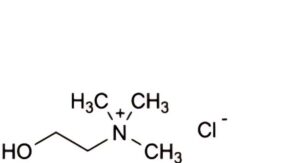
A. 2-hydroxy-N,N,N-trimethylethanaminium chloride (choline chloride),
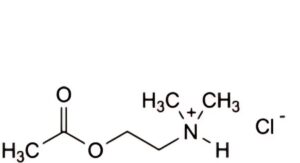
B. 2-(acetyloxy)-N,N-dimethylethanaminium chloride,
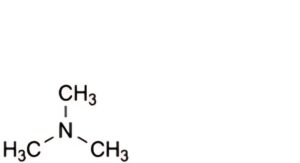
C. N,N-dimethylmethanamine.